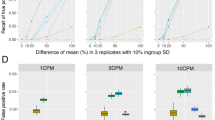
Abstract
Single-cell Assay for Transposase Accessible Chromatin using sequencing (scATAC-seq) is rapidly becoming a powerful technology to assess the epigenetic landscape of thousands of cells. However, the current great sparsity of the resulting data poses significant challenges to their interpretability and informativeness. Different computational methods are available, proposing ways to generate significant features from accessibility data and process them to obtain meaningful results. In particular, the most common way to interpret the raw scATAC-seq data is through peak-calling, generating the peaks as features. Nevertheless, this method is dataset-dependent because the peaks are related to the given dataset and can not be directly compared between different experiments. For this reason, this study wants to improve on the concept of the Gene Activity Matrix (GAM), which links the accessibility data to the genes, by proposing a Genomic-Annotated Gene Activity Matrix (GAGAM), which aims to label the peaks and link them to the genes through functional annotation of the whole genome. Using genes as features solves the problem of the feature dataset dependency allowing for the link of gene accessibility and expression. The latter is crucial for gene regulation understanding and fundamental for the increasing impact of multi-omics data. Results confirm that our method performs better than the previous GAMs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
10XGenomics: 5k peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from a healthy donor single cell ATAC dataset by cell ranger ATAC 1.0.1, 10x genomics, 17 December 2019
10XGenomics: fresh cortex from adult mouse brain (p50) single cell ATAC dataset by cell ranger ATAC 1.1.0, 10x genomics, 16 April 2019
10XGenomics: peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from a healthy donor single cell ATAC dataset by cell ranger ATAC 2.0.0, 10x genomics, 3 May 2021
Buenrostro, J.D., et al.: Integrated single-cell analysis maps the continuous regulatory landscape of human hematopoietic differentiation. Cell 173(6), 1535-1548.e16 (2018)
Carter, B., Zhao, K.: The epigenetic basis of cellular heterogeneity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 22(4), 235–250 (2021)
Chen, H., et al.: Assessment of computational methods for the analysis of single-cell ATAC-seq data. Genome Biol. 20(1) (2019). Article number: 241. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-019-1854-5
Chen, S., Lake, B.B., Zhang, K.: High-throughput sequencing of the transcriptome and chromatin accessibility in the same cell. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 1452–1457 (2019)
Chiquet, J.: aricode: efficient computations of standard clustering comparison measures. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/aricode/index.html
Danese, A., Richter, M.L., Chaichoompu, K., et al.: EpiScanpy: integrated single-cell epigenomic analysis. Nat. Commun. 12(D1), 5228 (2021)
Eisenberg, E., Levanon, E.Y.: Human housekeeping genes, revisited. Trends Genet. (TIG) 29(10), 569–574 (2013)
ENCODE: encode data portal. https://www.encodeproject.org
Hounkpe, B.W., et al.: HRT Atlas v1.0 database: redefining human and mouse housekeeping genes and candidate reference transcripts by mining massive RNA-seq datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 49(D1), D947–D955 (2021)
Hu, Y., An, Q., Sheu, K., Trejo, B., Fan, S., Guo, Y.: Single cell multi-omics technology: methodology and application. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 6, 28 (2018)
Allen Institute: 2010 Allen cell types database. https://portal.brain-map.org/atlases-and-data/rnaseq
Kelsey, G., Stegle, O., Reik, W.: Single-cell epigenomics: recording the past and predicting the future. Science 358(6359), 69–75 (2017)
Kent, W.J., Zweig, A.S., Barber, G., Hinrichs, A.S., Karolchik, D.: BigWig and BigBed: enabling browsing of large distributed datasets. Bioinformatics 26(17), 2204–2207 (2010)
Hubert, L., Arabie, P.: Comparing partitions. J. Classif. 2, 193–218 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01908075
Lareau, C.A., Duarte, F.M., Chew, C.G., et al.: Droplet-based combinatorial indexing for massive-scale single-cell chromatin accessibility. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 916–924 (2019)
Li, Y., Ma, L., Wu, D., Chen, G.: Advances in bulk and single-cell multi-omics approaches for systems biology and precision medicine. Briefings Bioinform. 22(5), bbab024 (2021)
Luu, P.L., Ong, P.T., Dinh, T.P., Clark, S.J.: Benchmark study comparing liftover tools for genome conversion of epigenome sequencing data. NAR Genomics Bioinform. 2(3), lqaa054 (2020)
Martini, L.: Study of cellular heterogeneity of mouse cerebral cortex, through joint scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq analysis, derived from SNARE-seq technique (2020)
Martini, L., Bardini, R., Di Carlo, S.: Meta-analysis of cortical inhibitory interneurons markers landscape and their performances in scRNA-seq studies. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), pp. 253–258 (2021), https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBM52615.2021.9669888
McInnes, L., Healy, J., Saul, N., Großberger, L.: UMAP: uniform manifold approximation and projection. J. Open Source Softw. 3(29), 861 (2018)
Moore, J.E., et al.: Expanded encyclopaedias of DNA elements in the human and mouse genomes. Nature 583(7818), 699–710 (2020)
O’Leary, N.A., et al.: Reference sequence (RefSeq) database at NCBI: current status, taxonomic expansion, and functional annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, D733–D745 (2016)
Pliner, H.A., et al.: Cicero predicts cis-regulatory DNA interactions from single-cell chromatin accessibility data. Mol. Cell 71, 1–14 (2018)
Satpathy, A.T., Granja, J.M., Yost, K.E., et al.: Massively parallel single-cell chromatin landscapes of human immune cell development and intratumoral T cell exhaustion. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 925–936 (2019)
Stuart, T., Satija, R., et al.: Single-cell chromatin state analysis with Signac. Nat. Methods 18(11), 1333–1341 (2021)
Subramanian, I., Verma, S., Kumar, S., Jere, A., Anamika, K.: Multi-omics data integration, interpretation, and its application. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/1177932219899051
Thibaud-Nissen, F., Souvorov, A., Murphy, T., et al.: Eukaryotic genome annotation pipeline. In: The NCBI Handbook [Internet]. 2nd edition. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US) (2013)
Trapnell, C., Cacchiarelli, D., Grimsby, J., et al.: The dynamics and regulators of cell fate decisions are revealed by pseudotemporal ordering of single cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 32, 381–386 (2014)
USCS: bigbedtobed too. genome.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/help/bigBed.html
USCS: USCS human CCRE track download. hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/gbdb/hg38/encode3/ccre/encodeCcreCombined.bb
USCS: USCS mouse CCRE track download. hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/gbdb/mm10/encode3/ccre/encodeCcreCombined.bb
Vinh, N.X., Epps, J., Bailey, J.: Information theoretic measures for clusterings comparison: is a correction for chance necessary? In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2009, pp. 1073–1080. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2009). https://doi.org/10.1145/1553374.1553511
Yan, F., et al.: From reads to insight: a hitchhiker’s guide to ATAC-seq data analysis. Genome Biol. 21(1), 1–16 (2020)
Zhang, X., et al.: CellMarker: a manually curated resource of cell markers in human and mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 47(D1), D721–D728 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Martini, L., Bardini, R., Savino, A., Di Carlo, S. (2022). GAGAM: A Genomic Annotation-Based Enrichment of scATAC-seq Data for Gene Activity Matrix. In: Rojas, I., Valenzuela, O., Rojas, F., Herrera, L.J., Ortuño, F. (eds) Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering. IWBBIO 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13347. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07802-6_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07802-6_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-07801-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-07802-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)