Abstract
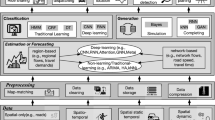
Understanding the associations between different traffic factors (e.g., time, vehicles, trees, and people) and the air pollution in a particular region is a challenging problem of great concern in Intelligent Transportation Systems. Most previous works primarily focused on efficient prediction of air pollution levels the given traffic imagery data. To the best of our knowledge, there exists no study that tries to discover hidden associations (or correlation) that exist between the traffic factors and the air pollution towards predicting PM2.5 levels within a certain period of time. With this motivation, this paper proposes a novel framework that aims to discover hidden associations that exist between the traffic factors and the air pollution towards predicting air pollution level in short- and medium-term time. Our framework has the following six steps: (i) Extract features from the traffic images using any machine learning algorithm, (ii) generate a new dataset by joining the extracted features dataset and air pollution dataset using time, (iii) transform this new dataset into an uncertain temporal database using fuzzy rules, (iv) apply uncertain periodic-frequent pattern mining techniques to discover hidden associations between various traffic factors and air pollution, (v) estimate air pollution level from a given image using transfer learning on a pre-trained model, and (vi) predict air pollution level using estimated air pollution level and mined patterns dataset. Experimental results show that our method can estimate and predict air pollution level with high accuracy (from 77% to 98%).
Kazuki was the first to introduce the idea presented in this paper.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Visionair (2020). https://vision-air.github.io/
Awan, F.M., Minerva, R., Crespi, N.: Improving road traffic forecasting using air pollution and atmospheric data: experiments based on LSTM recurrent neural networks. Sensors 20(13), 3749 (2020)
Bedregal, B.C.: On interval fuzzy negations. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 161(17), 2290–2313 (2010)
Bo, Q., Yang, W., Rijal, N., Xie, Y., Feng, J., Zhang, J.: Particle pollution estimation from images using convolutional neural network and weather features. In: 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 3433–3437. IEEE (2018)
Cao, F., Bao, Q.: A survey on image semantic segmentation methods with convolutional neural network. In: 2020 International Conference on Communications, Information System and Computer Engineering (CISCE), pp. 458–462. IEEE (2020)
Dao, M.-S., Zettsu, K., Rage, U.K.: IMAGE-2-AQI: aware of the surrounding air qualification by a few images. In: Fujita, H., Selamat, A., Lin, J.C.-W., Ali, M. (eds.) IEA/AIE 2021. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 12799, pp. 335–346. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79463-7_28
Ganji, A., Minet, L., Weichenthal, S., Hatzopoulou, M.: Predicting traffic-related air pollution using feature extraction from built environment images. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54(17), 10688–10699 (2020)
Hien, T.T., Chi, N.D.T., Nguyen, N.T., Takenaka, N., Huy, D.H., et al.: Current status of fine particulate matter (pm2.5) in Vietnam’s most populous city, Ho Chi Minh city. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 19(10), 2239–2251 (2019)
Junfei, Q., Zengzeng, H., Shengli, D.: Prediction of pm2.5 concentration based on weighted bagging and image contrast-sensitive features. Stochastic Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 34(3–4), 561–573 (2020)
Ke, L., Tai, Y.W., Tang, C.K.: Deep occlusion-aware instance segmentation with overlapping bilayers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4019–4028 (2021)
La, T.V., Dao, M.S., Kazuki, Tejima, R.K.U., Zettsu, K.: Improving the awareness of sustainable smart cities by analyzing lifelog images and IoT air pollution data. In: IEEE Big Data, pp. 3589–3594 (2021)
Liang, L., Gong, P.: Urban and air pollution: a multi-city study of long-term effects of urban landscape patterns on air quality trends. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–13 (2020)
Liu, L., Liu, W., Zheng, Y., Ma, H., Zhang, C.: Third-eye: a mobilephone-enabled crowdsensing system for air quality monitoring. Proc. ACM Interactive Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2(1), 1–26 (2018)
Ma, J., Li, K., Han, Y., Yang, J.: Image-based air pollution estimation using hybrid convolutional neural network. In: 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 471–476. IEEE (2018)
Mao, J., Phommasak, U., Watanabe, S., Shioya, H.: Detecting foggy images and estimating the haze degree factor. J. Comput. Sci. Syst. Biol. 7, 226–228 (2014)
Nguyen-Tai, T.L., Nguyen, D.H., Nguyen, M.T., Nguyen, T.D., Dang, T.H., Dao, M.S.: MNR-HCM data: a personal lifelog and surrounding environment dataset in Ho-Chi-Minh city, Viet Nam. In: Proceedings of the 2020 on Intelligent Cross-Data Analysis and Retrieval Workshop, pp. 21–26 (2020)
Núñez-Alonso, D., Pérez-Arribas, L.V., Manzoor, S., Cáceres, J.O.: Statistical tools for air pollution assessment: multivariate and spatial analysis studies in the Madrid region. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 9753927 (2019)
Pochwała, S., Anweiler, S., Deptuła, A., Gardecki, A., Lewandowski, P., Przysiężniuk, D.: Optimization of air pollution measurements with unmanned aerial vehicle low-cost sensor based on an inductive knowledge management method. Optim. Eng. 22(3), 1783–1805 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-021-09668-2
Uday Kiran, R., Likhitha, P., Dao, M.-S., Zettsu, K., Zhang, J.: Discovering periodic-frequent patterns in uncertain temporal databases. In: Mantoro, T., Lee, M., Ayu, M.A., Wong, K.W., Hidayanto, A.N. (eds.) ICONIP 2021. CCIS, vol. 1516, pp. 710–718. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92307-5_83
Rijal, N., Gutta, R.T., Cao, T., Lin, J., Bo, Q., Zhang, J.: Ensemble of deep neural networks for estimating particulate matter from images. In: 2018 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), pp. 733–738. IEEE (2018)
Shan, Y., Wang, X., Wang, Z., Liang, L., Li, J., Sun, J.: The pattern and mechanism of air pollution in developed coastal areas of china: From the perspective of urban agglomeration. PLoS ONE 15(9), 1–21 (2020)
Tan, M., Le, Q.: Efficientnet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 6105–6114. PMLR (2019)
Wu, D., Gong, J., Liang, J., Sun, J., Zhang, G.: Analyzing the influence of urban street greening and street buildings on summertime air pollution based on street view image data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 9(9), 500 (2020)
Zhao, P., Dao, M.S., Nguyen, T., Nguyen, T.B., Duc-Tien, D.N., Gurrin, C.: Overview of mediaeval 2020 insights for wellbeing: multimodal personal health lifelog data analysis. In: Proceedings of the MediaEval 2020 Workshop, vol. 2882. CEUR-WS.org (2020)
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Rage Uday Kiran, supervisor of Kazuki, for sharing his ideas and expertise on fuzzy sets, uncertain database creation, and mining patterns.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tejima, K., Dao, MS., Zettsu, K. (2022). MM-AQI: A Novel Framework to Understand the Associations Between Urban Traffic, Visual Pollution, and Air Pollution. In: Fujita, H., Fournier-Viger, P., Ali, M., Wang, Y. (eds) Advances and Trends in Artificial Intelligence. Theory and Practices in Artificial Intelligence. IEA/AIE 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13343. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08530-7_50
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08530-7_50
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-08529-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-08530-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)