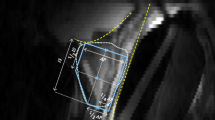
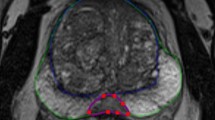
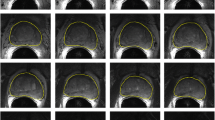
Abstract
Aim: To verify the accuracy of different segmentation algorithms applied on a dataset of 50 patients suffering from enlargement of the median lobe of the prostate district, to establish whether it is possible to support the work of medical physicians in radiomics analyses through semi-automatic segmentation approaches.
Materials and Methods: Seven algorithms were used for prostate segmentation in MR images and for the subsequent extraction of radiomics features. A statistical analysis was carried out considering the features extracted from semi-automatic and manual segmentations. The analysis was based on the ANOVA test, followed by the Tukey test to verify the repeatability of the algorithms, and on the calculation of the intraclass correlation coefficient to verify the reliability and robustness of the extracted features. Based on the correlation between the binary masks extracted for each algorithm and the corresponding binary mask of the medical physicians’ segmentation, a volumetric analysis was conducted.
Results: The best semi-automatic algorithm to support the medical physician among those evaluated is the “Fill between slices” algorithm, which is also the fastest of all. The least reliable algorithms are those based on the similarity of grey levels.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mobley, D., Feibus, A., Baum, N.: Benign prostatic hyperplasia and urinary symptoms: evaluation and treatment. Postgrad. Med. 127, 301–307 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/00325481.2015.1018799
Mitterbergera, M., et al.: Ultrasound of the prostate. Cancer Imaging 10, 40–48 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1102/1470-7330.2010.0004
Ghose, S., et al.: A survey of prostate segmentation methodologies in ultrasound, magnetic resonance and computed tomography images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2012.04.006
Jue, J.S., et al.: Re-examining prostate-specific antigen (PSA) density: defining the optimal PSA range and patients for using PSA density to predict prostate cancer using extended template biopsy. Urology 105, 123–128 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2017.04.015
EAU Pocket Guidelines. Edn. Present. EAU Annu. Congr. Amsterdam (2022)
Cutaia, G., et al.: Radiomics and prostate MRI: current role and future applications. J. Imaging 7, 34 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging7020034
Barone, S., et al.: Hybrid descriptive-inferential method for key feature selection in prostate cancer radiomics. Appl. Stoch. Model. Bus. Ind. 37, 961–972 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/asmb.2642
Cuocolo, R., et al.: Machine learning applications in prostate cancer magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 3, 35 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41747-019-0109-2
Schwier, M., et al.: Repeatability of multiparametric prostate MRI radiomics features. Sci. Rep. 9, 1–16 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45766-z
Alongi, P., et al.: Choline PET/CT features to predict survival outcome in high risk prostate cancer restaging: a preliminary machine-learning radiomics study. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging (2020). https://doi.org/10.23736/s1824-4785.20.03227-6
Alongi, P., et al.: Radiomics analysis of 18F-Choline PET/CT in the prediction of disease outcome in high-risk prostate cancer: an explorative study on machine learning feature classification in 94 patients. Eur. Radiol. 31(7), 4595–4605 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07617-8
Cuocolo, R., et al.: Deep learning whole-gland and zonal prostate segmentation on a public MRI dataset. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 54, 452–459 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.27585
Comelli, A., et al.: Deep learning-based methods for prostate segmentation in magnetic resonance imaging. Appl. Sci. 11, 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020782
Salvaggio, G., et al.: Deep learning network for segmentation of the prostate gland with median lobe enlargement in T2-weighted MR images: comparison with manual segmentation method. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1067/j.cpradiol.2021.06.006
Chevrefils, C., Chériet, F., Grimard, G., Aubin, C.-E.: Watershed segmentation of intervertebral disk and spinal canal from MRI images. In: Kamel, M., Campilho, A. (eds.) ICIAR 2007. LNCS, vol. 4633, pp. 1017–1027. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74260-9_90
Turkbey, B., et al.: Prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2.1: 2019 update of prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2. Eur. Urol. 76, 340–351 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EURURO.2019.02.033
Stanzione, A., et al.: Prostate volume estimation on MRI: accuracy and effects of ellipsoid and bullet-shaped measurements on PSA density. Acad. Radiol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2020.05.014
Cuocolo, R., et al.: Clinically significant prostate cancer detection on MRI: a radiomic shape features study. Eur. J. Radiol. 116, 144–149 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.05.006
Stefano, A., et al.: Performance of radiomics features in the quantification of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis from HRCT. Diagnostics 10, 306 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050306
Russo, G., et al.: Feasibility on the use of radiomics features of 11[C]-MET PET/CT in central nervous system tumours: preliminary results on potential grading discrimination using a machine learning model. Curr. Oncol. 28, 5318–5331 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060444
Stefano, A., et al.: Robustness of pet radiomics features: Impact of co-registration with mri. Appl. Sci. 11, 10170 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110170
Stefano, A., Comelli, A.: Customized efficient neural network for covid-19 infected region identification in ct images. J. Imaging 7, 131 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging7080131
Salvaggio, G., et al.: deep learning networks for automatic retroperitoneal sarcoma segmentation in computerized tomography. Appl. Sci. 12, 1665 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031665
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cairone, L. et al. (2022). Robustness of Radiomics Features to Varying Segmentation Algorithms in Magnetic Resonance Images. In: Mazzeo, P.L., Frontoni, E., Sclaroff, S., Distante, C. (eds) Image Analysis and Processing. ICIAP 2022 Workshops. ICIAP 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13373. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13321-3_41
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13321-3_41
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-13320-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-13321-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)