Abstract
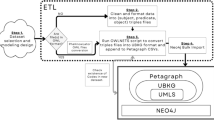
Background: Recent years are seeing a growing impetus in the semantification of scholarly knowledge at the fine-grained level of scientific entities in knowledge graphs. The Open Research Knowledge Graph (ORKG, orkg.org) represents an important step in this direction, with thousands of scholarly contributions as structured, fine-grained, machine-readable data. There is a need, however, to engender change in traditional community practices of recording contributions as unstructured, non-machine-readable text. For this in turn, there is a strong need for AI tools designed for scientists that permit easy and accurate semantification of their scholarly contributions. We present one such tool, ORKG-assays. Implementation: ORKG-assays is a freely available AI micro-service in ORKG written in Python designed to assist scientists obtain semantified bioassays as a set of triples. It uses an AI-based clustering algorithm which on gold-standard evaluations over 900 bioassays with 5,514 unique property-value pairs for 103 predicates shows competitive performance. Results and Discussion: As a result, semantified assay collections can be surveyed on the ORKG platform via tabulation or chart-based visualizations of key property values of the chemicals and compounds offering smart knowledge access to biochemists and pharmaceutical researchers in the advancement of drug development.
Supported by TIB Leibniz Information Centre for Science and Technology, the EU H2020 ERC project ScienceGraph (GA ID: 819536) and the ITN PERICO (GA ID: 812968).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anteghini, M., D’Souza, J., Dos Santos, V.A.M., Auer, S.: Scibert-based semantification of bioassays in the open research knowledge graph. In: EKAW-PD 2020, pp. 22–30 (2020)
Anteghini, M., D’Souza, J., Santos, V.A., Auer, S.: Easy semantification of bioassays (2021). arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.15182
Auer, S., et al.: Improving access to scientific literature with knowledge graphs. Bibliothek Forschung und Praxis 44(3), 516–529 (2020)
Beltagy, I., Lo, K., Cohan, A.: Scibert: A pretrained language model for scientific text. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP). pp. 3606–3611 (2019)
Brack, A., D’Souza, J., Hoppe, A., Auer, S., Ewerth, R.: Domain-independent extraction of scientific concepts from research articles. In: Jose, J.M., et al. (eds.) ECIR 2020. LNCS, vol. 12035, pp. 251–266. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-45439-5_17
Dessì, D., Osborne, F., Reforgiato Recupero, D., Buscaldi, D., Motta, E., Sack, H.: AI-KG: an automatically generated knowledge graph of artificial intelligence. In: Pan, J.Z., et al. (eds.) ISWC 2020. LNCS, vol. 12507, pp. 127–143. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62466-8_9
D’Souza, J., Auer, S., Pedersen, T.: SemEval-2021 Task 11: NLPContributionGraph - structuring scholarly nlp contributions for a research knowledge graph. In: Proceedings of the 15th SemEval-2021, pp. 364–376. ACL, August 2021
Kim, S., et al.: Literature information in pubchem: associations between pubchem records and scientific articles. J. Cheminformatics 8(1), 1–15 (2016)
Liu, H., Sarol, M.J., Kilicoglu, H.: UIUC_BioNLP at SemEval-2021 task 11: A cascade of neural models for structuring scholarly NLP contributions. In: Proceedings of the 15th SemEval-2021, pp. 377–386. ACL, August 2021
Luan, Y., He, L., Ostendorf, M., Hajishirzi, H.: Multi-task identification of entities, relations, and coreference for scientific knowledge graph construction. In: Proceedings of the 2018 EMNLP, pp. 3219–3232. ACL, October–November 2018
Oelen, A., Jaradeh, M.Y., Farfar, K.E., Stocker, M., Auer, S.: Comparing research contributions in a scholarly knowledge graph. In: CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol. 2526, pp. 21–26. RWTH, Aachen (2019)
Wang, Y., et al.: Pubchem’s bioassay database. Nucleic Acids Res. 40(D1), D400–D412 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
D’Souza, J. et al. (2022). The Digitalization of Bioassays in the Open Research Knowledge Graph. In: Strauss, C., Cuzzocrea, A., Kotsis, G., Tjoa, A.M., Khalil, I. (eds) Database and Expert Systems Applications. DEXA 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13426. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-12423-5_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-12423-5_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-12422-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-12423-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)