Abstract
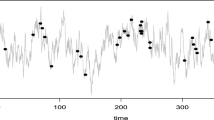
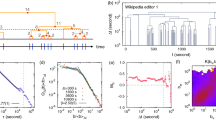
This paper proposes a method for determining the resolution for the processing of irregularly-sampled time series data to provide a balanced perspective of agents’ behaviour. The behaviour is described as a collection of prolonged events, which are characterised by start/open and end/close times in addition to other useful attributes. We propose the definition of an equilibrium resolution and carry out its analysis based on probabilistic assumptions. The resulting methods of determining the equilibrium resolution are tested on real-life time series data sets from the Financial and Travel problem domains.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-baghdadi, N., Wisniewski, W., Lindsay, D., Lindsay, S., Kalnishkan, Y., Watkins, C.: Structuring time series data to gain insight into agent behaviour. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data, pp. 5480–5490 (2019)
Al-Hmouz, R., Pedrycz, W., Balamash, A., Morfeq, A.: Granular representation schemes of time series: a study in an optimal allocation of information granularity. In: 2013 IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computational Intelligence (FOCI), pp. 44–51 (2013)
Arandia, E., Eck, B., McKenna, S.: The effect of temporal resolution on the accuracy of forecasting models for total system demand. Procedia Eng. 89, 916–925 (2014). 16th Water Distribution System Analysis Conference, WDSA2014
Athanasopoulos, G., Hyndman, R.J., Kourentzes, N., Petropoulos, F.: Forecasting with temporal hierarchies. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 262(1), 60–74 (2017)
Challet, D., Chicheportiche, R., Lallouache, M., Kassibrakis, S.: Statistically validated leadlag networks and inventory prediction in the foreign exchange market. Adv. Complex Syst. 22 p. (2018)
Krings, G., Karsai, M., Bernhardsson, S., Blondel, V.D., Saramäki, J.: Effects of time window size and placement on the structure of an aggregated communication network. EPJ Data Sci. 1(1), 1–16 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjds4
Lindsay, D.: Fxclienttrades. https://www.kaggle.com/davidlindsay1979/toptradingclientdata/kernels
Nason, G.P., Powell, B., Elliott, D., Smith, P.A.: Should we sample a time series more frequently?: decision support via multirate spectrum estimation. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A (Stat. Soc.) 180(2), 353–407 (2017)
Sulo, R., Berger-Wolf, T., Grossman, R.: Meaningful selection of temporal resolution for dynamic networks. In: Proceedings of the Eighth Workshop on Mining and Learning with Graphs, MLG 2010, pp. 127–136. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2010)
Tumminello, M., Miccichè, S., Lillo, F., Piilo, J., Mantegna, R.N.: Statistically validated networks in bipartite complex systems. PLoS ONE 6(3), e17994 (2011)
Wong, C.: Nyc taxi trips. http://www.andresmh.com/nyctaxitrips/
Wu, X., Shi, B., Dong, Y., Huang, C., Faust, L., Chawla, N.: Restful: resolution-aware forecasting of behavioral time series data, pp. 1073–1082 (2018)
Xue-dong, G., Chen, H.: The method of time granularity determination on time series based on structural similarity measure algorithm. In: The International Symposium on the Analytic Hierarchy Process (ISAHP) (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 IFIP International Federation for Information Processing
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wisniewski, W., Kalnishkan, Y., Lindsay, D., Lindsay, S. (2022). Equilibrium Resolution for Epoch Partitioning. In: Maglogiannis, I., Iliadis, L., Macintyre, J., Cortez, P. (eds) Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations. AIAI 2022. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, vol 647. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08337-2_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08337-2_32
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-08336-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-08337-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)