Abstract
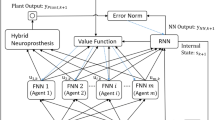
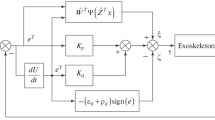
The challenges of the modern world accelerated the development of many fields of technology, including rehabilitation robotics. The focus of the robot-aided motor therapy is put on providing remote, home treatment. According to the conducted research, also, functional kinesiotherapy is a leading trend for the future. Therefore, designing a mechatronic device enabling such a workout is needed. The presented study is based on a concept of an upper extremity exoskeleton with free degrees of freedom. However, it is applicable for any exoskeleton with non-controlled joints. The paper corresponds to the problem of a control system for a not fully controlled robot; especially, as the mass parameters of the user’s limb remain unknown. Investigated prediction control is based on a recurrent neural network model of the system. The dynamics simulations are all performed without the usage of a physical device. Nevertheless, the outcomes of the trials prove, that such a control approach is suitable for the exoskeletons with free degrees of freedom. The results may be the base to adjust basic parameters of the neural networks used for similar applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dwivedi, Y.K., et al.: Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on information management research and practice: transforming education, work and life. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 55 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102211
Jnr, B.A.: Use of telemedicine and virtual care for remote treatment in response to COVID-19 pandemic. J. Med. Syst. 44(7) (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-020-01596-5
Bettger, J.P., Resnik, L.J.: Telerehabilitation in the age of COVID-19: an opportunity for learning health system research. Phys. Ther. 100(11), 1913–1916. Oxford University Press (2020). https://doi.org/10.1093/ptj/pzaa151
Akbari, A., Haghverd, F., Behbahani, S.: Robotic home-based rehabilitation systems design: from a literature review to a conceptual framework for community-based remote therapy during COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Robot. AI (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/FROBT.2021.612331
Manjunatha, H., Pareek, S., Jujjavarapu, S.S., Ghobadi ,M., Kesavadas, T., Esfahani, E.T.: Upper limb home-based robotic rehabilitation during COVID-19 outbreak. Front. Robot. AI (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/FROBT.2021.612834
Thant, A.A., et al.: Effects of task-oriented training on upper extremity functional performance in patients with sub-acute stroke: a randomized controlled trial. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 31(1), 82–87 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.31.82
Nordin, N., Xie, S.Q., Wünsche, B.: Assessment of movement quality in robot- assisted upper limb rehabilitation after stroke: a review. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 11(1), 1–23 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-0003-11-137
Tahamipour, Z.S.M., Hosseini Sani, S.K., Akbarzadeh, A., Kardan, I.: An assistive strategy for compliantly actuated exoskeletons using non-linear model predictive control method. In: Proceedings of the 26th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), pp. 982–987 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEE.2018.8472699
Batogowska, A., Słowikowski, J.: Atlas antropometryczny dorosłej ludności Polski dla potrzeb projektowania III. Warszawa: Instytut Wzornictwa Przemysłowego, Zakład Wydawnictw (1994)
McConville, J.T., Clauser, C.E., Churchill, T.D., Cuzzi, J., Kaleps, I.: Anthropometric relationships of body and body segment moments of inertia, December 1980. https://doi.org/10.21236/ADA097238
Guenzkofer, F., Bubb, H., Bengler, K.: Maximum elbow joint torques for digital human models. Int. J. Hum. Factors Model. Simul. 3(2) (2012). https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHFMS.2012.051092
Sariyildiz, E., Oboe, R., Ohnishi, K.: Disturbance observer-based robust control and its applications: 35th anniversary overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 67(3), 2042–2053. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2019.2903752
Boyko, N., Pobereyko, P.: Basic concepts of dynamic recurrent neural networks development. ECONTECHMOD Int. Q. J. Econ. Technol. Model. Process. 5(2), 63–68 (2016)
Xiu, Y., Zhang, W.: Multivariate chaotic time series prediction based on NARX neural networks, pp. 164–167 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2991/eame-17.2017.40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Falkowski, P. (2022). Predicting Dynamics of a Rehabilitation Exoskeleton with Free Degrees of Freedom. In: Szewczyk, R., Zieliński, C., Kaliczyńska, M. (eds) Automation 2022: New Solutions and Technologies for Automation, Robotics and Measurement Techniques. AUTOMATION 2022. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1427. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-03502-9_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-03502-9_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-03501-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-03502-9
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)