Abstract
Predictive maintenance depends on sources of data analysed through machine learning and data mining algorithms to identify and predict potential fault states. However, sources of raw data lack a layer of semantic abstraction providing a consistent way of interpreting data. The use of ontologies to describe data from structured and unstructured sources has been employed to provide a semantic layer delivering a consistent interpretation and meaning to data that can be exchanged between different entities. Data supplied by sensors is time-sensitive, as variations and fluctuations occur over periods and must be analysed regarding the period they occur. Transforming raw data and applying time constraints to fit the data to the semantic concepts is a process not frequently documented.
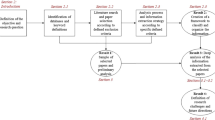
In this paper, we present an architecture for the transformation of data acquired through different sources – from sensors to contextual information supplied by management software – from JSON to ontology instances that can be used in a predictive maintenance scenario, alongside with machine learning and data mining solutions. Here, the different data sources are transformed semantic time-sensitive data, represented through means of an ontology and stored in a triple store.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kootanaee, J.A., Babu, K.N., Talari, F.H.: Just-in-time manufacturing system: from introduction to implement. Int. J. Econ. Bus. Financ. 1(2), 07–25 (2013)
Giustozzi, F., Saunier, J., Zanni-Merk, C.: Context modeling for Industry 4.0: an ontology-based proposal. Procedia Comput. Sci. 126, 675–684 (2018)
Canito, A., Corchado, J., Marreiros, G.: Bridging the gap between domain ontologies for predictive maintenance with machine learning. In: Rocha, Á., Adeli, H., Dzemyda, G., Moreira, F., Ramalho Correia, A.M. (eds.) WorldCIST 2021. AISC, vol. 1366, pp. 533–543. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72651-5_51
Pianism | Predictive and Prescriptive Automation in Smart Manufacturing. https://www.pianism.eu/. Accessed 12 Nov 2021
Cho, S., May, G., Kiritsis, D.: A semantic-driven approach for Industry 4.0. In: 15th International Conference of Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems, pp. 347–354 (2019)
Canito, A., Corchado, J., Marreiros, G.: A systematic review on time-constrained ontology evolution in predictive maintenance. Artif. Intell. Rev. 1–29 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-10079-z
Burek, P., Scherf, N., Herre, H.: Ontology patterns for the representation of in time. J. Biomed. Semantics 10 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13326-019-0206-4
Preventis, A., Marki, P., Petrakis, E.G.M., Batsakis, S.: CHRONOS: a tool for handling temporal ontologies in protégé. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, ICTAI, vol. 1, pp. 460–467. IEEE (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTAI.2012.69
Stanford Center for Biomedical Informatics Research. Protégé (2020). https://protege.stanford.edu/. Accessed 22 Feb 2021
Anagnostopoulos, E., Batsakis, S., Petrakis, E.: CHRONOS: a reasoning engine for qualitative temporal information in OWL. Procedia Comput. Sci. 22, 70–77 (2013)
Sbai, S., Louhdi, R.C.M., Behja, H., Chakhmoune, R.: JsonToOnto: building Owl2 ontologies from Json documents. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 10(10), 213–218 (2019)
Cheong, H.: Translating JSON Schema logics into OWL axioms for unified data validation on a digital data platform. Procedia Manuf. 28, 183–188 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The present work has been developed under the EUREKA - ITEA3 Project PIANISM (Itea-17008), PIANISM (ANI|P2020 40125) and supported by national funds through FCT – Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia through project UIDB/00760/2020 and Ph.D scholarship with reference SFRH/BD/147386/2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Canito, A., Nobre, A., Neves, J., Corchado, J., Marreiros, G. (2022). Applying Time-Constraints Using Ontologies to Sensor Data for Predictive Maintenance. In: Rocha, A., Adeli, H., Dzemyda, G., Moreira, F. (eds) Information Systems and Technologies. WorldCIST 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 469. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04819-7_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04819-7_38
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-04818-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-04819-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)