Abstract
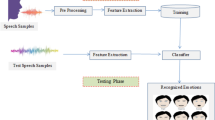
In recent times, voice emotional recognition has been established as a significant field in Human Computer Interaction (HCI). Human emotions are intrinsically expressed by linguistic (verbal content) information and paralinguistic information such as tone, emotional state, expressions and gestures which form the relevant basis for emotional analysis. Accounting the user’s affective state in HCI systems is essential to detect subtle user behaviour changes through which the computer can initiate interactions instead of simply responding to user commands. This paper aims to tackle existing problems in speech emotion recognition (SER) by taking into account the acoustic cues and prosodic parameters to detect user emotion. Here, the work will be mainly on the Ryerson Audio-Visual Database (RAVDESS) to extract Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) from signals to recognise emotion. The librosa library will be used for processing and extracting audio files before testing and classification is carried out using 4 different classifiers for a comparative study. This SER model is then integrated into a Telegram Bot to develop an intuitive, user-friendly interface as an application for psychological therapy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao, J., Mao, X., Chen, L.: Speech emotion recognition using DEEP 1d 2D CNN LSTM networks. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 47, 312–323 (2019)
Milton, A., Sharmy Roy, S., Tamil Selvi, S.: SVM scheme for Speech emotion recognition USING MFCC feature. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 69(9), 34–39 (2013)
Chenchah, F., Lachiri, Z.: Acoustic emotion recognition using linear and nonlinear cepstral coefficients. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 6(11) (2015)
Nwe, T.L., Foo, S.W., De Silva, L.C.: Speech emotion recognition using hidden Markov models. Speech Commun. 41(4), 603–623 (2003)
Demircan, S., Kahramanlı, H.: Feature extraction from speech data for emotion recognition. J. Adv. Comput. Networks 2(1), 28–30 (2014)
Le, D., Provost, E.M.: Emotion recognition from spontaneous speech using Hidden Markov models with deep belief networks. In: 2013 IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding (2013)
Tawari, A., Trivedi, M.: Speech emotion analysis in noisy real-world environment. In: 2010 International Conference on Pattern Recognition
Shaqra, F.A., Duwairi, R., Al-Ayyoub, M.: Recognizing emotion from speech based on age and gender using hierarchical models. In: The 10th International Conference on Ambient Systems, Networks and Technologies (ANT), 29 April–2 May 2019, Leuven, Belgium (2019)
Nediyanchath, A., Paramasivam, P., Yenigalla, P.: Multi-head attention for speech emotion recognition with auxiliary learning of gender recognition. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP)
Mao, Q., Dong, M., Huang, Z., Zhan, Y.: Learning salient features for Speech Emotion Recognition using convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 16(8), 2203–2213 (2014)
Nalini, N.J., Palanivel, S., Balasubramanian, M.: Speech emotion recognition using residual phase and MFCC features. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 5(6), 4515–4527 (2013)
Livingstone, S.R., Russo, F.A.: The ryerson audio-visual database of emotional speech and song (RAVDESS): a dynamic, multimodal set of facial and vocal expressions in North American English. PLoS ONE 13(5), e0196391 (2018)
Alim, S.A., Alang Rashid, N.K.: Some Commonly Used Speech Feature Extraction Algorithms. Pub: 12th Dec, 2018
Lausen, A., Hammerschmidt, K.: Emotion recognition and confidence ratings predicted by vocal stimulus type and prosodic parameters. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, vol. 7, no. 1 (2020)
Sanjita, B.R., Nipunika, A.: Speech Emotion Recognition using MLP Classifier. IJESC, vol. 10, no. 5, May 2020
Amjad, A., Khan, L.: Effect on speech emotion classification of a feature selection approach using a convolutional neural network. Peer J. Comput. Sci., 7, Pub: 3rd Nov, 2021
Martin, O., Kotsia, I., Macq, B.: The eNTERFACE’ 05 audio-visual emotion database. In: 22nd International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW'06); Pub: 24th Apr, 2006
Madhavi, A., Priya Valentina, A., Mounika, K., Rohit, B., Nagma, S.: Comparative analysis of different classifiers for speech emotion recognition. In: Kiran Mai, C., Kiranmayee, B.V., Favorskaya, M.N., Chandra Satapathy, S., Raju, K.S. (eds.) Proceedings of International Conference on Advances in Computer Engineering and Communication Systems. LAIS, vol. 20, pp. 523–538. Springer, Singapore (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-9293-5_48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nag, I., Syed, S.A., Basu, S., Shaw, S., Banik, B.G. (2022). Telegram Bot for Emotion Recognition Using Acoustic Cues and Prosody. In: Mukhopadhyay, S., Sarkar, S., Dutta, P., Mandal, J.K., Roy, S. (eds) Computational Intelligence in Communications and Business Analytics. CICBA 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1579. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-10766-5_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-10766-5_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-10765-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-10766-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)