Abstract
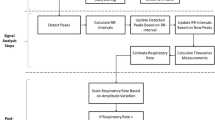
Remote-photoplethysmography (rPPG) is an attractive technology that can measure vital signs at a distance without contact. Previous remote-photoplethysmography studies focused mainly on eliminating the artifact such as motion but finding the optimal setup or hyperparameters are also an important factor influencing the performance. As one of them, window size is the length of the signal used to calculate the vital signs once in a spectral method and has not been analyzed in detail in previous works. In general, the use of a long window size increases the re-liability of the estimations, but it cannot reflect continuously changing physiological responses of human. Also, using too short window size increases uncertainty. In this paper, we compare and analyze the pulse rate estimation results according to window sizes from short to long using CHROM, which is one of the popular rPPG algorithms. Results on the PURE dataset showed that the longer the window size, the higher the SNR and the lower the RMSE. At a window size of about 4 s (120 frames), the SNR was switched from negative to positive and an acceptable error rate (RMSE < 5) was observed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Hann, G., Jeanne, V.: Robust pulse rate from chrominance-based rppg. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60, 2878–2886 (2013)
Verkruysse, W., Svaasand, L.O., Nelson, J.S.: Remote plethysmographic imaging using ambient light. Opt. Express 16(26), 21434–21445 (2008)
Lewandowska, M., Rumiński, J., Kocejko, T.: Measuring pulse rate with a webcam – a non-contact method for evaluating cardiac activity. In: IEEE Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems, pp. 405–410 (2011)
Ming, P., Daniel, J., McDuff, R., Picard, W.: Non-contact, automated cardiac pulse measurements using video imaging and blind source separation. Opt. Express 18(10), 10762–10774 (2010)
Wang, W., Brinker, A.C., Stuijk, S., de Hann, G.: Algorithmic principles of remote PPG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64, 1479–1491 (2017)
OpenCV deep learning module samples ‘OpenCV dnn face detector’. https://github.com/opencv/opencv/tree/master/samples/dnn. Accessed 01 Oct 2021
Henriques, J.F., et al.: High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37, 583–596 (2014)
Phung, S.L., Bouzerdoum, A., Chai, D.: A novel skin color model in YCbCr color space and its application to human face detection. In: Proceedings. International Conference on Image Processing, vol. 1. IEEE (2002)
De Haan, G., Jeanne, V.: Robust pulse rate from chrominance-based rPPG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60(10), 2878–2886 (2013)
Chatterjee, A., Roy, U.K.: PPG based heart rate algorithm improvement with Butterworth IIR filter and Savitzky-Golay FIR filter. In: 2018 2nd International Conference on Electronics, Materials Engineering and Nano-Technology (IEMENTech). IEEE (2018)
Stricker, R., Müller, S., Gross, H.M.: Non-contact video-based pulse rate measurement on a mobile service robot. In: IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, pp. 1056–1062 (2014)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the NRF (National Research Foundation) of Korea funded by the Korea government (Ministry of Science and ICT) (NRF-2019R1A2C4070681).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shin, Y.J., Han, W.J., Suh, K.H., Lee, E.C. (2022). Effect of Time Window Size for Converting Frequency Domain in Real-Time Remote Photoplethysmography Extraction. In: Kim, JH., Singh, M., Khan, J., Tiwary, U.S., Sur, M., Singh, D. (eds) Intelligent Human Computer Interaction. IHCI 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13184. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98404-5_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98404-5_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-98403-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-98404-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)