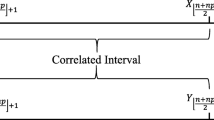
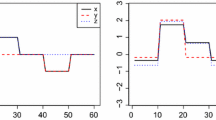
Abstract
Similarity metrics measure distance to a compared time series. It allows for a classification and dependency search. These metrics are used for the selection of additional time series in forecasting, which involves advanced information on the target time series, known as exogenous data. Several studies demonstrate an accuracy gain by including such data that represents the environment for the target time series. Yet, robust significance analysis represents a key prerequisite for the correct context identification towards and accurate time series forecast.
For this reason, this article presents current similarity metrics and demonstrates significant aspects in aligning time series. The concept of dynamic comparison and its importance will be discussed as a basis for a robust perceptual significance analysis. By employing a pair of exemplary load and exogenous time series, alignment capabilities of promising distance metrics were tested, thus demonstrating gaps for an effective perceptual computing methodology. Finally, this paper examines prerequisites necessary for a new robust significance analysis methodology on three characteristic exogenous and target time-series combinations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abanda, A., Mori, U., Lozano, J.A.: A review on distance based time series classification. arXiv:1806.04509 [cs, stat], June 2018. http://arxiv.org/abs/1806.04509, arXiv: 1806.04509
Chen, L.: On the marriage of Lp-norms and edit distance. In: Proceedings of the 30th VLDB Conference, p. 12. Toronto, Canada, (2004)
Chen, L., Özsu, M.T., Oria, V.: Robust and fast similarity search for moving object trajectories. In: Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data - SIGMOD 2005, p. 491. ACM Press, Baltimore, Maryland (2005). https://doi.org/10.1145/1066157.1066213, http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=1066157.1066213
Chen, Y., Nascimento, M., Ooi, B., Tung, A.: SpADe: on shape-based pattern detection in streaming time series. In: Proceedings - International Conference on Data Engineering, pp. 786–795, May 2007. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2007.367924
Christen, R., Mazzola, L., Denzler, A., Portmann, E.: Exogenous data for load forecasting: a review. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence. pp. 489–500. SCITEPRESS - Science and Technology Publications, Budapest, Hungary (2020). https://doi.org/10.5220/0010213204890500, https://www.scitepress.org/DigitalLibrary/Link.aspx?doi=10.5220/0010213204890500
Henson, C., Sheth, A., Thirunarayan, K.: Semantic perception: converting sensory observations to abstractions. IEEE Internet Comput. 16(2), 26–34 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/MIC.2012.20
Jeong, Y.S., Jeong, M.K., Omitaomu, O.A.: Weighted dynamic time warping for time series classification. Pattern Recogn. 44(9), 2231–2240 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2010.09.022. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S003132031000484X
Jiang, G., Wang, W., Zhang, W.: A novel distance measure for time series: maximum shifting correlation distance. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 117, 58–65 (Jan 2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2018.11.013. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167865518308985
Keogh, E.J., Pazzani, M.J.: Derivative dynamic time warping. In: Proceedings of the 2001 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 1–11. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, April 2001. https://doi.org/10.1137/1.9781611972719.1. https://epubs.siam.org/doi/10.1137/1.9781611972719.1
Khan, N.M., Lin, S., Guan, L., Guo, B.: A visual evaluation framework for in-home physical rehabilitation. In: 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia, pp. 237–240, December 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISM.2014.21
Latecki, L.J., Megalooikonomou, V., Wang, Q., Lakaemper, R., Ratanamahatana, C.A., Keogh, E.: Elastic partial matching of time series. In: Jorge, A.M., Torgo, L., Brazdil, P., Camacho, R., Gama, J. (eds.) PKDD 2005. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 3721, pp. 577–584. Springer, Heidelberg (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/11564126_60
Nakamura, T., Taki, K., Nomiya, H., Seki, K., Uehara, K.: A shape-based similarity measure for time series data with ensemble learning. Pattern Anal. Appl. 16(4), 535–548 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-011-0262-6. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10044-011-0262-6
Oğul, H.: ALoT: a time-series similarity measure based on alignment of textures. In: Yin, H., Camacho, D., Novais, P., Tallón-Ballesteros, A.J. (eds.) IDEAL 2018. LNCS, vol. 11314, pp. 576–585. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03493-1_60
Sakoe, H., Chiba, S.: Dynamic programming algorithm optimization for spoken word recognition. IEEE Trans. Acoustics Speech Sig. Process. 26(1), 43–49 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASSP.1978.1163055
Stefan, A., Athitsos, V., Das, G.: The Move-Split-Merge Metric for Time Series. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 25(6), 1425–1438 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2012.88
Tomasi, G., van den Berg, F., Andersson, C.: Correlation optimized warping and dynamic time warping as preprocessing methods for chromatographic data. J. Chemometrics 18(5), 231–241 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/cem.859, https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cem.859
Zhao, Y.: The robustness of forecast combination in unstable environments: a Monte Carlo study of advanced algorithms. Empirical Econ. 61(1), 173–199 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00181-020-01864-w
Acknowledgment
Thanks to Ben Haymond for his help in the language editing of this abstract.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Christen, R., Mazzola, L., Denzler, A., Portmann, E. (2022). Distance Metrics for Evaluating the Use of Exogenous Data in Load Forecasting. In: Ciucci, D., et al. Information Processing and Management of Uncertainty in Knowledge-Based Systems. IPMU 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1602. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08974-9_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08974-9_37
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-08973-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-08974-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)