Abstract
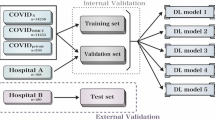
CheXNet is not a surprise for Deep Learning (DL) community as it was primarily designed for radiologist-level pneumonia detection in Chest X-rays (CXRs). In this paper, we study CheXNet to analyze CXRs to detect the evidence of Covid-19. On a dataset of size 4, 600 CXRs (2, 300 Covid-19 positive cases and 2, 300 non-Covid cases (Healthy and Pneumonia cases)) and with k(=5) fold cross-validation technique, we achieve the following performance scores: accuracy of 0.98, AUC of 0.99, specificity of 0.98 and sensitivity of 0.99. On such a large dataset, our results can be compared with state-of-the-art results.
Authors Credit Statement. Authors contributed equally to the paper.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World health organization (2020) naming the coronavirus disease (Covid-19) and the virus that causes it. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technical-guidance/naming-the-coronavirus-disease-%28covid-2019%29-and-the-virus-that-causes-it
Hui, D.S., et al.: The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health-the latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 91, 264–266 (2020)
World health organization (2020) coronavirus disease (Covid-2019) situation reports. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports
Santosh, K.C.: COVID-19 prediction models and unexploited data. J. Med. Syst. 44(9), 170 (2020)
Li, M., et al.: Coronavirus disease (Covid-19): spectrum of CT findings and temporal progression of the disease. Acad. Radiol. 27(5), 603–608 (2020)
Kong, W., Agarwal, P.P.: Chest imaging appearance of Covid-19 infection. Radiol.: Cardiothorac. Imaging 2(1), e200028 (2020)
Huang, C., et al.: Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 395(10223), 497–506 (2020)
Ng, M.-Y., et al.: Imaging profile of the Covid-19 infection: radiologic findings and literature review. Radiol.: Cardiothorac. Imaging 2(1), e200034 (2020)
Santosh, K.C., Ghosh, S.: Covid-19 imaging tools: how big data is big? J. Med. Syst. 45(7), 1–8 (2021)
Santosh, K.C.: AI-driven tools for coronavirus outbreak: need of active learning and cross-population train/test models on multitudinal/multimodal data. J. Med. Syst. 44(5), 1–5 (2020)
Santosh, K.C., Vajda, S., Antani, S., Thoma, G.R.: Edge map analysis in chest X-rays for automatic pulmonary abnormality screening. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 11(9), 1637–1646 (2016)
Karargyris, A., et al.: Combination of texture and shape features to detect pulmonary abnormalities in digital chest X-rays. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 11(1), 99–106 (2016)
Vajda, S., et al.: Feature selection for automatic tuberculosis screening in frontal chest radiographs. J. Med. Syst. 42(8), 1–11 (2018)
Santosh, K.C., Antani, S.: Automated chest X-ray screening: can lung region symmetry help detect pulmonary abnormalities? IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(5), 1168–1177 (2017)
Kang, M., Gurbani, S.S., Kempker, J.A.: The published scientific literature on Covid-19: an analysis of pubmed abstracts. J. Med. Syst. 45(1), 1–2 (2021)
Wang, L., Lin, Z.Q., Wong, A.: Covid-net: a tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of Covid-19 cases from chest X-ray images. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–12 (2020)
Narin, A., Kaya, C., Pamuk, Z.: Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (Covid-19) using X-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Anal. Appl. 24, 1–14 (2021)
Marques, G., Agarwal, D., de la Torre Díez, I.: Automated medical diagnosis of Covid-19 through efficientnet convolutional neural network. Appl. Soft Comput. 96, 106691 (2020)
Apostolopoulos, I.D., Mpesiana, T.A.: Covid-19: automatic detection from X-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 43(2), 635–640 (2020)
Mukherjee, H., Ghosh, S., Dhar, A., Obaidullah, S.M., Santosh, K.C., Roy, K.: Deep neural network to detect Covid-19: one architecture for both CT scans and chest X-rays. Appl. Intell. 51, 1–13 (2020)
Das, D., Santosh, K.C., Pal, U.: Truncated inception net: Covid-19 outbreak screening using chest X-rays. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 43(3), 915–925 (2020)
Loey, M., Manogaran, G., Khalifa, N.E.M.: A deep transfer learning model with classical data augmentation and CGAN to detect Covid-19 from chest CT radiography digital images. Neural Comput. Appl. 1–13 (2020)
Ozturk, T., Talo, M., Yildirim, E.A., Baloglu, U.B., Yildirim, O., Acharya, U.R.: Automated detection of Covid-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 103792 (2020)
Kermany, D., Zhang, K., Goldbaum, M., et al.: Labeled optical coherence tomography (OCT) and chest X-ray images for classification. Mendeley Data 2(2) (2018)
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Van Der Maaten, L., Weinberger, K.Q.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4700–4708 (2017)
Rajpurkar, P., et al.: ChexNet: radiologist-level pneumonia detection on chest X-rays with deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.05225 (2017)
Wang, X., Peng, Y., Lu, L., Lu, Z., Bagheri, M., Summers, R.M.: ChestX-ray8: hospital-scale chest X-ray database and benchmarks on weakly-supervised classification and localization of common thorax diseases. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2097–2106 (2017)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.-J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 248–255. IEEE (2009)
Mahbub, M.K., Biswas, M., Gaur, L., Alenezi, F., Santosh, K.C.: Deep features to detect pulmonary abnormalities in chest X-rays due to infectious diseaseX: Covid-19, pneumonia, and tuberculosis. Inf. Sci. 592, 389–401 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Santosh, K., Ghosh, S. (2022). CheXNet for the Evidence of Covid-19 Using 2.3K Positive Chest X-rays. In: Santosh, K., Hegadi, R., Pal, U. (eds) Recent Trends in Image Processing and Pattern Recognition. RTIP2R 2021. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1576. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07005-1_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07005-1_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-07004-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-07005-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)