Abstract
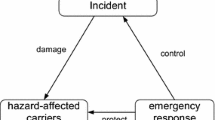
In order to improve the efficiency of emergency response and optimize the utilization of emergency resources, domain experts actively create role network of emergency response. Creating emergency role network manually is a time-consuming and labor-intensive task. An approach to extracting role networks from emergency plans is proposed, and then the extracted role relation network is made a quantitative analysis in this paper. First, role relation network is generated from emergency plan, which includes the emergency department and personnel are identified through a Bi-LSTM-CRF network, coreference resolution is implemented based on RoBERTa-E2E-Coref model, role relation is extracted based on the RoBRETa-CasRel model, and role relation network of emergency response is generated based on identified roles and their relationship. Second, role relation network from emergency plan with different levels were analyzed quantitatively by using the complex network analysis methods. Finally, experiment evaluation and a case study are given based on the real data sets, and the results show that the proposed approach can be used to assist emergency decision-makers to create role relation networks of emergency response. In addition, through the analysis of the extracted role relationship network, the quality of the emergency plan can be indirectly reflected.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 April 2022
The original version of the book was inadvertently published with an incorrect funder information in the acknowledgement in chapter 16. This has been corrected.
References
Kirschenbaum, A., Rapaport, C.: Informal social networks as generic contingency plans. J. Conting. Crisis Manag. 26(4), 453–460 (2018)
Guo, W., Zeng, Q., Duan, H., et al.: Text quality analysis of emergency response plans. IEEE Access 8, 9441–9456 (2020)
Jiang, Y.W., Wang, Q., Zhu, Y.B.: How occupational disease prevention and treatment apparatus to respond to public health emergency incidents. Zhonghua lao dong wei sheng zhi ye bing za zhi Zhonghua laodong weisheng zhiyebing zazhi Chinese J. Ind. Hyg. Occupat. Dis. 27(5), 319–320 (2009)
Huang, X., Liu, Q.: Strategy of establishing the super network emergency plan system in coastal cities of China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 23(9), 13062–13086 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01199-7
Uhr, C.: Multi-organizational Emergency Response Management. A Framework for Further Development. Department of Fire Safety Engineering and Systems Safety, Lund University, Lund, Sweden (2009)
Zhang, Y.C., Liu, Y., Zhang, H., et al.: The research of information dissemination model on online social network. Acta Physica Sinica 60(5), 60–66 (2011)
Jiang-Tao, K., Jian, H., Jian-Xing, G., et al.: Evaluation methods of node importance in undirected weighted networks based on complex network dynamics models. Acta Physica Sinica 67(9) (2018)
Tian, J.H., Shi, S.Z., Zhao, Y., et al.: Complex network analysis of law on Chinese herbal drugs intervention on radiation induced lung injury. Zhongguo Zhong yao za zhi Zhongguo zhongyao zazhi China J. Chin. Materia Medica 43(14), 3018–3025 (2018)
Duan, M., Jiang, Y., Chen, X., et al.: Degree centrality of the functional network in schizophrenia patients. Sheng wu yi xue gong cheng xue za zhi J. Biomed. Eng. Shengwu yixue gongchengxue zazhi 34(6), 837–841 (2017)
Li, J., Sun, A., Han, J., et al.: A survey on deep learning for named entity recognition. In: IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, vol. 99, pp. 1–1 (2020)
Tang, B., Wang, X., Yan, J., et al.: Entity recognition in Chinese clinical text using attention-based CNN-LSTM-CRF. BMC Med. Inf. Dec. Mak. 19(3), 89–97 (2019)
Le Thi, T., Phan Thi, T., Quan Thanh, T.: Machine learning using context vectors for object coreference resolution. Computing 1, 20 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-021-00902-4
Lee, K., He, L., Lewis, M., et al.: End-to-end neural coreference resolution. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.07045 (2017)
Joshi, M., Levy, O., Weld, D.S., et al.: BERT for coreference resolution: Baselines and analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.09091 (2019)
Li, Y.: Research on Chinese entity relation extraction method based on deep learning. In: 2021 International Conference on Communications, Information System and Computer Engineering (CISCE). IEEE, pp. 731–735 (2021)
Wei, Z., Su, J., Wang, Y., et al.: A novel hierarchical binary tagging framework for joint extraction of entities and relations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.03227 (2019)
Wang, Y.Y., Lin, F., Jiang, Z.L.: Pattern of acupoint selection based on complex network analysis technique. Zhongguo zhen jiu Chinese Acupunct. Moxib. 31(1), 85–88 (2011)
Sun, H., Feng, G., Gao, Z.: Key factors of the severity of chronic subjective tinnitus: a complex network analysis. Lin Chuang J. Clin. Otorhinolaryngol. Head, Neck Surg. 35(7), 586–592 (2021)
Hu, R.X., Yu, D.D., Li, H.M., et al.: Exploring efficacy of Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis in treatment of acute cerebral infarction based on two complex network analysis methods. Zhongguo China J. Chinese Materia Medica 46(14), 3722–3731 (2021)
Kong, J.T., Huang, J.G., Li, J.X.: Evaluation methods of node importance in undirected weighted networks based on complex network dynamics models. Acta Physica Sinica (2018)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1931207 and No. 61702306), Sci. & Tech. Development Fund of Shandong Province of China (No. ZR2019LZH001, No. ZR2017BF015 and No. ZR2017MF027), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2021QG038), the Humanities and Social Science Research Project of the Ministry of Education (No. 18YJAZH017), Shandong Chongqing Science and technology cooperation project (No.cstc2020jscx-lyjsAX0008), Sci. & Tech. Development Fund of Qingdao (No. 21-1-5-zlyj-1-zc), the Taishan Scholar Program of Shandong Province, SDUST Research Fund (No. 2015TDJH102 and No. 2019KJN024) and National Statistical Science Research Project (No. 2021LY053).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 IFIP International Federation for Information Processing
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhao, H., Zeng, Q., Guo, W., Ni, W. (2022). Automatic Generation and Analysis of Role Relation Network from Emergency Plans. In: Shi, Z., Zucker, JD., An, B. (eds) Intelligent Information Processing XI. IIP 2022. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, vol 643. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-03948-5_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-03948-5_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-03947-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-03948-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)