Abstract
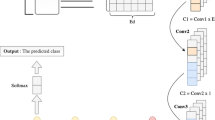
Consumer review helpfulness has a significant role in purchase decision making in an online shopping environment. Deep learning modules with pre-trained word embeddings are predominantly used to asses review helpfulness. Pre-trained word embeddings are trained on generic corpora and lack in incorporating domain knowledge and sentiment information of a word. Moreover, pre-trained embeddings fail to capture the subtle change of semantics of same word with different parts of speech. In this work, we propose HORIE (Heplfulness of Online Reviews with Improved Embedding) which improve pre-trained embedding with domain, sentiment and parts of speech information and analyse helpfulness as classification problem. In HORIE, domain knowledge is acquired from domain specific corpora. The average of pre-trained and domain specific embedding is combined with vectorized sentiment information, extracted from lexical dictionaries, along with POS tag information. Later, we apply a dual CNN based model for classification of reviews. HORIE is tested with five different domain and compare our performance with existing embeddings. We also compare our approach with handcrafted feature sets and existing helpfulness classification technique. AUROC is used as a metric. Our approach shows improvement over existing approaches.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnihotri, A., Bhattacharya, S.: Online review helpfulness: role of qualitative factors. Psychol. Mark. 33(11), 1006–1017 (2016)
Cao, Q., Duan, W., Gan, Q.: Exploring determinants of voting for the “helpfulness’’ of online user reviews: a text mining approach. Decis. Support Syst. 50(2), 511–521 (2011)
Chen, C., et al.: Review helpfulness prediction with embedding-gated CNN. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.09896 (2018)
Chen, C., Yang, Y., Zhou, J., Li, X., Bao, F.: Cross-domain review helpfulness prediction based on convolutional neural networks with auxiliary domain discriminators. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 2 (Short Papers), pp. 602–607 (2018)
Chen, C.C., Tseng, Y.D.: Quality evaluation of product reviews using an information quality framework. Decis. Support Syst. 50(4), 755–768 (2011)
Chua, A.Y., Banerjee, S.: Understanding review helpfulness as a function of reviewer reputation, review rating, and review depth. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 66(2), 354–362 (2015)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805 (2018)
Diaz, G.O., Ng, V.: Modeling and prediction of online product review helpfulness: a survey. In: Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 698–708 (2018)
Du, J., Rong, J., Wang, H., Zhang, Y.: Helpfulness prediction for online reviews with explicit content-rating interaction. In: Cheng, R., Mamoulis, N., Sun, Y., Huang, X. (eds.) WISE 2020. LNCS, vol. 11881, pp. 795–809. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-34223-4_50
Duan, W., Gu, B., Whinston, A.B.: Do online reviews matter?-an empirical investigation of panel data. Decis. Support Syst. 45(4), 1007–1016 (2008)
Fan, M., Feng, C., Guo, L., Sun, M., Li, P.: Product-aware helpfulness prediction of online reviews. In: The World Wide Web Conference, pp. 2715–2721 (2019)
Filieri, R.: What makes online reviews helpful? A diagnosticity-adoption framework to explain informational and normative influences in e-WOM. J. Bus. Res. 68(6), 1261–1270 (2015)
He, R., McAuley, J.: Ups and downs: modeling the visual evolution of fashion trends with one-class collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 507–517 (2016)
Huang, A.H., Chen, K., Yen, D.C., Tran, T.P.: A study of factors that contribute to online review helpfulness. Comput. Hum. Behav. 48, 17–27 (2015)
Kiritchenko, S., Zhu, X., Cherry, C., Mohammad, S.: NRC-Canada-2014: detecting aspects and sentiment in customer reviews. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2014), pp. 437–442 (2014)
Krishnamoorthy, S.: Linguistic features for review helpfulness prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(7), 3751–3759 (2015)
Malik, M., Hussain, A.: Helpfulness of product reviews as a function of discrete positive and negative emotions. Comput. Hum. Behav. 73, 290–302 (2017)
Marcus, M., Santorini, B., Marcinkiewicz, M.A.: Building a large annotated corpus of english: the penn treebank (1993)
