Abstract
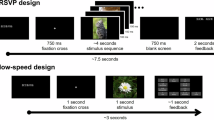
This paper focuses on EEG-based visual recognition, aiming to predict the visual object class observed by a subject based on his/her EEG signals. One of the main challenges is the large variation between signals from different subjects. It limits recognition systems to work only for the subjects involved in model training, which is undesirable for real-world scenarios where new subjects are frequently added. This limitation can be alleviated by collecting a large amount of data for each new user, yet it is costly and sometimes infeasible. To make the task more practical, we introduce a novel problem setting, namely subject adaptive EEG-based visual recognition. In this setting, a bunch of pre-recorded data of existing users (source) is available, while only a little training data from a new user (target) are provided. At inference time, the model is evaluated solely on the signals from the target user. This setting is challenging, especially because training samples from source subjects may not be helpful when evaluating the model on the data from the target subject. To tackle the new problem, we design a simple yet effective baseline that minimizes the discrepancy between feature distributions from different subjects, which allows the model to extract subject-independent features. Consequently, our model can learn the common knowledge shared among subjects, thereby significantly improving the recognition performance for the target subject. In the experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our method under various settings. Our code is available at here (https://github.com/DeepBCI/Deep-BCI).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, W.W., et al.: Decoding music attention from “EEG headphones”: a user-friendly auditory brain-computer interface. In: ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 985–989. IEEE (2021)
Anuragi, A., Sisodia, D.S.: Alcohol use disorder detection using EEG signal features and flexible analytical wavelet transform. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 52, 384–393 (2019)
Bos, D.O., Reuderink, B.: Brainbasher: a BCI game. In: Extended Abstracts of the International Conference on Fun and Games, pp. 36–39. Eindhoven University of Technology Eindhoven, The Netherlands (2008)
Chambayil, B., Singla, R., Jha, R.: Virtual keyboard BCI using eye blinks in EEG. In: 2010 IEEE 6th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications, pp. 466–470. IEEE (2010)
Dai, M., Zheng, D., Na, R., Wang, S., Zhang, S.: EEG classification of motor imagery using a novel deep learning framework. Sensors 19(3), 551 (2019)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 248–255 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848
Eidel, M., Kübler, A.: Wheelchair control in a virtual environment by healthy participants using a p300-BCI based on tactile stimulation: training effects and usability. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 14 (2020)
Eroğlu, K., Kayıkçıoğlu, T., Osman, O.: Effect of brightness of visual stimuli on EEG signals. Behav. Brain Res. 382, 112486 (2020)
Foxe, J.J., Simpson, G.V., Ahlfors, S.P.: Parieto-occipital 10 hz activity reflects anticipatory state of visual attention mechanisms. NeuroReport 9(17), 3929–3933 (1998)
Ghifary, M., Kleijn, W.B., Zhang, M., Balduzzi, D.: Domain generalization for object recognition with multi-task autoencoders. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2551–2559 (2015)
Grizou, J., Iturrate, I., Montesano, L., Oudeyer, P.Y., Lopes, M.: Calibration-free BCI based control. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 28 (2014)
Huang, H., et al.: An EEG-based brain computer interface for emotion recognition and its application in patients with disorder of consciousness. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 12(4), 832–842 (2019)
Hwang, S., Hong, K., Son, G., Byun, H.: EZSL-GAN: EEG-based zero-shot learning approach using a generative adversarial network. In: 2019 7th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface, BCI, pp. 1–4 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/IWW-BCI.2019.8737322
Hwang, S., Hong, K., Son, G., Byun, H.: Learning CNN features from de features for EEG-based emotion recognition. Pattern Anal. Appl. 23(3), 1323–1335 (2020)
Hwang, S., Ki, M., Hong, K., Byun, H.: Subject-independent EEG-based emotion recognition using adversarial learning. In: 2020 8th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface, BCI, pp. 1–4 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/BCI48061.2020.9061624
Hwang, S., Lee, P., Park, S., Byun, H.: Learning subject-independent representation for EEG-based drowsy driving detection. In: 2021 9th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface, BCI, pp. 1–3 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/BCI51272.2021.9385364
Hwang, S., Park, S., Kim, D., Lee, J., Byun, H.: Mitigating inter-subject brain signal variability for EEG-based driver fatigue state classification. In: ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP, pp. 990–994 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP39728.2021.9414613
Jeon, S., Hong, K., Lee, P., Lee, J., Byun, H.: Feature stylization and domain-aware contrastive learning for domain generalization. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (2021)
