Abstract
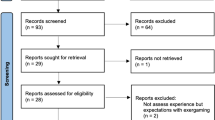
With the number and proportion of aging populations growing rapidly around the world, new forms of exercise such as exergames have been introduced and popularized in daily activities. This review highlights the potential benefits of exergames as an exercise platform for older adults. The purpose of this review is to explore the physical and mental effects of exergame use on older adults and to compare the differences between single-player and multiple-player interaction, traditional and new exercise modes and young and old age. Searches were conducted in Science Direct and Web of Science for articles published from 2013 to 2021 in journals and proceedings. In the 22 articles reviewed, we found that the most common exergame device is the Xbox Kinect, followed by the Nintendo Wii™. Exergame interventions were mostly set at 30 to 50 min, 2 or 3 times per week for 6 or 8 weeks. In addition, the sample size is relatively concentrated between 20 and 50. The experiment was conducted in a single-group pre-post design (no control group) or pre-post control group design (at least one control group). In many studies, exergames were found to have a positive effect on physical activity, cognitive function and sociability, as well as improving their mood and attitudes toward exergames, although a few studies found no significant effects. Especially in the home environment or in situations where older adults are unable to leave the house for some reason, exergames can be used as an alternative to traditional exercise and have a positive impact on the physical and mental health of older adults.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Comeras-Chueca, C., et al.: Assessment of active video games’ energy expenditure in children with overweight and obesity and differences by gender. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17(18), 6714 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17186714
Oh, Y., Yang, S.: Defining exergames and exergaming. In: Proceedings of Meaningful Play, pp. 1–17 (2010)
Agmon, M., Perry, C.K., Phelan, E., Demiris, G., Nguyen, H.Q.: A pilot study of Wii Fit exergames to improve balance in older adults. J. Geriatric Phys. Therapy 34, 161–167 (2011)
Goble, D.J., Cone, B.L., Fling, B.W.: Using the Wii Fit as a tool for balance assessment and neurorehabilitation: the first half decade of “Wii-search.” J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 11, 12 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-0003-11-12
Warburton, D.E.R.: The health benefits of active gaming: separating the myths from the virtual reality. Curr. Cardiovasc. Risk Rep. 7, 251–255 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12170-013-0322-0
Forsberg, A., Nilsagård, Y., Boström, K.: Perceptions of using videogames in rehabilitation: a dual perspective of people with multiple sclerosis and physiotherapists. Disabil. Rehabil. 37, 338–344 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3109/09638288.2014.918196
Plow, M., Finlayson, M.: Potential benefits of nintendo Wii Fit among people with multiple sclerosis: a longitudinal pilot study. Int. J. MS Care 13, 21–30 (2011). https://doi.org/10.7224/1537-2073-13.1.21
Prosperini, L., Fortuna, D., Giannì, C., Leonardi, L., Marchetti, M.R., Pozzilli, C.: Home-based balance training using the Wii balance board: a randomized, crossover pilot study in multiple sclerosis. Neurorehabil. Neural Rep. 27, 516–525 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1177/1545968313478484
Robinson, J., Dixon, J., Macsween, A., van Schaik, P., Martin, D.: The effects of exergaming on balance, gait, technology acceptance and flow experience in people with multiple sclerosis: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 7, 8 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13102-015-0001-1
World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health
Zheng, H., Li, J., Salmon, C.T., Theng, Y.-L.: The effects of exergames on emotional well-being of older adults. Comput. Hum. Behav. 110, 106383 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106383
Li, J., Theng, Y.-L., Foo, S.: Play mode effect of exergames on subthreshold depression older adults: a randomized pilot trial. Front. Psychol. 11, 552416 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.552416
Chen, F.X., King, A.C., Hekler, E.B.: “Healthifying” exergames: improving health outcomes through intentional priming. In: Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 1855–1864. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA (2014)
Zangirolami-Raimundo, J., et al.: Contrasting performance between physically active and sedentary older people playing exergames. Medicine 98, (2019). https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000014213
Mackintosh, K.A., Standage, M., Staiano, A.E., Lester, L., McNarry, M.A.: Investigating the physiological and psychosocial responses of single- and dual-player exergaming in young adults. Games Health J. 5, 375–381 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1089/g4h.2016.0015
Chua, P.-H., Jung, Y., Lwin, M., Theng, Y.-L.: Let’s play together: effects of video-game play on intergenerational perceptions among youth and elderly participants. Comput. Hum. Behav. 29, 2303–2311 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2013.04.037
Osmanovic, S., Pecchioni, L.: Beyond entertainment: motivations and outcomes of video game playing by older adults and their younger family members. Games Culture 11, 130–149 (2015)
