Abstract
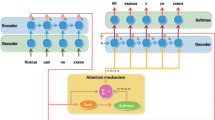
With the evolution of speech technologies, the need to understand and process the poorly spoken language has gradually become a necessity. However, the lack of resources is the main computational processing challenge. We present, in this paper, an effort to create a Neural Machine Translation (NMT) model in order to translate the spoken language in Tunisia: The Tunisian Dialect (TD) into the Arabic Standard Language (MSA). Indeed, NMT tasks require an enormous amount of training data which represents a problematic for low resourced languages like TD. For this, two contributions will be presented in this paper, the first consists of the creating of a parallel corpus TD-MSA. Then, by exploiting the resulting corpus, we proposed a configuration of a neural translation model that achieved a BLEU score of 67.56%.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Ibrahim, R., Duwairi, R.M.: Neural machine translation from Jordanian dialect to modern standard Arabic. In: 2020 11th International Conference on Information and Communication Systems (ICICS), pp. 173–178 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICS49469.2020.239505
Bahdanau, D., Cho, K., Bengio, Y.: Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate (2016)
Baniata, L.H., Park, S., Park, S.B.: A neural machine translation model for Arabic dialects that utilizes multitask learning (MTL). Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 10 (2018)
Bouamor, H., et al.: The MADAR Arabic dialect corpus and lexicon. In: Proceedings of the 11th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference. Miyazaki, Japan (2018)
Boujelbane, R., Khemekhem, M.E, Belguith, L.H.: Mapping rules for building a Tunisian dialect lexicon and generating corpora. In: Proceedings of the Sixth International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, pp. 419–428. Asian Federation of Natural Language Processing, Nagoya, Japan (2013). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/I13-1048
Boukadida, N.: Connaissances phonologiques et morphologiques dérivationnelles et apprentissage de la lecture en arabe (etude longitudinale) (2008)
Cho, K., van Merriënboer, B., Bahdanau, D., Bengio, Y.: On the properties of neural machine translation: encoder-decoder approaches. In: Proceedings of SSST-8, Eighth Workshop on Syntax, Semantics and Structure in Statistical Translation, pp. 103–111. Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha, Qatar (2014). https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/W14-4012. https://aclanthology.org/W14-4012
Fadaee, M., Bisazza, A., Monz, C.: Data augmentation for low-resource neural machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), pp. 567–573. Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver, Canada (2017). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P17-2090. https://aclanthology.org/P17-2090
Folajimi, Y., Isaac, O.: Using statistical machine translation (SMT) as a language translation tool for understanding Yoruba language (2012). https://doi.org/10.13140/2.1.3522.8485
Hamdi, A., Boujelbane, R., Habash, N., Nasr, A.: The effects of factorizing root and pattern mapping in bidirectional Tunisian - standard Arabic machine translation. In: MT Summit 2013. p. pas d’édition papier. France (2013). https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00908761
Kchaou, S., Boujelbane, R., Hadrich-Belguith, L.: Parallel resources for Tunisian Arabic dialect translation. In: Proceedings of the Fifth Arabic Natural Language Processing Workshop, pp. 200–206. Association for Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain (2020). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.wanlp-1.18
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization (2017)
Masmoudi, A., Khmekhem, M.E., Estève, Y., Belguith, L.H., Habash, N.: A corpus and phonetic dictionary for Tunisian Arabic speech recognition. In: Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC2014), pp. 306–310. European Language Resources Association (ELRA), Reykjavik, Iceland (2014). http://www.lrec-conf.org/proceedings/lrec2014/pdf/454_Paper.pdf
Nagy, A., Nanys, P., Konrád, B.F., Bial, B., Ács, J.: Syntax-based data augmentation for Hungarian-English machine translation (2022)
Przystupa, M., Abdul-Mageed, M.: Neural machine translation of low-resource and similar languages with backtranslation. In: Proceedings of the Fourth Conference on Machine Translation (Volume 3: Shared Task Papers, Day 2), pp. 224–235. Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy (2019). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/W19-5431. https://aclanthology.org/W19-5431
Richburg, A., Eskander, R., Muresan, S., Carpuat, M.: An evaluation of subword segmentation strategies for neural machine translation of morphologically rich languages. In: Proceedings of the The Fourth Widening Natural Language Processing Workshop, pp. 151–155. Association for Computational Linguistics, Seattle, USA (2020). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.winlp-1.40. https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.winlp-1.40
Takezawa, T., Genichiro, K., Masahide, M., Eiichiro, S.: Multilingual spoken language corpus development for communication research. In: Chinese Spoken Language Processing, pp. 781–791 (2006)
Tapo, A.A., et al.: Neural machine translation for extremely low-resource African languages: a case study on Bambara. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Technologies for MT of Low Resource Languages, pp. 23–32. Association for Computational Linguistics, Suzhou, China (2020). https://aclanthology.org/2020.loresmt-1.3
Vu, V.H., Nguyen, P., Nguyen, H., Shin, J.C., Ock, C.Y.: Korean-vietnamese neural machine translation with named entity recognition and part-of-speech tags. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. E103.D, 866–873 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1587/transinf.2019EDP7154
Zribi, I., Boujelbane, R., Masmoudi, A., Ellouze, M., Belguith, L., Habash, N.: A conventional orthography for Tunisian Arabic. In: Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC2014), pp. 2355–2361. European Language Resources Association (ELRA), Reykjavik, Iceland (2014). http://www.lrec-conf.org/proceedings/lrec2014/pdf/219_Paper.pdf
Zribi, I., Kammoun, I., Ellouze, M., Hadrich Belguith, L., Blache, P.: Sentence boundary detection for transcribed Tunisian Arabic. In: Konvens-2016. RUHR-UNIVERSITAT BOCHUM, Bochum, Germany (2016), https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01462133
Zribi, I., Ellouze, M., Belguith, L., Blache, P.: Spoken Tunisian Arabic corpus “stac’’: transcription and annotation. Res. Comput. Sci. 90, 123–135 (2015). https://doi.org/10.13053/rcs-90-1-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Emna, A., Kchaou, S., Boujelban, R. (2022). Neural Machine Translation of Low Resource Languages: Application to Transcriptions of Tunisian Dialect. In: Bennour, A., Ensari, T., Kessentini, Y., Eom, S. (eds) Intelligent Systems and Pattern Recognition. ISPR 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1589. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08277-1_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08277-1_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-08276-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-08277-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)