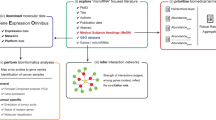
Abstract
Established text mining approaches can be used to identify miRNAs mentioned in published papers and preprints. Here, we apply such a targeted approach to the LitCovid literature collection in order to find viral miRNAs published in connection to SARS-CoV-2. As LitCovid aims at being a comprehensive collection of literature on new findings on SARS-CoV-2 and the COVID-19 pandemic, it is perfectly suited for our goal of finding all reported SARS-CoV-2 miRNAs. The identified miRNAs provide an up-to-date and quite comprehensive collection of potential viral miRNAs, which is a useful resource for further research to fight the current pandemic.
We identified 564 putative SARS-CoV-2 miRNAs together with the respective evidences, i.e. the original publications, and collect them for critical review. The text mining method and the corresponding synonym list are optimized for finding viral miRNAs and the results are manually curated. Since not all miRNAs were experimentally verified, the collection might contain false positives, but it is highly sensitive. Moreover, the text mining approach and resulting collection of miRNA candidates can be useful resources for further SARS-CoV-2 research and for experimental validation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aydemir, M.N., Aydemir, H.B., Korkmaz, E.M., Budak, M., Cekin, N., Pinarbasi, E.: Computationally predicted SARS-CoV-2 encoded microRNAs target NFKB, JAK/STAT and TGFB signaling pathways. Gene Reports 22 (2021)
Chen, Q., Allot, A., Lu, Z.: Keep up with the latest coronavirus research. Nature 579, 193–194 (2020)
Chen, Q., Allot, A., Lu, Z.: LitCovid: an open database of COVID-19 literature. Nucl. Acids Res. 49, D1534–D1540 (2021)
Demirci, M.D.S., Adan, A.: Computational analysis of microRNA-mediated interactions in SARS-CoV-2 infection. PeerJ 8, e9369 (2020)
Dong, E., Du, H., Gardner, L.: An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet. Infect. Dis 20, 533–534 (2020)
Fu, Z., et al.: A virus-derived microRNA-like small RNA serves as a serum biomarker to prioritize the COVID-19 patients at high risk of developing severe disease. Cell Discov. 7, 1–4 (2021)
Honnibal, M., et al.: explosion/spaCy: v2.1.7: improved evaluation, better language factories and bug fixes, August 2019
Joppich, M.: Integrative bioinformatics applications for complex human disease contexts, November 2021
Joppich, M., Weber, C., Zimmer, R.: Using context-sensitive text mining to identify miRNAs in different stages of atherosclerosis. Thromb. Haemost. 119, 1247–1264 (2019)
Kaiser, R., et al.: Self-sustaining IL-8 loops drive a prothrombotic neutrophil phenotype in severe COVID-19. JCI Insight 6 (2021)
Karimi, E., Azari, H., Yari, M., Tahmasebi, A., Azad, M.H., Mousavi, P.: Interplay between SARS-CoV-2-derived miRNAs, immune system, vitamin D pathway and respiratory system. J. Cell Mol. Med. 25, 7825–7839 (2021)
Khan, M.A.A.K., Sany, M.R.U., Islam, M.S., Islam, A.B.M.M.K.: Epigenetic regulator miRNA pattern differences among SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and SARS-CoV-2 world-wide isolates delineated the mystery behind the epic pathogenicity and distinct clinical characteristics of pandemic COVID-19. Front. Genet. 11 (2020)
Kozomara, A., Birgaoanu, M., Griffiths-Jones, S.: MiRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucl. Acids Res. 47, D155–D162 (2019)
Liao, M., et al.: Single-cell landscape of bronchoalveolar immune cells in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 26, 842–844 (2020)
Liu, Z., et al.: SARS-CoV-2 encoded microRNAs are involved in the process of virus infection and host immune response. J. Biomed. Res. 35, 216 (2021)
Meng, F., et al.: Viral MicroRNAs encoded by nucleocapsid gene of SARS-CoV-2 are detected during infection, and targeting metabolic pathways in host cells. Cells 10(7), 1762 (2021)
Merino, G.A., et al.: Novel SARS-CoV-2 encoded small RNAs in the passage to humans. Bioinformatics 36, 5571–5581 (2020)
Mishra, R., Kumar, A., Ingle, H., Kumar, H.: The interplay between viral-derived miRNAs and host immunity during infection. Front. Immunol. 10, 3079 (2020)