Sousa, C.V., et al.: Active video games in fully immersive virtual reality elicit moderate-to-vigorous physical activity and improve cognitive performance in sedentary college students. J. Sport Health Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jshs.2021.05.002
Liao, Y.-Y., Chen, I.-H., Hsu, W.-C., Tseng, H.-Y., Wang, R.-Y.: Effect of exergaming versus combined exercise on cognitive function and brain activation in frail older adults: a randomised controlled trial. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 64, 101492 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rehab.2021.101492
Naugle, K.E., Naugle, K.M., Wikstrom, E.A.: Cardiovascular and affective outcomes of active gaming: using the nintendo Wii as a cardiovascular training tool. J. Strength Cond. Res. 28, 443–451 (2014)
Xu, X., Li, J., Pham, T., Salmon, C., Theng, Y.-L.: Improving psychosocial well-being of older adults through exergaming: the moderation effects of intergenerational communication and age cohorts. Games Health J. 5, 389–397 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1089/g4h.2016.0060
Li, C., Li, J., Pham, T., Theng, Y.-L., Chia, B.: Promoting Healthy and Active Ageing through Exergames: Effects of Exergames on Senior Adults’ Psychosocial Well-Being. Presented at the (2018)
Gonçalves, A.R., Muñoz, J.E., Gouveia, É.R., Cameirão, M., Bermúdez i Badia, S.: Effects of prolonged multidimensional fitness training with exergames on the physical exertion levels of older adults. Vis. Comput. 37(1), 19–30 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01736-0
Yang, C.-M., Chen Hsieh, J., Chen, Y.-C., Yang, S.-Y., Lin, H.-C.: Effects of Kinect exergames on balance training among community older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Medicine 99, e21228 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000021228
Silva, E., Lange, B., Bacha, J., Pompeu, J.E.: Effects of the interactive videogame nintendo Wii sports on upper limb motor function of individuals with post-polio syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. Games Health J. 9, 461–471 (2020)
Karahan, Y.A., Tok, F., Taskin, H., Kucuksarac, S., Basaran, A., Yildirim, P.: Effects of exergames on balance, functional mobility, and quality of life of geriatrics versus home exercise programme: randomized controlled study. Central Eur. J. Public Health 23, S14–S18 (2015). https://doi.org/10.21101/cejph.a4081
Nguyen, H.V., Huang, H.-C., Wong, M.-K., Yang, Y.-H., Huang, T.-L., Teng, C.-I.: Moderator roles of optimism and weight control on the impact of playing exergames on happiness: the perspective of social cognitive theory using a randomized controlled trial. Games Health J. 7, 246–252 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1089/g4h.2017.0165
Moreira, N.B., Rodacki, A.L.F., Costa, S.N., Pitta, A., Bento, P.C.B.: Perceptive-cognitive and physical function in prefrail older adults: exergaming versus traditional multicomponent training. Rejuven. Res. 24, 28–36 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1089/rej.2020.2302
Ogawa, E., et al.: Effects of exergaming on cognition and gait in older adults at risk for falling. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 52, 1 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000002167
Cavalcante, M.M., et al.: Exergame training-induced neuroplasticity and cognitive improvement in institutionalized older adults: a preliminary investigation. Physiol. Behav. 241, 113589 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2021.113589
Taylor, L., Kerse, N., Klenk, J., Borotkanics, R., Maddison, R.: Exergames to improve the mobility of long-term care residents: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Games Health J. 7, 37–42 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1089/g4h.2017.0084
Willaert, J., de Vries, A., Tavernier, J., Van Dieen, J., Jonkers, I., Verschueren, S.: Does a novel exergame challenge balance and activate muscles more than existing off-the-shelf exergames? J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 17, (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-019-0628-3
Stephen L. Crites, Jr., Fabrigar, L.R., Petty, R.E.: Measuring the affective and cognitive properties of attitudes: conceptual and methodological issues. Person. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 20, 619–634 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167294206001
Gao, Y., Mandryk, R.L.: GrabApple: the design of a casual exergame. In: Anacleto, J.C., Fels, S., Graham, N., Kapralos, B., Saif El-Nasr, M., Stanley, K. (eds.) ICEC 2011. LNCS, vol. 6972, pp. 35–46. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24500-8_5
Sonderegger, A., Schmutz, S., Sauer, J.: The influence of age in usability testing. Appl. Ergon. 52, 291–300 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apergo.2015.06.012
Acknowledgement
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China 72101100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, Y., Zhong, R. (2022). Effects of Exergames Intervention on Older Adults: A Review. In: Rau, PL.P. (eds) Cross-Cultural Design. Applications in Business, Communication, Health, Well-being, and Inclusiveness. HCII 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13313. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06050-2_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06050-2_32
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-06049-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-06050-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)