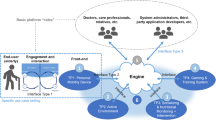
Abstract
As the aging population continues to increase globally, the development of methods to support the independent living of the elderly is becoming increasingly essential. Although smart home technology is expected to be used to support independent living in the homes of the elderly, the barriers to introducing this technology into the homes of elderly people are high. To support the continuation of independent living tailored to each elderly person, we aim to realize a system that can be composed and adjusted by the elderly themselves to turn their homes into smart homes using an easy-to-understand framework and an age-friendly interface that visualizes the framework. In this study, we developed a simple system described by a combination of trigger and action and a straightforward iPad configuration application. To evaluate the usability of the developed system, we performed an experiment in which young people experienced the configuration and adjustment of the system in a simulated environment. The results showed that the average time required for setting up the system was approximately 2 min, and the average of the system usability scale to evaluate the configuration system was 78.5, which was sufficiently high, indicating that the system was acceptable. In the future, we will verify whether this system can be accepted by the elderly as well.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare: Overview of Reiwa 2nd year simple life table. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/life/life20/. Accessed 22 Feb 2022
Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare: Annual health, labour and welfare report 2016. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/wp/hakusyo/kousei/16/. Accessed 22 Feb 2022
Alam, M.R., Reaz, M.B.I., Ali, M.A.M.: A review of smart homes-past, present, and future. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C (Appl. Rev.) 42(6), 1190–1203 (2012)
Scanaill, C.N., et al.: A review of approaches to mobility telemonitoring of the elderly in their living environment. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 34(4), 547–563 (2006)
Peetoom, K.K., Lexis, M.A., Joore, M., Dirksen, C.D., De Witte, L.P.: Literature review on monitoring technologies and their outcomes in independently living elderly people. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 10(4), 271–294 (2015)
Azimi, I., Rahmani, A.M., Liljeberg, P., Tenhunen, H.: Internet of things for remote elderly monitoring: a study from user-centered perspective. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. , 1–17 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-016-0387-y
Balta-Ozkan, N., Davidson, R., Bicket, M., Whitmarsh, L.: Social barriers to the adoption of smart homes. Energy Policy 63, 363–374 (2013)
Pal, D., Funilkul, S., Vanijja, V., Papasratorn, B.: Analyzing the elderly users’ adoption of smart-home services. IEEE Access 6, 51238–51252 (2018)
Alzahrani, T., Michelle, H., Dick, W.: Barriers and facilitators to using smart home technologies to support older adults: perspectives of three stakeholder groups. Int. J. Healthcare Inf. Syst. Inf. 16(4), 1–14 (2021)
Haigh, K.Z., Kiff, L.M., Ho, G.: The independent lifestyle assistant: lessons learned. Assist. Technol. 18(1), 87–106 (2006)
Kleinberger, T., Becker, M., Ras, E., Holzinger, A., Müller, P.: Ambient intelligence in assisted living: Enable elderly people to handle future interfaces. In: Stephanidis, C. (ed.) UAHCI 2007. LNCS, vol. 4555, pp. 103–112. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73281-5_11
Fischer, G.: End-user development and meta-design: foundations for cultures of participation. In: Pipek, V., Rosson, M.B., de Ruyter, B., Wulf, V. (eds.) IS-EUD 2009. LNCS, vol. 5435, pp. 3–14. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00427-8_1
Woo, J., Lim, Y.: User experience in do-it-yourself-style smart homes. In: Proceedings of the 2015 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, pp. 779–790. ACM, New York (2015)
Desolda, G., Ardito, C., Matera, M.: Empowering end users to customize their smart environments: model, composition paradigms, and domain-specific tools. ACM Trans. Comput. Hum. Interact. 24(2), 1–52 (2017)
Ghiani, G., Manca, M., Paternò, F., Santoro, C.: Personalization of context-dependent applications through trigger-action rules. ACM Trans. Comput. Hum. Interact. 24(2), 1–33 (2017)