Morales, L., Oliveros, J.C., Fernandez-Delgado, R., tenOever, B.R., Enjuanes, L., Sola, I.: SARS-CoV-encoded small RNAs contribute to infection-associated lung pathology. Cell Host Microbe 21, 344–355 (2017)
Neumann, M., King, D., Beltagy, I., Ammar, W.: ScispaCy: fast and robust models for biomedical natural language processing. In: BioNLP 2019 - SIGBioMed Workshop on Biomedical Natural Language Processing, Proceedings of the 18th BioNLP Workshop and Shared Task (2019)
Nicolai, L., et al.: Vascular neutrophilic inflammation and immunothrombosis distinguish severe COVID-19 from influenza pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 19, 574–581 (2021)
Pawlica, P., et al.: SARS-CoV-2 expresses a microRNA-like small RNA able to selectively repress host genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 118, e2116668118 (2021)
Pekayvaz, K., et al.: Protective immune trajectories in early viral containment of non-pneumonic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Commun. 13, 1018 (2022)
Qureshi, A., Thakur, N., Monga, I., Thakur, A., Kumar, M.: VIRmiRNA: a comprehensive resource for experimentally validated viral miRNAs and their targets. Database J. Biol. Databases Curation 2014 (2014)
Rahaman, M., Komanapalli, J., Mukherjee, M., Byram, P.K., Sahoo, S., Chakravorty, N.: Decrypting the role of predicted SARS-CoV-2 miRNAs in COVID-19 pathogenesis: a bioinformatics approach. Comput. Biol. Med. 136, 104669 (2021)
Roy, S., et al.: Identification and host response interaction study of SARS-CoV-2 encoded miRNA-like sequences: an in silico approach. Comput. Biol. Med. 134, 104451 (2021)
Saini, S., Saini, A., Thakur, C.J., Kumar, V., Gupta, R.D., Sharma, J.K.: Genome-wide computational prediction of miRNAs in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) revealed target genes involved in pulmonary vasculature and antiviral innate immunity. Mol. Biol. Res. Commun. 9, 83 (2020)
Sarma, A., Phukan, H., Halder, N., Madanan, M.G.: An in-silico approach to study the possible interactions of miRNA between human and SARS-CoV-2. Comput. Biol. Chem. 88, 107352 (2020)
Satyam, R., et al.: miRNAs in SARS-CoV 2: a spoke in the wheel of pathogenesis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 27, 1628–1641 (2020)
Singh, M., et al.: A virus-derived microRNA targets immune response genes during SARS-CoV-2 infection. EMBO Rep. 23, e54341 (2022)
Verma, S., Dwivedy, A., Kumar, N., Biswal, B.K.: Computational prediction of SARS-CoV-2 encoded miRNAs and their 2 putative host targets. bioRxiv (2020)
Wilk, A.J., et al.: A single-cell atlas of the peripheral immune response in patients with severe COVID-19. Nat. Med. 26, 1070–1076 (2020)
Wyler, E., et al.: Transcriptomic profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infected human cell lines identifies HSP90 as target for COVID-19 therapy. iScience 24, 102151 (2021)
Yu, T.Y., Chen, M., Wang, C.D.: Annotation of miRNAs in the COVID-19 Novel Coronavirus. J. Electron. Sci. Technol. 19, 100060 (2021)
Zhu, Y., et al.: SARS-CoV-2-encoded MiRNAs inhibit host type i interferon pathway and mediate allelic differential expression of susceptible gene. Front. Immunol. 12 (2021)
Çetin, Z., Bayrak, T., Oğul, H., İlker Saygılı, E., Akkol, E.K.: Predicted SARS-CoV-2 miRNAs associated with epigenetic viral pathogenesis and the detection of new possible drugs for Covid-19. Curr. Drug Deliv. 18, 1595–1610 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work as been supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), CRC1123, project Z02 (MJ+RZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Schubö, A., Hadziahmetovic, A., Joppich, M., Zimmer, R. (2022). Collecting SARS-CoV-2 Encoded miRNAs via Text Mining. In: Rojas, I., Valenzuela, O., Rojas, F., Herrera, L.J., Ortuño, F. (eds) Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering. IWBBIO 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13346. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07704-3_35
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07704-3_35
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-07703-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-07704-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)