Abstract
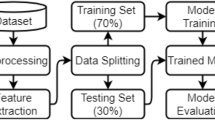
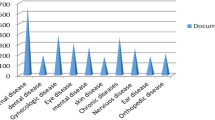
Pakistan is one of the major coal producing country and also have the most serious coal mine accidents around the world. The proposed study performs experiments on a dataset contain reviews based on accident reasons occurred during mining work to reduce the accident rate. The aim of this study achieved by categorizing the reasons into different classes on the behalf of human behavior, roof dropping, and smoke inhalation. Then perform preprocessing on the reviews to clean the data. After preprocessing, the bag-of-words and TF-IDF are used singly and in combination to preserve meaningful information in extracted feature form. Finally, the Random Forest, Naive Bayes classifier, SVM, Decision Tree, Logistic Regression and proposed ensemble LSD (LR+SVM+DT) models are used to classify the accident reasons to analyze the most occurring once. The performance of the proposed approach is evaluated using average accuracy, precision, recall, and f1 score. The experiments reveal that a combined feature improved the performance of machine learning models. Ensemble LSD outperforms the other models and achieves 94% true acceptance rate when combined with TF-IDF and Bag of words.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GOP, Pakistan 2025: One Nation One Vision, Ministry of Planning, Development and Reform, Government of Pakistan, Islamabad (2014)
Haibin, L., Guangrong, L.: Study on characteristics of coal mine intrinsic safety and strategies of management. China Saf. Sci. J. 17(4), 67–72 (2007)
Wang, C., Zhang, C.L., Liu, L.: Analysis on coal mine safety status in China and its countermeasures. Appl. Mech. Mater. 448–453, 3814–3817 (2014)
Husain, V.: Obstacles in the sustainable development of artisanaland small-scale mines in Pakistan and remedial measures. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 250(1), 135–140 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.2005.250.01.13
Jadoon, K.G., Akbar, S., Edwards, J.S.: Safety trends in small-scale coal mines in developing countries with particular reference to China: India
Joy, J.: Occupational safety risk management in Australian mining. Occup. Med. 54(5), 311–315 (2004)
Sari, M., Duzgun, S., Karpuz, C., Sevtap, Selçuk, A.: Accident analysis of two Turkish underground coal mines. Saf. Sci 42(8), 675–690 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2003.11.002
Chu, C., Jain, R., Muradian, N., Zhang, G.: Statistical analysis of coal mining safety in China with reference to the impact of technology. J. South Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 116(1), 73–78 (2016)
Wu, L., Jiang, Z., Cheng, W., Zuo, X., Lv, D., Yao, Y.: Major accident analysis and prevention of coal mines in China from the year of 1949 to 2009. Min. Sci. Technol. (China) 21(5), 693–699 (2011)
Karra, V.K.: Analysis of non-fatal and fatal injury rates for mine operator and contractor employees and the influence of work location. J. Saf. Res. 36, 413–421 (2005)
Gerassis, S., Saavedra, A., Taboada, J., Alonso, E., Fernando, G., Alonso, E.: Differentiating between fatal and non-fatal mining accidents using artificial intelligence techniques. 0930 (2019)
Sanmiquel, L., Bascompta, M., Rossell, J.M., Anticoi, H.F., Guash, E.: Analysis of occupational accidents in underground and surface mining in Spain using data-mining techniques. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 15(3), 462 (2018)
Bennett, J.D., Passmore, D.L.: Probability of death, disability, and restricted work activity in United States underground bituminous coal mines, 1975–1981. J. Saf. Res. 15(2), 69–76 (1984)
Sanmiquel, L., Rossell, J.M., Vintro, C.: Study of Spanish mining accidents using data mining techniques. Saf. Sci. 75, 49–55 (2015)
Ajayi, A., Oyedele, L., Delgado, J.M.D., Akanbi, L., Bilal, M., Akinade, O., Olawale, O.: Big data platform for health and safety accident prediction. World J. Sci. Technol. Sustain. Dev. (2019)
