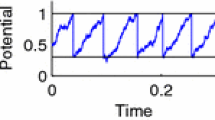
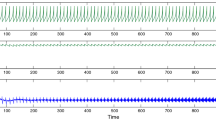
Abstract
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) have been extensively used for the description of problems arising from biological systems and for constructing neuromorphic computing models. The third generation of ANNs, namely, spiking neural networks (SNNs), inspired by biological neurons enable a more realistic mimicry of the human brain. A large class of the problems from these domains is characterized by the necessity to deal with the combination of neurons, spikes and synapses via integrate-and-fire neuron models. Motivated by important applications of the integrate-and-fire of neurons in neuromorphic computing for bio-medical studies, the main focus of the present work is on the analysis of the effects of additive and multiplicative types of random input currents together with a random refractory period on a leaky integrate-and-fire (LIF) synaptic conductance neuron model. Our analysis is carried out via Langevin stochastic dynamics in a numerical setting describing a cell membrane potential. We provide the details of the model, as well as representative numerical examples, and discuss the effects of noise on the time evolution of the membrane potential as well as the spiking activities of neurons in the LIF synaptic conductance model scrutinized here. Furthermore, our numerical results demonstrate that the presence of a random refractory period in the LIF synaptic conductance system may substantially influence an increased irregularity of spike trains of the output neuron.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauermann, J., Lindner, B.: Multiplicative noise is beneficial for the transmission of sensory signals in simple neuron models. Biosystems 178, 25–31 (2019)
Brigner, W.H., et al.: Three artificial spintronic leaky integrate-and-fire neurons. SPIN 10(2), 2040003 (2020)
Burkitt, A.: A review of the integrate-and-fire neuron model: I. homogeneous synaptic input. Biological Cybern. 95(2), 97–112 (2006)
Burkitt, A.: A review of the integrate-and-fire neuron model: II. inhomogeneous synaptic input and network properties. Biol. Cybern. 95(1), 1–19 (2006)
Cavallari, S., Panzeri, S., Mazzoni, A.: Comparison of the dynamics of neural interactions between current-based and conductance-based integrate-and-fire recurrent networks. Front. Neural Circuits 8, 12 (2014)
Chen, X., Yajima, T., Inoue, I.H., Iizuka, T.: An ultra-compact leaky integrate-and-fire neuron with long and tunable time constant utilizing pseudo resistors for spiking neural networks. J. Appl. Phys. 61, SC1051 (2021). Accepted for publication in Japanese
Chowdhury, S.S., Lee, C., Roy, K.: Towards understanding the effect of leak in spiking neural networks. Neurocomputing 464, 83–94 (2021)
Christodoulou, C., Bugmann, G.: Coefficient of variation vs. mean interspike interval curves: What do they tell us about the brain? Neurocomputing 38–40, 1141–1149 (2001)
Dayan, P., Abbott, L.F.: Theoretical Neuroscience. The MIT Press, Massachusetts (2005)
Dutta, S., Kumar, V., Shukla, A., Mohapatra, N.R., Ganguly, U.: Leaky integrate and fire neuron by charge-discharge dynamics in floating-body mosfet. Sci. Rep. 7(8257), 8257 (2017)
Faisal, A.D., Selen, L.P.J., Wolpert, D.M.: Noise in the nervous system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 292–303 (2008)
Fardet, T., Levina, A.: Simple models including energy and spike constraints reproduce complex activity patterns and metabolic disruptions. PLoS Comput. Biol. 16(12), e1008503 (2020)
Gallinaro, J.V., Clopath, C.: Memories in a network with excitatory and inhibitory plasticity are encoded in the spiking irregularity. PLoS Comput. Biol. 17(11), e1009593 (2021)
Gerstner, W., Kistler, W.M., Naud, R., Paninski, L.: Neuronal Dynamics: from single neurons to networks and models of cognition. Cambridge University Press (2014)
Gerum, R.C., Schilling, A.: Integration of leaky-integrate-and-fire neurons in standard machine learning architectures to generate hybrid networks: A surrogate gradient approach. Neural Comput. 33, 2827–2852 (2021)
