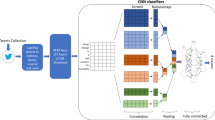
Abstract
Global warming or climate change is one of the most trend topics of the decade in the world, according to scientists the earth is getting warm more every year, hence people are more and more complaining about this phenomenon, some of them believe that climate change is happening, and we should worry and act about it. Despite that, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) confirms that global warming is real and causes climate change, the majority of people are still in doubt about that, this group is generally called deniers or skeptics who think that it is not real and not caused by human. This group of people is costing a lot for countries, by affecting others who think that we should take corrective actions toward global warming. Thus, it is required to create models that identify the impact of people’s thoughts to help governments for achieving better control of their citizens. In this work we present a new model for analyzing public opinion on social media platforms especially Twitter about climate change subject, we adopted the Sentiment Analysis technique, which is a field of natural language processing, we provided an effective model based on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for detecting people's reviews on climate change in social media platforms. Our model may assist decision-makers in producing appropriate strategies to ameliorate the impacts of the climate change phenomenon.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AlBadani, B., Shi, R., Dong, J.: A novel machine learning approach for sentiment analysis on Twitter incorporating the universal language model fine-tuning and SVM. Appl. Syst. Innov. 5(1), 13 (2022)
Nezhad, Z.B., Deihimi, M.A.: Twitter sentiment analysis from Iran about COVID 19 vaccine. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 16(1), 102367 (2022)
Hidayat, T.H.J., Ruldeviyani, Y., Aditama, A.R., Madya, G.R., Nugraha, A.W., Adisaputra, M.W.: Sentiment analysis of twitter data related to Rinca Island development using Doc2Vec and SVM and logistic regression as classifier. Proc. Comput. Sci. 197, 660–667 (2022)
Becken, S., Stantic, B., Chen, J., Connolly, R.M.: Twitter conversations reveal issue salience of aviation in the broader context of climate change. J. Air Transp. Manag. 98, 102157 (2022)
Al-Rawi, A., Kane, O., Bizimana, A.J.: Topic modelling of public Twitter discourses, part bot, part active human user, on climate change and global warming. J. Environ. Med. 2(1), 31–53 (2021)
Fownes, J.R., Yu, C., Margolin, D.B.: Twitter and climate change. Sociol. Compass 12(6), e12587 (2018)
Chen, X., Zou, L., Zhao, B.: Detecting climate change deniers on twitter using a deep neural network. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing, pp. 204–210, February 2019
Taboada, M., Brooke, J., Tofiloski, M., Voll, K., Stede, M.: Lexicon-based methods for sentiment analysis. Comput. Linguist. 37(2), 267–307 (2011)
Bansal, B., Srivastava, S.: On predicting elections with hybrid topic based sentiment analysis of tweets. Proc. Comput. Sci. 135, 346–353 (2018)
Khan, R., et al.: Crime Detection Using Sentiment Analysis (2021)
Ramirez-Tinoco, F.J., et al.: Use of sentiment analysis techniques in healthcare domain. In: Alor-Hernández, G., Sánchez-Cervantes, J.L., Rodríguez-González, A., Valencia-García, R. (eds.) Current Trends in Semantic Web Technologies: Theory and Practice. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol. 815, pp. 189–212. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-06149-4_8
Lydiri, M., El Mourabit, Y., El Habouz, Y.: A new sentiment analysis system of climate change for smart city governance based on deep learning. In: Ben Ahmed, M., Rakıp Karaș, İ, Santos, D., Sergeyeva, O., Boudhir, A.A. (eds.) Innovations in Smart Cities Applications Volume 4. LNNS, vol. 183, pp. 17–28. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66840-2_2
Liu, H.: Sentiment analysis of citations using word2vec. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.00177 (2017)
Gao, B., Pavel, L. : On the properties of the softmax function with application in game theory and reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.00805 (2017)
Canada Foundation for Innovation JELF Grant to Chris Bauch, University of Waterloo
Koenecke, A., Feliu-Fabà, J.: Learning twitter user sentiments on climate change with limited labeled data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.07342 (2019)
Kabaghe, C., Qin, J.: Classifying tweets based on climate change stance. Training 66(60.9), 61 (2020)
Kirelli, Y., Arslankaya, S.: Sentiment analysis of shared tweets on global warming on Twitter with data mining methods: a case study on Turkish language. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2020 (2020)
Xia, E., Yue, H., Liu, H.: Tweet sentiment analysis of the 2020 US presidential election. In Companion Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, pp. 367–371, April 2021
Yang, L., Li, Y., Wang, J., Sherratt, R.S.: Sentiment analysis for E-commerce product reviews in Chinese based on sentiment lexicon and deep learning. IEEE Access 8, 23522–23530 (2020)
Antypas, D., Preece, A., Collados, J.C.: Politics and Virality in the Time of Twitter: A Large-Scale Cross-Party Sentiment Analysis in Greece, Spain and United Kingdom. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.00396 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lydiri, M., El Habouz, Y., Zougagh, H. (2022). Sentiment Analysis Decision System for Tracking Climate Change Opinion in Twitter. In: Fakir, M., Baslam, M., El Ayachi, R. (eds) Business Intelligence. CBI 2022. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, vol 449. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06458-6_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06458-6_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-06457-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-06458-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)