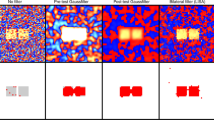
Abstract
Multi-center fMRI studies help accumulate significant number of subjects to increase the statistical power of data analyses. However, the seemingly ambitious gain is hindered by the fact that differences between centers have significant effects on the imaging results. We present a novel machine learning (ML) based technique, which uses non-linear regression with multi-voxel based anatomically informed contextual information, to help normalize multi-center fMRI data to a chosen reference center. Accuracy graphs were obtained by thresholding the estimated maps at high p-values of \(p < 0.001\) after kernel density estimation. Results indicate significant reduction in spurious activations and more importantly, enhancement of the genuine activation clusters. Group level ROI based analysis reveals changes in activation pattern of clusters that are consistent with their role in cognitive function. Furthermore, as the mapping functions exhibit the tendency to induce sensitivity to the regions associated with the task they can help identify small but significant activations which could otherwise be lost due to population based inferences across centers.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogawa, S., Lee, T.M., Kay, A.R., Tank, D.W.: Brain magnetic resonance imaging with contrast dependent on blood oxygenation 87(24), 9868–9872 (1990). http://www.pnas.org/content/87/24/9868
Parrish, T.B., Gitelman, D.R., LaBar, K.S., Mesulam, M., et al.: Impact of signal-to-noise on functional MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 44(6), 925–932 (2000)
Beckmann, C.F., Jenkinson, M., Smith, S.M.: General multilevel linear modeling for group analysis in fMRI. Neuroimage 20(2), 1052–1063 (2003)
Horn, J.D.V., Grafton, S.T., Rockmore, D., Gazzaniga, M.S.: Sharing neuroimaging studies of human cognition 7(5), 473–481 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1231. http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v7/n5/abs/nn1231.html
Kelemen, A., Liang, Y.: Multi-center correction functions for magnetization transfer ratios of MRI scans. J. Health Med. Inform. 3, 2 (2011)
Machielsen, W.C., Rombouts, S.A., Barkhof, F., Scheltens, P., Witter, M.P.: fMRI of visual encoding: Reproducibility of activation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 9(3), 156–164 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0193(200003)9:3<156::AID-HBM4>3.0.CO;2-Q
Keator, D.B., et al.: The function biomedical informatics research network data repository. Neuroimage 124, 1074–1079 (2016)
Gountouna, V.-E., et al.: Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) reproducibility and variance components across visits and scanning sites with a finger tapping task, NeuroImage 49(1), 552–560 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.07.026. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811909007988
Gorgolewski, K., et al.: Nipype: a flexible, lightweight and extensible neuroimaging data processing framework in python. Front. Neuroinform. 5, 13 (2011)
Cox, R.W.: AFNI: software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput. Biomed. Res. 29(3), 162–173 (1996)
Worsley, K.J., Friston, K.J.: Analysis of fMRI time-series revisited-again. Neuroimage 2(3), 173–181 (1995)
Smith, S.M., et al.: Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 23, S208–S219 (2004)
Pereira, J., Acosta-Cabronero, J., Pengas, G., Xiong, L., Nestor, P., Williams, G.: VBM with viscous fluid registration of gray matter segments in SPM. Front. Aging Neurosci. 5, 30 (2012)
Worsley, K., et al.: A general statistical analysis for fMRI data 15(1), 1–15 (2002) . https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2001.0933. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811901909334
Poldrack, R.A., Mumford, J.A., Nichols, T.E.: Handbook of Functional MRI Data Analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2011)
Theano Development Team: Theano: a Python framework for fast computation of mathematical expressions. arXiv e-prints \(\rm {abs}\)/1605.02688. http://arxiv.org/abs/1605.02688
Sutskever, I., Martens, J., Dahl, G., Hinton, G.: On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2013), pp. 1139–1147 (2013)
Pedregosa, F., et al.: Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
Friedman, L., Glover, G.H.: The FBIRN consortium, reducing interscanner variability of activation in a multicenter fMRI study: controlling for signal-to-fluctuation-noise-ratio (SFNR) differences. NeuroImage 33(2), 471–481 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.07.012. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811906007944
Friedman, L., Glover, G.H., Krenz, D., Magnotta, V.: Reducing inter-scanner variability of activation in a multicenter fMRI study: role of smoothness equalization. NeuroImage 32(4), 1656–1668 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.03.062. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811906004435
Thomas, A.J., Bathula, D.: Reducing inter-scanner variability in multi-site fMRI data: exploring choice of reference activation map and use of correction functions. In: 2015 International Conference on Computing, Communication & Automation (ICCCA), pp. 1187–1192. IEEE (2015)
Thomas, A.J., Bathula, D.: Reducing inter-scanner variability in multi-site fMRI activations using correction functions: a preliminary study. In: Singh, R., Vatsa, M., Majumdar, A., Kumar, A. (eds.) Machine Intelligence and Signal Processing. AISC, vol. 390, pp. 109–117. Springer, New Delhi (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2625-3_10
Acknowledgements
Financial assistance from DST (grant no. SB/FTP/ETA-353/2013) New Delhi, India to DRB. The data used in this study was acquired through and provided by the Biomedical Informatics Research Network under the following support: U24-RR021992, Function BIRN and U24 GM104203, Bio-Informatics Research Network Coordinating Center (BIRN-CC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Thomas, A.J., Bathula, D.R. (2022). 3D Multi-voxel Pattern Based Machine Learning for Multi-center fMRI Data Normalization. In: Raman, B., Murala, S., Chowdhury, A., Dhall, A., Goyal, P. (eds) Computer Vision and Image Processing. CVIP 2021. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1568. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-11349-9_45
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-11349-9_45
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-11348-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-11349-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)