Abstract
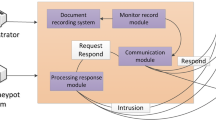
In recent years, as cyber-attacks have become more and more rampant, power grid networks are also facing more and more security threats, which have gradually become the focus attention of attackers. Traditional defense methods are represented by intrusion detection systems and firewalls, whose main purpose is to keep attackers out. However, with the diversification, concealment and complexity of attack methods, traditional defense methods are usually difficult to cope with the endless attack methods. To this end, this paper proposes a new type of honeypot system based on deception defense technology. While retaining the nature of the honeypot, it adopts dynamic deception approach to actively collect unused IP addresses in the power grid networks. Then, these unused IP addresses are used to construct dynamic virtual hosts. When an attacker initiates network access to these dynamic virtual hosts, they will proactively respond to the attacker or redirect the attack traffic to the honeypot in the background, thereby deceiving and trapping the attacker. The experimental results show that the proposed honeypot system can effectively expands the monitoring range of traditional honeypots and has a good defense effect against unknown attacks, thus effectively making up for the shortcomings of traditional defense methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qiu, M.: Low-power low-latency data allocation for hybrid scratch-pad memory. IEEE Embed. Syst. Lett. 6(4), 69–72
Qiu, M., et al.: RNA nanotechnology for computer design and in vivo computation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A (2013)
Guo, Y., et al.: Optimal data allocation for scratch-pad memory on embedded multi-core systems. In: IEEE ICPP Conference, pp. 464–471 (2011)
Zhang, L., Qiu, M., Tseng, W., Sha, E.: Variable partitioning and scheduling for MPSoC with virtually shared scratch pad memory. J. Signal Process. Syst. 58(2), 247–265 (2010)
Lu, R., Jin, X., Zhang, S., Qiu, M., Wu, X.: A study on big knowledge and its engineering issues. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 31(9), 1630–1644 (2018)
Guo, Q., et al.: A remote test method for power grid security and stability control system and its engineering application. In: E3S Web of Conference. EDP Science, p. 260 (2021)
Eskandarpour, R., Gokhale, P., Khodaei, A., et al.: Quantum computing for enhancing grid security. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 35(5), 4135–4137 (2020)
Aoufi, S., et al.: Survey of false data injection in smart power grid: attacks, countermeasures and challenges. J. Inform. Secur. Appl. 54, 102518 (2020)
Butt, O.M., Zulqarnain, M., Butt, T.M.: Recent advancement in smart grid technology: future prospects in the electrical power network. Ain Shams Eng. J. 12(1), 687–695 (2021)
Gunduz, M.Z., Das, R.: Cyber-security on smart grid: threats and potential solutions. Comput. Netw. 169, 107094 (2020)
Bou-Harb, E., Debbabi, M., Assi, C.: Cyber scanning: a comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 16(3), 1496–1519 (2013)
Cho, J.-H., et al.: Toward proactive, adaptive defense: a survey on moving target defense. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 22(10), 709–745 (2020)
Thakur, K., Qiu, M., Gai, K., Ali, M.: An investigation on cyber security threats and security models. In: IEEE CSCloud (2015)
Gai, K., Qiu, M., Sun, X., Zhao, H.: Security and privacy issues: a survey on FinTech. In: SmartCom, pp. 236–247 (2016)
Zhang, Z., et al.: Jamming ACK attack to wireless networks and a mitigation approach. In: IEEE GLOBECOM Conference, pp. 1–5 (2008)
Qiu, M., et al.: A novel energy-aware fault tolerance mechanism for wireless sensor networks. In: IEEE/ACM Conference on Green Computing and Communications (2011)
Antonatos, S., Akritidis, P., Markatos, E.P., et al.: Defending against hitlist worms using network address space randomization. Comput. Netw. 51(12), 3471–3490 (2007)
Jafarian, J.H., Al-Shaer, E., Duan, Q.: An effective address mutation approach for disrupting reconnaissance attacks. IEEE TIFS 10(12), 2562–2577 (2015)
Jajodia, S., et al.: Cyber Deception. Springer, Heidelberg (2016)
Qiu, H., Qiu, M., Lu, Z.: Selective encryption on ECG data in body sensor network based on supervised machine learning. Inf. Fusion 55, 59–67 (2020)
Qiu, H., Qiu, M., Memmi, G., Ming, Z., Liu, M.: A dynamic scalable blockchain based communication architecture for IoT. In: SmartBlock, 159–166 (2018)
Naik, N., Jenkins, P., Savage, N., et al.: A computational intelligence enabled honeypot for chasing ghosts in the wires. Complex Intell. Syst. 7(1), 477–494 (2021)
Sun, Y., Tian, Z., Li, M., et al.: Honeypot identification in softwarized industrial cyber-physical systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 17(8), 5542–5551 (2020)
Mondal, A., Goswami, T.: Enhanced Honeypot cryptographic scheme and privacy preservation for an effective prediction in cloud security. Microprocess. Microsyst. 81, 103719 (2021)
Ziaie Tabari, A., Ou, X.: A multi-phased multi-faceted iot honeypot ecosystem. In: ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, pp. 2121–2123 (2020)
Naik, N., et al.: D-FRI-Honeypot: a secure sting operation for hacking the hackers using dynamic fuzzy rule interpolation. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Feng, M. et al. (2022). A Novel Deception Defense-Based Honeypot System for Power Grid Network. In: Qiu, M., Gai, K., Qiu, H. (eds) Smart Computing and Communication. SmartCom 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13202. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97774-0_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97774-0_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-97773-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-97774-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)