Hull, B.P., Leigh, J., Driscoll, T.R., Mandryk, J.: Factors associated with occupational injury severity in the New South Wales underground coal mining industry. SSDlO925-7535 (95) 00064-X (1996)
Xu, J., Lv, X.: Establishing a georeferenced spatio-temporal database for Chinese coal mining accidents between 2000 and 2015 (2018)
Mengmeng, P., Qing, L., Chuanpeng X.: Towards Consistent Interpretations of Coal Geochemistry Data on Whole-Coal versus Ash Bases through Machine Learning Na Xu 1. Minerals 10, 328 (2020)
Issac, B., Jap, W.J.: Implementing spam detection using Bayesian and porter stemmer keyword stripping approaches. In: Proceedings of IEEE Region Conference (TENCON), pp. 1–5 (2009)
Joulin, A.E., Grave, P., Bojanowski, M.T.: Bag of tricks for efficient text classification arXiv:1607.01759 (2016)
Huang, Y., J., Powers, R., Montelione, G.T.: Protein NMR recall, precision, and F-measure scores (RPF scores): structure quality assessment measures based on information retrieval statistics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127(6), 1665–1674 (2005)
Mathanker, S.K., Weckler, P.R., Bowser, T.J., Wang, N., Maness, N.O.: Adaboost classifiers for pecan defect classification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 77(1), 60–68 (2011)
Guzman, E., El-Haliby, M., Bruegge, B.: Ensemble methods for app review classification: an approach for software evolution (N). In: Proceedings of 30th IEEE (2015)
Rustam, F., Ashraf, I., Mehmood, A., Ullah, S., Choi, G.: Tweets classification on the base of sentiments for US airline companies. Entropy 21(11), 1078 (2019)
Elorrieta, F., et al.: A machine learned classifier for RR Ly
Heaton, J.: An empirical analysis of feature engineering for predictive modelling. In: Proceedings of SoutheastCon, pp. 1–6 (2016)
Hu, X., Downie, J.S., Ehmann, A.F.: Lyric text mining in music mood classification. Am. Music 183(5), 2–209 (2009)
Yu, B.: An evaluation of text classification methods for literary study. Literary Linguistic Comput. 23(3), 327–343 (2008)
Mushtaq, M.F.: BHCNet: neural network-based brain hemorrhage classification using head CT Scan. IEEE Access 9, 113901–113916 (2021)
Loper, E., Bird, S.: NLTK: the natural language toolkit arXiv:cs/0205028 (2002)
Kotsiantis, S.B., Zaharakis, I., Pintelas, P.: Supervised machine learning: A review of classification techniques. Emerg. Artif. Intell. Appl. Comput. Eng. 160, 3–24 (2007)
Svetnik, V., Liaw, A., Tong, C., Culberson, J.C., Sheridan, R.P., Feuston, B.P.: Random forest: a classification and regression tool for compound classification and QSAR modelling. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci 43(6), 1947–1958 (2003)
Biau, G., Scornet, E.: A random forest guided tour. TEST 25(2), 197–227 (2016)
Breiman, L.: Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn 24(2), 123–140 (1996)
Schapire, R.E.: A brief introduction to boosting. In: Proceedings of IJCAI, vol. 99, pp. 1401–1406 (1999)
Breiman, L.: Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 24(2), 123–140 (1996)
Sebastiani, F.: Machine learning in automated text categorization. ACM Comput. Surv 34(1), 1–47 (2002)
Zhang, F., Zhenqi, H., Yaokun, F., Kun, Y., Qunying, W., Zewei, F.: A new identification method for surface cracks from UAV images based on machine learning in coal mining areas. Remote Sens. 12(10), 1571 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Javaid, M.A. et al. (2022). LSD: Discrimination of Coal Mining Accident’s Causes Based on Ensemble Machine Learning. In: Ghazali, R., Mohd Nawi, N., Deris, M.M., Abawajy, J.H., Arbaiy, N. (eds) Recent Advances in Soft Computing and Data Mining. SCDM 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 457. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-00828-3_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-00828-3_39
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-00827-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-00828-3
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)