Jin, Z., Zhou, G., Gao, D., Zhang, Y.: EEG classification using sparse bayesian extreme learning machine for brain-computer interface. Neural Comput. Appl. 32(11), 6601–6609 (2020)
Kavasidis, I., Palazzo, S., Spampinato, C., Giordano, D., Shah, M.: Brain2Image: converting brain signals into images. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1809–1817 (2017)
Khurana, V., et al.: A survey on neuromarketing using EEG signals. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCDS.2021.3065200
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2015)
Ko, W., Oh, K., Jeon, E., Suk, H.I.: VIGNet: a deep convolutional neural network for EEG-based driver vigilance estimation. In: 2020 8th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface, BCI, pp. 1–3. IEEE (2020)
Kumar, P., Saini, R., Roy, P.P., Sahu, P.K., Dogra, D.P.: Envisioned speech recognition using EEG sensors. Pers. Ubiquit. Comput. 22(1), 185–199 (2018)
Lee, J., Won, K., Kwon, M., Jun, S.C., Ahn, M.: CNN with large data achieves true zero-training in online P300 brain-computer interface. IEEE Access 8, 74385–74400 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988057
Lee, S.H., Lee, M., Lee, S.W.: Neural decoding of imagined speech and visual imagery as intuitive paradigms for BCI communication. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 28(12), 2647–2659 (2020)
Li, M., et al.: The MindGomoku: an online P300 BCI game based on bayesian deep learning. Sensors 21(5), 1613 (2021)
Long, M., Cao, Y., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 97–105 (2015)
Mahato, S., Paul, S.: Detection of major depressive disorder using linear and non-linear features from EEG signals. Microsyst. Technol. 25(3), 1065–1076 (2019)
Placidi, G., Di Giamberardino, P., Petracca, A., Spezialetti, M., Iacoviello, D.: Classification of emotional signals from the deap dataset. In: International Congress on Neurotechnology, Electronics and Informatics, vol. 2, pp. 15–21. SCITEPRESS (2016)
Qin, W., Yu, C.: Neural pathways conveying novisual information to the visual cortex. Neural Plast. 2013, 864920 (2013)
Ramsey, N.F., Van De Heuvel, M.P., Kho, K.H., Leijten, F.S.: Towards human BCI applications based on cognitive brain systems: an investigation of neural signals recorded from the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 14(2), 214–217 (2006)
Runnova, A., Selskii, A., Kiselev, A., Shamionov, R., Parsamyan, R., Zhuravlev, M.: Changes in EEG alpha activity during attention control in patients: association with sleep disorders. J. Personalized Med. 11(7), 601 (2021)
Rutkowski, T.M., Koculak, M., Abe, M.S., Otake-Matsuura, M.: Brain correlates of task-load and dementia elucidation with tensor machine learning using oddball BCI paradigm. In: ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP, pp. 8578–8582. IEEE (2019)
Salenius, S., Kajola, M., Thompson, W., Kosslyn, S., Hari, R.: Reactivity of magnetic parieto-occipital alpha rhythm during visual imagery. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 95(6), 453–462 (1995)
Schirrmeister, R.T., et al.: Deep learning with convolutional neural networks for EEG decoding and visualization. Hum. Brain Mapp. 38(11), 5391–5420 (2017)
Spampinato, C., Palazzo, S., Kavasidis, I., Giordano, D., Souly, N., Shah, M.: Deep learning human mind for automated visual classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6809–6817 (2017)
Stewart, A.X., Nuthmann, A., Sanguinetti, G.: Single-trial classification of EEG in a visual object task using ICA and machine learning. J. Neurosci. Methods 228, 1–14 (2014)
Vert, J.P., Tsuda, K., Schölkopf, B.: A primer on kernel methods. Kernel Methods Comput. Biol. 47, 35–70 (2004)
Wolpaw, J.R., et al.: Brain-computer interface technology: a review of the first international meeting. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 8(2), 164–173 (2000)
Yuan, Y., Xun, G., Jia, K., Zhang, A.: A multi-view deep learning framework for EEG seizure detection. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 23(1), 83–94 (2018)
Zhang, D., Yao, L., Chen, K., Monaghan, J.: A convolutional recurrent attention model for subject-independent EEG signal analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 26(5), 715–719 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2019.2906824
Zhou, M., et al.: Epileptic seizure detection based on EEG signals and CNN. Front. Neuroinform. 12, 95 (2018)
Zickler, C., et al.: BCI applications for people with disabilities: defining user needs and user requirements. In: Assistive Technology from Adapted Equipment to Inclusive Environments, AAATE, vol. 25, pp. 185–189 (2009)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by Institute for Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2017-0-00451: Development of BCI based Brain and Cognitive Computing Technology for Recognizing Users Intentions using Deep Learning, No. 2020-0-01361: Artificial Intelligence Graduate School Program (YONSEI UNIVERSITY)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lee, P., Hwang, S., Jeon, S., Byun, H. (2022). Subject Adaptive EEG-Based Visual Recognition. In: Wallraven, C., Liu, Q., Nagahara, H. (eds) Pattern Recognition. ACPR 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13189. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-02444-3_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-02444-3_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-02443-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-02444-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)