Abdallah, R., Xu, L., Shi, W.: Lessons and experiences of a DIY smart home. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Smart Internet of Things, pp. 1–6. ACM, New York (2017)
Jakobi, T., et al.: Evolving needs in IoT control and accountability: a longitudinal study on smart home intelligibility. In: Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, pp. 1–28. ACM, New York (2018)
Kang, S., et al. : Design and implementation of age-friendly activity for supporting elderly’s daily life by IoT. In: Jia, Z., Gavriel, S. (eds.) HCII 2019. LNCS, vol. 11593, pp. 353–368. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22015-0_28
Maswadi, K., Ghani, N.B.A., Hamid, S.B.: Systematic literature review of smart home monitoring technologies based on IoT for the elderly. IEEE Access 8, 92244–92261 (2020)
Stavropoulos, T.G., Papastergiou, A., Mpaltadoros, L., Nikolopoulos, S., Kompatsiaris, I.: IoT wearable sensors and devices in elderly care: a literature review. Sensors 20(10), 2826 (2020)
Almeida, A., et al.: A critical analysis of an IoT-aware AAL system for elderly monitoring. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 97, 598–619 (2019)
Pinto, S., Cabral, J., Gomes, T.: We-care: an IoT-based health care system for elderly people. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, pp. 1378–1383. IEEE (2017)
Coradeschi, S., et al.: GiraffPlus: a system for monitoring activities and physiological parameters and promoting social interaction for elderly. In: Hippe, Z.S., Kulikowski, J.L., Mroczek, T., Wtorek, J. (eds.) Human-Computer Systems Interaction: Backgrounds and Applications 3. AISC, vol. 300, pp. 261–271. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-08491-6_22
ISO: Ergonomics of human-system interaction - part 210: human centred design for interactive systems. ISO 9241-210:2010. ISO, Geneva (2010)
Borelli, E., et al.: HABITAT: an IoT solution for independent elderly. Sensors 19(5), 1258 (2019)
Hwang, A.S., Hoey, J.: Smart home, the next generation: closing the gap between users and technology. In: AAAI Fall Symposium: Artificial Intelligence for Gerontechnology, pp. 14–21. Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto (2012)
Coughlin, J., D'Ambrosio, L.A., Reimer, B., Pratt, M.R.: Older adult perceptions of smart home technologies: implications for research, policy and market innovations in healthcare. In: 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 1810–1815. IEEE (2007)
Davis, S., Roudsari, A., Raworth, R., Courtney, K.L., Mackay, L.: Shared decision-making using personal health record technology: a scoping review at the crossroads. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 24(4), 857–866 (2017)
Chan, M., Estève, D., Escriba, C., Campo, E.: A review of smart homes – present state and future challenges. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 91(1), 55–81 (2008)
Baig, M.M., Afifi, S., GholamHosseini, H., Mirza, F.: A systematic review of wearable sensors and IoT-based monitoring applications for older adults – a focus on ageing population and independent living. J. Med. Syst. 43(8), 233 (2019)
Perumal, T., Datta, S.K., Bonnet, C.: IoT device management framework for smart home scenarios. In: 2015 IEEE 4th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics, pp. 54–55. IEEE (2016)
Sovacool, B.K., Furszyfer Del Rio, D.D.: Smart home technologies in Europe: a critical review of concepts, benefits, risks and policies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 120, 109663 (2020)
Castelli, N., et al.: What happened in my home?: an end-user development approach for smart home data visualization. In: Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 853–866. ACM, New York (2017)
Blase, U., McManus, E., Ho, M.P.Y., Littman, M.L.: Practical trigger-action programming in the smart home. In: Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on human factors in computing systems, pp. 803–812. ACM, New York (2014)
Dahl, Y., Reidar-Martin, S.: End-user composition interfaces for smart environments: a preliminary study of usability factors. In: Aaron, M. (ed.) DUXU 2011. LNCS, vol. 6770, pp. 118–127. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21708-1_14
Litvinova, E., Vuorimaa, P.: Engaging end users in real smart space programming. In: Proceedings of the 2012 ACM Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, pp. 1090–1095. ACM, New York (2012)