Guo, T., Pan, K., Sun, B., Wei, L., Y., Zhou, Y.N., W, Y.A.: Adjustable leaky-integrate-and-fire neurons based on memristor coupled capacitors. Materials Today Advances 12, 100192 (2021)
Hendrycks, D., Dietterich, T.: Benchmarking neural network robustness to common corruptions and perturbations. In: International Conference on Learning (2019)
Jaras, I., Harada, T., Orchard, M.E., Maldonado, P.E., Vergara, R.C.: Extending the integrate-and-fire model to account for metabolic dependencies. Eur. J. Neurosci. 54(3), 5249–5260 (2021)
Kepecs, A., Lisman, J.: Information encoding and computation with spikes and bursts. Network: Comput. Neural Syst. 14, 103–118 (2003)
Latimer, K.W., Rieke, F., Pillow, J.W.: Inferring synaptic inputs from spikes with a conductance-based neural encoding model. eLife 8(e47012) (2019)
Li, S., Liu, N., Yao, L., Zhang, X., Zhou, D., Cai, D.: Determination of effective synaptic conductances using somatic voltage clamp. PLoS Comput. Biol. 15(3), e1006871 (2019)
Mahdi, A., Sturdy, J., Ottesen, J.T., Olufsen, M.S.: Modeling the afferent dynamics of the baroreflex control system. PLoS Comput. Biol. 9(12), e1003384 (2013)
Maimon, G., Assad, J.A.: Beyond Poisson: Increased spike-time regularity across primate parietal cortex. Neuron 62(3), 426–440 (2009)
Nandakumar, S.R., Boybat, I., Gallo, M.L., Eleftheriou, E., Sebastian, A., Rajendran, B.: Experimental demonstration of supervised learning in spiking neural networks with phase change memory synapses. Sci. Rep. 10(8080), 1–11 (2020)
Roberts, J.A., Friston, K.J., Breakspear, M.: Clinical applications of stochastic dynamic models of the brain, part i: a primer. Biol. Psychiatry: Cogn. Neuroscience Neuroimaging 2, 216–224 (2017)
So, R.Q., Kent, A.R., Grill, W.M.: Relative contributions of local cell and passing fiber activation and silencing to changes in thalamic fidelity during deep brain stimulation and lesioning: a computational modeling study. J. Comput. Neurosci. 32, 499–519 (2012)
Stiefel, K.M., Englitz, B., Sejnowski, T.J.: Origin of intrinsic irregular firing in cortical interneurons. PNAS 110(19), 7886–7891 (2013)
Teeter, C., et al.: Generalized leaky integrate-and-fire models classify multiple neuron types. Nature Commun. 9(709), 1–15 (2018)
Teka, W., Marinov, T.M., Santamaria, F.: Neuronal integration of synaptic input in the fluctuation-driven regime. J. Neurosci. 24(10), 2345–2356 (2004)
Teka, W., Marinov, T.M., Santamaria, F.: Neuronal spike timing adaptation described with a fractional leaky integrate-and-fire model. PLoS Comput. Biol. 10(3), e1003526 (2014)
Van Pottelbergh, T., Drion, G., Sepulchre, R.: From biophysical to integrate-and-fire modeling. Neural Comput. 33(3), 563–589 (2021)
Woo, J., Kim, S.H., Han, K., Choi, M.: Characterization of dynamics and information processing of integrate-and-fire neuron models. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 54, 445601 (2021)
Acknowledgment
Authors are grateful to the NSERC and the CRC Program for their support. RM is also acknowledging support of the BERC 2022–2025 program and Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities through the Agencia Estatal de Investigacion (AEI) BCAM Severo Ochoa excellence accreditation SEV-2017-0718 and the Basque Government fund AI in BCAM EXP. 2019/00432.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Thieu, T.K.T., Melnik, R. (2022). Effects of Noise on Leaky Integrate-and-Fire Neuron Models for Neuromorphic Computing Applications. In: Gervasi, O., Murgante, B., Hendrix, E.M.T., Taniar, D., Apduhan, B.O. (eds) Computational Science and Its Applications – ICCSA 2022. ICCSA 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13375. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-10522-7_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-10522-7_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-10521-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-10522-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)