Abstract
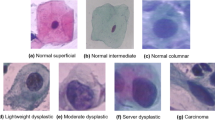
Cervical cancer is a very common cancer among women. Cytopathologists use a microscope to examine cell slides collected from the patient’s cervix to determine if it is cancerous. However, manually checking the slides to diagnose cancer is a very difficult task, not only time-consuming but also error-prone. A computer-aided diagnosis system can automatically and accurately screen cervical cell images. In this study, we propose a framework called DVT to perform classification tasks. We use SIPaKMeD and CRIC datasets together. On 11-class classification tasks, DVT achieves an accuracy of 87.35%. In the comparative experiment, DVT performs better than the CNN and VT models alone.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Šarenac, T., Mikov, M.: Cervical cancer, different treatments and importance of bile acids as therapeutic agents in this disease. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 484 (2019)
Saslow, D., et al.: American cancer society, American society for colposcopy and cervical pathology, and American society for clinical pathology screening guidelines for the prevention and early detection of cervical cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 62(3), 147–172 (2012)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020), https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929
Plissiti, M.E., Dimitrakopoulos, P., Sfikas, G., Nikou, C., Krikoni, O., Charchanti, A.: Sipakmed: a new dataset for feature and image based classification of normal and pathological cervical cells in pap smear images. In: 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 3144–3148. IEEE (2018)
Rezende, M.T., et al.: Cric searchable image database as a public platform for conventional pap smear cytology data. Sci. Data 8(1), 1–8 (2021)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014). https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., Wojna, Z.: Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2818–2826 (2016)
Touvron, H., Cord, M., Douze, M., Massa, F., Sablayrolles, A., Jégou, H.: Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 10347–10357. PMLR (2021)
Yuan, L., et al.: Tokens-to-token vit: training vision transformers from scratch on imagenet. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.11986 (2021), https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.11986
Rahaman, M.M., et al.: A survey for cervical cytopathology image analysis using deep learning. IEEE Access 8, 61687–61710 (2020)
Xue, D., et al.: An application of transfer learning and ensemble learning techniques for cervical histopathology image classification. IEEE Access 8, 104603–104618 (2020)
Khamparia, A., Gupta, D., de Albuquerque, V.H.C., Sangaiah, A.K., Jhaveri, R.H.: Internet of health things-driven deep learning system for detection and classification of cervical cells using transfer learning. J. Supercomput. 76(11), 8590–8608 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03159-4
Rahaman, M.M., et al.: Deepcervix: a deep learning-based framework for the classification of cervical cells using hybrid deep feature fusion techniques. Comput. Biol. Med. 136, 104649 (2021)
Shi, J., Wang, R., Zheng, Y., Jiang, Z., Zhang, H., Yu, L.: Cervical cell classification with graph convolutional network. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 198, 105807 (2021)
Liu, W., et al.: Is the aspect ratio of cells important in deep learning? A robust comparison of deep learning methods for multi-scale cytopathology cell image classification: From convolutional neural networks to visual transformers. Comput. Biol. Med. 105026 (2021)
Li, C., Zhang, J., Kulwa, F., Qi, S., Qi, Z.: A SARS-CoV-2 microscopic image dataset with ground truth images and visual features. In: Peng, Y., et al. (eds.) PRCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12305, pp. 244–255. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60633-6_20
Rahaman, M.M., et al.: Identification of covid-19 samples from chest x-ray images using deep learning: a comparison of transfer learning approaches. J. Xray Sci. Technol. 28(5), 821–839 (2020)
Ismael, A.M., Şengür, A.: Deep learning approaches for covid-19 detection based on chest x-ray images. Expert Syst. Appl. 164, 114054 (2021)
Li, C., et al.: A review for cervical histopathology image analysis using machine vision approaches. Artif. Intell. Rev. 53(7), 4821–4862 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09808-7
Li, C., et al.: A comprehensive review of computer-aided whole-slide image analysis: from datasets to feature extraction, segmentation, classification and detection approaches. Artif. Intell. Rev. 1–70 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-10121-0
Chen, H., et al.: IL-MCAM: an interactive learning and multi-channel attention mechanism-based weakly supervised colorectal histopathology image classification approach. Comput. Biol. Med. 143, 105265 (2022)
Hu, W., et al.: GasHisSDB: a new gastric histopathology image dataset for computer aided diagnosis of gastric cancer. Comput. Biol. Med. 105207 (2022)
Hameed, Z., Zahia, S., Garcia-Zapirain, B., Javier Aguirre, J., María Vanegas, A.: Breast cancer histopathology image classification using an ensemble of deep learning models. Sensors 20(16), 4373 (2020)
Li, C., Wang, K., Xu, N.: A survey for the applications of content-based microscopic image analysis in microorganism classification domains. Artif. Intell. Rev. 51(4), 577–646 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9572-4
Zhang, J., et al.: A comprehensive review of image analysis methods for microorganism counting: from classical image processing to deep learning approaches. Artif. Intell. Rev. 1–70 (2021)
Kosov, S., Shirahama, K., Li, C., Grzegorzek, M.: Environmental microorganism classification using conditional random fields and deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recogn. 77, 248–261 (2018)
Zhang, J., et al.: LCU-Net: a novel low-cost u-net for environmental microorganism image segmentation. Pattern Recogn. 115, 107885 (2021)
Diniz, N., et al.: A deep learning ensemble method to assist cytopathologists in pap test image classification. J. Imaging 7(7), 111 (2021)
Srinivas, A., Lin, T.Y., Parmar, N., Shlens, J., Abbeel, P., Vaswani, A.: Bottleneck transformers for visual recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.11605 (2021). https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.11605
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.C.: Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4510–4520 (2018)
Ma, N., Zhang, X., Zheng, H.-T., Sun, J.: ShuffleNet V2: practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11218, pp. 122–138. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01264-9_8
Szegedy, C., Ioffe, S., Vanhoucke, V., Alemi, A.A.: Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 4278–4284 (2017). https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/3298023.3298188
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, W., Li, C., Sun, H., Hu, W., Chen, H., Grzegorzek, M. (2022). DVT: Application of Deep Visual Transformer in Cervical Cell Image Classification. In: Pietka, E., Badura, P., Kawa, J., Wieclawek, W. (eds) Information Technology in Biomedicine. ITIB 2022. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1429. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-09135-3_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-09135-3_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-09134-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-09135-3
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)