Abstract
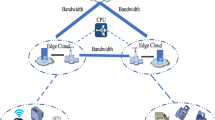
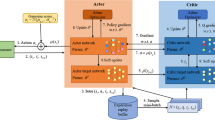
Due to its high maneuverability and flexibility, there have been a growing popularity to adopt Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) on Mobile Edge Computing (MEC), serving as edge platforms in infrastructure- unavailable scenarios, e.g., disaster rescue, field operation. Owing to the weak workload, UAVs are typically equipped with limited computing and energy resources. Hence, it is crucial to design efficient edge computation offloading algorithms which could achieve high edge computing performance while keeping low energy consumption. A variety of UAV assisted computation offloading algorithms have been proposed, most of which focus on the scheduling of computation offloading in a centralized way and could become infeasible when the network size increases greatly. To address the issue, we propose a semi-distributed computation offloading framework based on Multi-Agent Twin Delayed (MATD3) deep deterministic policy gradient to minimize the average system cost of the MEC network. We adopt the actor-critic reinforcement learning framework to learn an offloading decision model for each User Equipment (UE), so that each UE could make near-optimal computation offloading decisions by its own and does not suffer from the booming of the network size. Extensive experiments are carried out via numerical simulation and the experimental results verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zeng, Y., Zhang, R., Lim, T.J.: Wireless communications with unmanned aerial vehicles: opportunities and challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 54(5), 36–42 (2016)
Qiu, H., Qiu, M., Memmi, G., Ming, Z., Liu, M.: A dynamic scalable blockchain based communication architecture for IoT. In: SmartBlock, pp. 159–166 (2018)
Qiu, H., Qiu, M., Lu, Z.: Selective encryption on ECG data in body sensor network based on supervised machine learning. Inf. Fusion 55, 59–67 (2020)
Li, J., Gao, H., Lv, T., Lu, Y.: Deep reinforcement learning based computation offloading and resource allocation for MEC. In: IEEE Conference (WCNC), pp. 1–6 (2018)
Qiu, L., Gai, K., Qiu, M.: Optimal big data sharing approach for tele-health in cloud computing. In: IEEE SmartCloud, pp. 184–189 (2016)
Lu, Z., Wang, N., et al.: IoTDeM: an IoT big data-oriented MapReduce performance prediction extended model in multiple edge clouds. JPDC 118, 316–327 (2018)
Qiu, M., et al.: Energy minimization with soft real-time and DVS for uniprocessor and multiprocessor embedded systems. In: IEEE DATE Conference, pp. 1–6 (2007)
Liu, M., et al.: H infinite state estimation for discrete-time chaotic systems based on a unified model. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. (B). 42(4), 1053–1063 (2012)
Qiu, M., et al.: A novel energy-aware fault tolerance mechanism for wireless sensor networks. In: ACM International Conference on Green Computing and Communications (2011)
Zhang, Z., et al.: Jamming ACK attack to wireless networks and a mitigation approach. In: IEEE GLOBECOM Conference, pp. 1–5 (2008)
Qiu, M., Cao, D., et al.: Data transfer minimization for financial derivative pricing using Monte Carlo simulation with GPU in 5G. J. Commun. Syst. 29(16), 2364–2374 (2016)
Kaleem, Z., Yousaf, M., Qamar, A., et al.: UAV-empowered disaster-resilient edge architecture for delay-sensitive communication. IEEE Netw. 33(6), 124–132 (2019)
Zhou, F., Wu, Y., Hu, R.Q., Qian, Y.: Computation rate maximization in UAV-enabled wireless powered mobile-edge computing systems. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 36(9), 1927–1941 (2018)
Zeng, Y., Zhang, R.: Energy-efficient UAV communication with trajectory optimization. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 16(6), 3747–3760 (2017)
Zhou, X., Wu, Q., Yan, S., Shu, F., Li, J.: UAV-enabled secure communications: Joint trajectory and transmit power optimization. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 68(4), 4069–4073 (2019)
Li, M., Cheng, N., et al.: Energy-efficient UAV-assisted mobile edge computing: resource allocation and trajectory optimization. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(3), 3424–3438 (2020)
Zeng, Y., Xu, X., Zhang, R.: Trajectory design for completion time minimization in UAV-enabled multicasting. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 17(4), 2233–2246 (2018)
ANasir, A.A., Tuan, H.D., Duong, T.Q., Poor, H.V.: UAV-enabled communication using NOMA in arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.03604 (2018)
Ackermann, J., Gabler, V., Osa, T., Sugiyama, M.: Reducing overestimation bias in multi-agent domains using double centralized critics (2019)
Puterman, M.L.: Markov Decision Processes: Discrete Stochastic Dynamic Programming. Wiley, NY, USA (2014)
Mir, Z.H., Filali, F.: LTE and IEEE 802.11p for vehicular networking: a performance evaluation. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2014(1), 1–15 (2014)
Kwak, J., Kim, Y., Lee, J., Chong, S.: DREAM: dynamic resource and task allocation for energy minimization in mobile cloud systems. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 33(12), 2510–2523 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
He, H., Ren, T., Qiu, Y., Hu, Z., Li, Y. (2022). Multi-agent Computation Offloading in UAV Assisted MEC via Deep Reinforcement Learning. In: Qiu, M., Gai, K., Qiu, H. (eds) Smart Computing and Communication. SmartCom 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13202. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97774-0_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97774-0_38
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-97773-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-97774-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)