Abstract
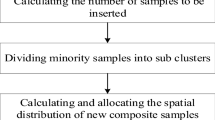
Data imbalance handling is important to have unbiased learning during model training of classification tasks. Synthetic minority over-sampling technique (SMOTE) is primarily used for data imbalance handling. Conventional SMOTE algorithm and its variants mainly deal with upsampling the class data that is based solely on the amplitude values of features and their neighbors. However, the spatio-temporal data corresponding to satellite remote sensing images, comes with the additional location information, i.e. longitude and latitude. This has to be incorporated in the data upsampling case in order to have semantically and physically useful data. Hence, we propose a new pipeline named, ‘Spatial-SMOTE’ to upsample the data by retaining the significance of spatial distribution aspect in the overall upsampling process. The effectiveness of this approach is shown on land-use land-cover classification task using the time series data for a particular study area. We identified the relation between different classes based on their semantic distances and formulated two cases- one with high semantic distance and other with low. It is to be observed that the proposed method of Spatial-SMOTEing the minority class works well for both the cases. We also tested the effectiveness of the proposed approach over synthetically induced class imbalances for both low and high semantically differing classes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Talukdar, S., et al.: Land-use land-cover classification by machine learning classifiers for satellite observation - a review. Remote Sens. 12(7), 1135 (2020)
Thabtah, F., et al.: Data imbalance in classification: experimental evaluation. Inf. Sci. 513, 429–441 (2020)
Chawla, N.V., et al.: SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 16, 321–357 (2002)
Galar, M., et al.: A review on ensembles for the class imbalance problem: bagging-, boosting-, and hybrid-based approaches. IEEE Trans. SMC, Part C 42(4), 463–484 (2011)
He, H.: Garcia: learning from imbalanced data. TKDE 21(9), 1263–1284 (2009)
Han, H., et al: Borderline-SMOTE: a new over-sampling method in imbalanced data sets learning. In: International Conference on Intelligent Computing, pp. 878–887 (2005)
Tang, B., He, H.: KernelADASYN: kernel based adaptive synthetic data generation for imbalanced learning. In: CEC, pp. 664–671 (2015)
Barua, S., et al.: MWMOTE-majority weighted minority oversampling technique for imbalanced data set learning. TKDE 26(2), 405–425 (2012)
Vega, C., et al.: A new small area estimation algorithm to balance between statistical precision and scale. IJAEOG 97, 102303 (2021)
Creswell, A., et al.: Generative adversarial networks: an overview. IEEE Signal Process. Maga. 35(1), 53–65 (2018)
Bhattacharjee, S., Ghosh, S.K., Chen, J.: Spatial interpolation. In: Semantic Kriging for Spatio-temporal Prediction. SCI, vol. 839, pp. 19–41. Springer, Singapore (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8664-0_2
Musin, O.R.: Properties of the delaunay triangulation. In: 13th Annual Symposium on Computational Geometry, pp. 424–426 (1997)
Shukla, K., et al.: Mapping spatial distribution of particulate matter using kriging and inverse distance weighting at supersites of megacity Delhi. Sustain. Cities Soc. 54, 101997 (2020)
TiSeLaC dataset. https://www.timeseriesclassification.com/description.php?Dataset=Tiselac. Accessed 16 June 2020
Das, G.: SemBnet: a semantic bayesian network for multivariate prediction of meteorological time series data. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 93, 192–201 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gavas, R.D., Ghosh, S.K., Pal, A. (2024). Spatial-SMOTE: An Approach for Handling Class Imbalance in Spatial Time Series Data. In: Ghosh, A., King, I., Bhattacharyya, M., Sankar Ray, S., K. Pal, S. (eds) Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence. PReMI 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13102. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-12700-7_50
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-12700-7_50
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-12699-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-12700-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)