Abstract
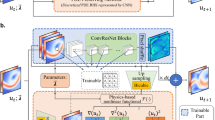
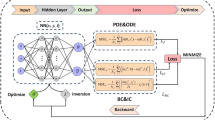
Physics-informed neural networks allow models to be trained by physical laws described by general nonlinear partial differential equations. However, traditional architectures of this approach struggle to solve more challenging time-dependent problems. In this work, we present a novel physics-informed framework for solving time-dependent partial differential equations. Using only the governing differential equations and problem initial and boundary conditions, we generate a latent representation of the problem’s spatio-temporal dynamics. Our model utilizes discrete cosine transforms to encode spatial frequencies and re-current neural networks to process the time evolution. This efficiently and flexibly produces a compressed representation which is used for additional conditioning of physics-informed models. We show experimental results on the Taylor-Green vortex solution to the Navier-Stokes equations. Our proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Taylor-Green vortex relative to other physics-informed baseline models.
B. Wu and W. Byeon—Equal contribution.
B. Wu—Work done during NVIDIA AI Research Residency.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar, L., Sochen, N.: Unsupervised deep learning algorithm for PDE-based forward and inverse problems. arXiv:1904.05417 (2019)
Bhatnagar, S., Afshar, Y., Pan, S., Duraisamy, K., Kaushik, S.: Prediction of aerodynamic flow fields using convolutional neural networks. Comput. Mech. 64(2), 525–545 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-019-01740-0
Cho, K., et al.: Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv:1406.1078 (2014)
Esmaeilzadeh, S., et al.: MeshfreeFlowNet: a physics-constrained deep continuous space-time super-resolution framework. In: SC20, pp. 1–15. IEEE (2020)
Guo, X., Li, W., Iorio, F.: Convolutional neural networks for steady flow approximation. In: KDD (2016)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hennigh, O.: Lat-net: compressing Lattice Boltzmann flow simulations using deep neural networks. arXiv:1705.09036 (2017)
Hennigh, O., et al.: NVIDIA SimNet™: an AI-accelerated multi-physics simulation framework. In: Paszynski, M., Kranzlmüller, D., Krzhizhanovskaya, V.V., Dongarra, J.J., Sloot, P.M.A. (eds.) ICCS 2021. LNCS, vol. 12746, pp. 447–461. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-77977-1_36
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Kashefi, A., Mukerji, T.: Physics-informed PointNet: a deep learning solver for steady-state incompressible flows and thermal fields on multiple sets of irregular geometries. arXiv:2202.05476 (2022)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Li, Z., et al.: Fourier neural operator for parametric partial differential equations (2020)
Mattey, R., Ghosh, S.: A physics informed neural network for time-dependent nonlinear and higher order partial differential equations. arXiv:2106.07606 (2021)
Meng, X., Li, Z., Zhang, D., Karniadakis, G.E.: PPINN: parareal physics-informed neural network for time-dependent PDEs. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 370, 113250 (2020)
Raissi, M., Perdikaris, P., Karniadakis, G.E.: Physics-informed neural networks: a deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 378, 686–707 (2019)
Smith, J.D., Azizzadenesheli, K., Ross, Z.E.: EikoNet: solving the eikonal equation with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 59(12), 10685–10696 (2020). IEEE
Taylor, G.I., Green, A.E.: Mechanism of the production of small eddies from large ones. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A-Math. Phys. Sci. 158(895), 499–521 (1937). The Royal Society London
Xu, K., Qin, M., Sun, F., Wang, Y., Chen, Y.K., Ren, F.: Learning in the frequency domain. In: CVPR, pp. 1740–1749 (2020)
Yu, B., et al.: The deep ritz method: a deep learning-based numerical algorithm for solving variational problems. arXiv:1710.00211 (2017)
Zhu, Y., Zabaras, N.: Bayesian deep convolutional encoder-decoder networks for surrogate modeling and uncertainty quantification. J. Comput. Phys. 366, 415–447 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wu, B., Hennigh, O., Kautz, J., Choudhry, S., Byeon, W. (2022). Physics Informed RNN-DCT Networks for Time-Dependent Partial Differential Equations. In: Groen, D., de Mulatier, C., Paszynski, M., Krzhizhanovskaya, V.V., Dongarra, J.J., Sloot, P.M.A. (eds) Computational Science – ICCS 2022. ICCS 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13351. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08754-7_45
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08754-7_45
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-08753-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-08754-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)