Abstract
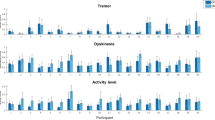
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that presents motor (tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and instability) and non-motor dysfunctions. In this study we present a methodology to monitor the evolution of motor symptoms of Parkinson disease patients remotely, and its application to asses the effects of an experimental therapeutic intervention based on acoustic stimulation in a two months’ study. Monitoring is based on wearing a commercial smartwatch while performing a set of exercises extracted from the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale. Three indicators are extracted from the triaxial accelerometer’s signals to monitor tremor and bradykinesia. Results of the evolution of these indicators over a 2 months’ study are shown for two PD patients following a therapeutic intervention based on acoustic stimulation and a healthy control group of similar age and gender. The feasibility of using consumer smartwatches for remote monitoring of motor symptom’s is discussed together with its limitations, specially regarding long-term assessment of acoustic stimulation interventions.
Supported by Instrumentation and applied acoustics research group.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tecapark. https://www.i2a2.upm.es/tecapark. Accessed 7 Jan 2022
Bloem, B.R., de Vries, N.M., Ebersbach, G.: Nonpharmacological treatments for patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 30(11), 1504–1520 (2015)
Díez-Cirarda, M., Ibarretxe-Bilbao, N., Peña, J., Ojeda, N.: Neurorehabilitation in Parkinson’s disease: a critical review of cognitive rehabilitation effects on cognition and brain. Neural Plast. 2018, 2651918 (2018)
Garcia-Argibay, M., Santed, M.A., Reales, J.M.: Efficacy of binaural auditory beats in cognition, anxiety, and pain perception: a meta-analysis. Psychol. Res. 83(2), 357–372 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-018-1066-8
García-Casares, N., Martín-Colom, J.E., García-Arnés, J.A.: Music therapy in Parkinson’s disease. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 19(12), 1054–1062 (2018)
Gálvez, G., Recuero, M., Canuet, L., Del-Pozo, F.: Short-term effects of binaural beats on EEG power, functional connectivity, cognition, gait and anxiety in Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Neural Syst. 28(5), 1750055 (2018)
Johns, P.: Chapter 13-Parkinson’s disease. In: Clinical Neuroscience, pp. 163–179 (2014)
Luis-Martínez, R., Monje, M.H.G., Antonini, A., Sánchez-Ferro, A., Mestre, T.A.: Technology-enabled care: integrating multidisciplinary care in Parkinson’s disease through digital technology. Front. Neurol. 11, 575975 (2020)
Mahadevan, N., et al.: Development of digital biomarkers for resting tremor and bradykinesia using a wrist-worn wearable device. NPJ Digit. Med. 3, 5 (2020)
Monje, M.H.G., Foffani, G., Obeso, J., Sánchez-Ferro, Á.: New sensor and wearable technologies to aid in the diagnosis and treatment monitoring of Parkinson’s disease. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 21, 111–143 (2019)
Poewe, W.: Parkinson disease Primer - a true team effort. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 6(1), 31 (2020)
Powers, R., et al.: Smartwatch inertial sensors continuously monitor real-world motor fluctuations in Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 13(579), eabd7865 (2021)
Prasad, R., Babu, S., Siddaiah, N., Rao, K.: A review on techniques for diagnosing and monitoring patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 7(203), 2 (2016)
Rovini, E., Maremmani, C., Cavallo, F.: How wearable sensors can support Parkinson’s disease diagnosis and treatment: a systematic review. Front. Neurosci. 11, 555 (2017)
Sigcha, L., et al.: Automatic resting tremor assessment in Parkinson’s disease using smartwatches and multitask convolutional neural networks. Sensors (Basel) 21(1), 291 (2021)
Sigcha, L., Pavón, I., Arezes, P., Costa, N., De Arcas, G., López, J.M.: Occupational risk prevention through smartwatches: precision and uncertainty effects of the built-in accelerometer. Sensors 18(11) (2018). https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/18/11/3805
Sihvonen, A.J., Särkämö, T., Leo, V., Tervaniemi, M., Altenmüller, E., Soinila, S.: Music-based interventions in neurological rehabilitation. Lancet Neurol. 16(8), 648–660 (2017)
Swerdlow, N.R., Bhakta, S.G., Light, G.A.: Room to move: plasticity in early auditory information processing and auditory learning in schizophrenia revealed by acute pharmacological challenge. Schizophr. Res. 199, 285–291 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work has been funded by grant TECA-PARK_55_01 under the POCTEP 0348_CIE_6_E program of Fundacion General del CSIC. The authors would like to thank the Parkinson’s associations of Madrid, Valladolid, Burgos, Asturias, Jovellanos and Hogar Santa Estefânia de Guimaraes for their participation in this study, and also to Dr. J. C. Martiınez-Castrillo, Dr. M. Gago and Dra. M. Blazquez for their contributions and continuous support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sigcha, L., Gonzalez Calleja, D., Pavón, I., López, J., de Arcas, G. (2022). Monitoring Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease Under Long Term Acoustic Stimulation. In: Ferrández Vicente, J.M., Álvarez-Sánchez, J.R., de la Paz López, F., Adeli, H. (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Neuroscience: Affective Analysis and Health Applications. IWINAC 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13258. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06242-1_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06242-1_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-06241-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-06242-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)