Abstract
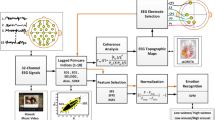
This paper describes well-known classification techniques which are evaluated for emotion classification. The aim of this work is the comparison of different channel selection techniques to achieve fast computation for electroencephalogram (EEG) data. Swarm intelligence algorithms belong to the class of nature-inspired algorithms which are very useful in achieving high accuracies while reducing the computing cost. In this paper different channel optimization techniques are compared to each other. They are applied to the DEAP dataset to find the most suitable channels in the context of emotion recognition. For channel selection, principal component analysis (PCA), maximum relevance-minimum redundancy (mRMR), particle swarm optimization (PSO), cuckoo search (CS) and grey wolf optimization (GWO) were investigated. By applying these optimization algorithms, the number of EEG channels could be reduced from 32 to 20 while the accuracy remained nearly the same. The proposed optimizations techniques saved between two- and seven-hours of computing time in training the Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory model to classify emotions, while the computing time without channel selection took 18 h. Among these algorithms, mRMR and CS obtained the most promising results. By using mRMR a total computing time of 11 h with an accuracy of 92.74% for arousal and 92.36% for valence was achieved. For CS a total computing time of 15 h was achieved, with an accuracy of 93.33% for arousal and 93.67% for valence.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jasper, H.: Report of the committee on methods of clinical examination in electroencephalography. The ten-twenty electrode system of the International Federation. Electroencephalography Clin. Neurophysiol. 10, 370–375 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(58)90053-1
Nuwer, M.R.: 10–10 electrode system for EEG recording. Clin. Neurophysiol. Offic. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 129, 1103 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2018.01.065
Silva, J., Burgos, F., Shin-Ting, W.: Interactive visualization of the cranio-cerebral correspondences for 10/20, 10/10 and 10/5 systems. In: 2016 29th SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images - SIBGRAPI 2016, pp. 424–431 (2017)
Torres-García, A.A., Reyes-García, C.A., Villaseñor-Pineda, L., García-Aguilar, G.: Implementing a fuzzy inference system in a multi-objective EEG channel selection model for imagined speech classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 59, 1–12 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.04.011
He, L., Hu, Y., Li, Y., Li, D.: Channel selection by Rayleigh coefficient maximization based genetic algorithm for classifying single-trial motor imagery EEG. Neurocomputing 121, 423–433 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2013.05.005
Alotaiby, T., El-Samie, F.E.A., Alshebeili, S.A., Ahmad, I.: A review of channel selection algorithms for EEG signal processing. EURASIP J. Adv. Sig. Process. 2015(1), 1–21 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13634-015-0251-9
Rizon, M., Murugappan, R., Nagarajan, R., Yacoob, S.: Asymmetric ratio and FCM based salient channel selection for human emotion detection using EEG. WSEAS Trans. Signal Process. 4, 596–603 (2008)
Jatupaiboon, N., Pan-ngum, S., Israsena, P.: Emotion classification using minimal EEG channels and frequency bands. In: Proceedings of 10th International Joint Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE 2013) (Khon Kaen, Thailand, 2013), vol. (2013)
Ansari-Asl, K., Chanel, G., Pun, T.: A channel selection method for EEG classification in emotion assessment based on synchronization likelihood. In: 15th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2007), Poznan, Poland, 3–7 September 2007 (2007)
Yildirim, E., Kaya, Y., Kilic, F.: A channel selection method for emotion recognition from EEG based on swarm-intelligence algorithms. IEEE Access 9, 109889–109902 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3100638
Wang, Z., Hu, S., Liu, G., Song, H.: Channel selection method based on CNNSE for EEG emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of IEEE 14th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Knowledge Engineering (ISKE 2019). (2019)
Wang, Z., Hu, S., Song, H.: Channel selection method for EEG emotion recognition using normalized mutual information. IEEE Access 7, 143303–143311 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2944273
Pane, E., Wibawa, A., Purnomo, M.: Channel selection of EEG emotion recognition using stepwise discriminant analysis. In: International Conference on Computer Engineering, Network and Intelligent Multimedia (CENIM) (2018)
Al-Qazzaz, N., Sabir, M., Ali, S., Ahmad, S., Grammer, K.: Effective EEG channels for emotion identification over the brain regions using differential evolution algorithm. In: 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 4703–4706 (2019)
Tong, L., Zhao, J., Fu, W.: Emotion recognition and channel selection based on EEG signal. In: 2018 11th International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation (ICICTA), 101–105 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICTA.2018.00031
Zhao, C., et al.: F-score based EEG channel selection methods for emotion recognition. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on E-health Networking, Application & Services (HEALTHCOM) (2021)
Xu, H., Wang, X., Li, W., Wang, H., Bi, Q.: Research on EEG channel selection method for emotion recognition. In: Proceeding of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics. Dali, China, December 2019 (2019)
Koelstra, S., et al.: DEAP: a database for emotion analysis; using physiological signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 3, 18–31 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/T-AFFC.2011.15
Jolliffe, I.T.: Principal Component Analysis. Springer Series in Statistics. Springer, New York (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/b98835
Naik, G.R.: Advances in Principal Component Analysis. Springer, Singapore (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6704-4
Peng, H., Long, F., Ding, C.: Feature selection based on mutual information: criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Machine Intell. 27, 1226–1238 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2005.159
Ramírez-Gallego, S., et al.: Fast-mRMR: fast minimum redundancy maximum relevance algorithm for high-dimensional big data. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 32, 134–152 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/int.21833
Tang, J., Liu, G., Pan, Q.: A review on representative swarm intelligence algorithms for solving optimization problems: applications and trends. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sinica 8, 1627–1643 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/JAS.2021.1004129
Carbas, S., Toktas, A., Ustun, D.: Nature-Inspired Metaheuristic Algorithms for Engineering Optimization Applications. Springer, Singapore (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6773-9
Yang, X.-S. (ed.): Cuckoo Search and Firefly Algorithm. SCI, vol. 516. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-02141-6
Nature-Inspired Computation and Swarm Intelligence, vol.. Elsevier (2020)
Ali, M., El-Hameed, M.A., Farahat, M.A.: Effective parameters’ identification for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell models using grey wolf optimizer. Renew. Energy 111, 455–462 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.04.036
Russell, J.A.: A circumplex model of affect. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 39, 1161–1178 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1037/h0077714
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9, 1735–1780 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
Acharya, D., et al.: Multi-class emotion classification using EEG signals. In: Garg, D., Wong, K., Sarangapani, J., Gupta, S.K. (eds.) IACC 2020. CCIS, vol. 1367, pp. 474–491. Springer, Singapore (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0401-0_38
Pedregosa, F., et al.: Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
Jingwei, T.: Wrapper-Feature-Selection-Toolbox-Python. GitHub. GitHub repository, (2021)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Balic, S., Kleybolte, L., Märtin, C. (2022). A Swarm Intelligence Approach: Combination of Different EEG-Channel Optimization Techniques to Enhance Emotion Recognition. In: Kurosu, M. (eds) Human-Computer Interaction. Technological Innovation. HCII 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13303. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05409-9_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05409-9_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-05408-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-05409-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)