McAuley, J., Targett, C., Shi, Q., Van Den Hengel, A.: Image-based recommendations on styles and substitutes. In: Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 43–52 (2015)
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G.S., Dean, J.: Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 26, 3111–3119 (2013)
Olatunji, I.E., Li, X., Lam, W.: Context-aware helpfulness prediction for online product reviews. In: Wang, F.L., et al. (eds.) AIRS 2019. LNCS, vol. 12004, pp. 56–65. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42835-8_6
Pennington, J., Socher, R., Manning, C.D.: Glove: global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 1532–1543 (2014)
Petroni, F., Plachouras, V., Nugent, T., Leidner, J.L.: attr2vec: jointly learning word and contextual attribute embeddings with factorization machines. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long Papers), pp. 453–462 (2018)
Qu, X., Li, X., Rose, J.R.: Review helpfulness assessment based on convolutional neural network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.09016 (2018)
Rezaeinia, S.M., Rahmani, R., Ghodsi, A., Veisi, H.: Sentiment analysis based on improved pre-trained word embeddings. Expert Syst. Appl. 117, 139–147 (2019)
Rosenthal, S., Farra, N., Nakov, P.: Semeval-2017 task 4: sentiment analysis in twitter. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2017), pp. 502–518 (2017)
Saumya, S., Singh, J.P., Baabdullah, A.M., Rana, N.P., Dwivedi, Y.K.: Ranking online consumer reviews. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 29, 78–89 (2018)
Saumya, S., Singh, J.P., Dwivedi, Y.K.: Predicting the helpfulness score of online reviews using convolutional neural network. Soft Comput. 1–17 (2019)
Schuff, D., Mudambi, S.: What makes a helpful online review? A study of customer reviews on amazon.com. MIS Q. 34(1), 185–200 (2012)
Singh, J.P., Irani, S., Rana, N.P., Dwivedi, Y.K., Saumya, S., Roy, P.K.: Predicting the “helpfulness” of online consumer reviews. J. Bus. Res. 70, 346–355 (2017)
Sun, X., Han, M., Feng, J.: Helpfulness of online reviews: examining review informativeness and classification thresholds by search products and experience products. Decis. Support Syst. 124, 113099 (2019)
Tractinsky, N., Srinivasan Rao, V.: Incorporating social dimensions in web-store design. Hum. Syst. Manag. 20(2), 105–121 (2001)
Weiss, S.M., Indurkhya, N., Zhang, T., Damerau, F.: Text Mining: Predictive Methods for Analyzing Unstructured Information. Springer, New York (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-34555-0
Xiong, W., Litman, D.: Automatically predicting peer-review helpfulness. In: Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pp. 502–507 (2011)
Xiong, W., Litman, D.: Empirical analysis of exploiting review helpfulness for extractive summarization of online reviews. In: Proceedings of COLING 2014, the 25th International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Technical Papers, pp. 1985–1995 (2014)
Xu, X., Wang, X., Li, Y., Haghighi, M.: Business intelligence in online customer textual reviews: understanding consumer perceptions and influential factors. Int. J. Inf. Manage. 37(6), 673–683 (2017)
Yang, Z., Dai, Z., Yang, Y., Carbonell, J., Salakhutdinov, R.R., Le, Q.V.: Xlnet: generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 5753–5763 (2019)
Zhang, Z., Ma, Y., Chen, G., Wei, Q.: Extending associative classifier to detect helpful online reviews with uncertain classes. In: 2015 Conference of the International Fuzzy Systems Association and the European Society for Fuzzy Logic and Technology (IFSA-EUSFLAT 2015). Atlantis Press (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mitra, S., Jenamani, M. (2024). HORIE: Helpfulness of Online Reviews with Improved Embedding. In: Ghosh, A., King, I., Bhattacharyya, M., Sankar Ray, S., K. Pal, S. (eds) Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence. PReMI 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13102. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-12700-7_62
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-12700-7_62
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-12699-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-12700-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)