Caivano, D., Fogli, D., Lanzilotti, R., Piccinno, A., Cassano, F.: Supporting end users to control their smart home: design implications from a literature review and an empirical investigation. J. Syst. Softw. 144, 295–313 (2018)
Brich, J., Walch, M., Rietzler, M., Weber, M., Schaub, F.: Exploring end user programming needs in home automation. ACM Trans. Comput. Hum. Interact. 24(2), 1–35 (2017)
Serna, M.A., Sreenan, C.J., Fedor, S.: A visual programming framework for wireless sensor networks in smart home applications. In: 2015 IEEE Tenth International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing 2015, pp. 1–6. IEEE (2015)
Manca, M., Paternò, F., Santoro, C., Corcella, L.: Supporting end-user debugging of trigger-action rules for IoT applications. Int. J. Hum Comput Stud. 123, 56–69 (2019)
Woo, J., Lim, Y.: Routinoscope: collaborative routine reflection for routine-driven do-it-yourself smart homes. Int. J. Des. 14(3), 19–36 (2020)
Chang, H., Tsai, T., Chang, Y., Chang, Y.: Touch panel usability of elderly and children. Comput. Hum. Behav. 37(C), 258–269 (2014)
Murata, A., Iwase, H.: Usability of touch-panel interfaces for older adults. Hum. Factors 47(4), 767–776 (2005)
Park, E., Cho, Y., Han, J., Kwon, S.J.: Comprehensive approaches to user acceptance of Internet of Things in a smart home environment. IEEE Internet Things J. 4(6), 2342–2350 (2017)
Shin, J., Park, Y., Lee, D.: Who will be smart home users? An analysis of adoption and diffusion of smart homes. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 134, 246–253 (2018)
Park, E., Kim, S., Kim, Y., Kwon, S.J.: Smart home services as the next mainstream of the ICT industry: determinants of the adoption of smart home services. Univ. Access Inf. Soc. 17, 175–190 (2018)
Hubert, M., et al.: The influence of acceptance and adoption drivers on smart home usage. Eur. J. Mark. 53(6), 1073–1098 (2019)
Pal, D., Vanijja, V.: Perceived usability evaluation of Microsoft Teams as an online learning platform during COVID-19 using system usability scale and technology acceptance model in India. Child Youth Serv. Rev. 119, 105535 (2020)
Yoshioka, D., et al.: Evaluation of IoT-setting method among senior citizens in Japan. In: Qin, G., Jia, Z. (eds.) HCII 2021. LNCS, vol. 12786, pp. 278–292. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78108-8_21
Dey, A.K., Abowd, G.D., Salber, D.: A conceptual framework and a toolkit for supporting the rapid prototyping of context-aware applications. Hum. Comput. Interact. 16(2), 97–166 (2001)
Mynatt, E.D., Essa, I., Rogers, W.: Increasing the opportunities for aging in place. In: Proceedings on the 2000 Conference on Universal Usability, pp. 65–71. ACM, New York (2000)
Meyer, S., Rakotonirainy, A.: A survey of research on context-aware homes. In: Proceedings of the Australasian information security workshop conference on ACSW frontiers 2003, vol. 21, pp. 159–168. Australian Computer Society, Sydney (2003)
Benmansour, A., Bouchachia, A., Feham, M.: Multioccupant activity recognition in pervasive smart home environments. ACM Comput. Surv. 48(3), 1–36 (2015)
Kawsar, F., Nakajima, T., Fujinami, K.: Deploy spontaneously: supporting end-users in building and enhancing a smart home. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, pp. 282–291. ACM, New York (2008)
Coutaz, J., Crowley, J.L.: A first-person experience with end-user development for smart homes. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 15(2), 26–39 (2016)
Acknowledgments
The research was partially supported from the following funds: JSPS Program for Leading Graduate Schools (Graduate Program in Gerontology, Global Leadership Initiative for an Age Friendly Society, The University of Tokyo), Foundation of Support Center for Advanced Telecommunications Technology Research (SCAT), JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP19K14028, JP20H01753, and JP20K20494.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yoshizaki, R. et al. (2022). Design and Verification of a Smart Home Management System for Making a Smart Home Composable and Adjustable by the Elderly. In: Gao, Q., Zhou, J. (eds) Human Aspects of IT for the Aged Population. Technology in Everyday Living. HCII 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13331. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05654-3_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05654-3_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-05653-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-05654-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)