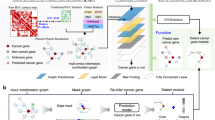
Abstract
Simultaneous mutations in synthetic lethality genes can lead to cancer cell apoptosis and it can be utilized in cancer target therapy. However, high-throughput wet laboratory screening methods are expensive and time-consuming. Computational methods are therefore a good complement to the prediction of synthetic lethality. Recently, graph embedding-based methods have been developed to predict synthetic lethal gene pairs. Here, we proposed a novel synthetic lethality prediction method based on bidirectional attention learning. Through aggregating biological multi-omics data, we can construct the node embedding representation and the graph link representation respectively. The correlation between gene pairs with these two feature representations is calculated using a multilayer perceptron as a decoder. The correlation with high gene pair score is predicted as potential synthetic lethal pair.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan, D.A., Giaccia, A.J.: Harnessing synthetic lethal interactions in anticancer drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 10(5), 351–364 (2011)
Du, D., Roguev, A., Gordon, D.E., et al.: Genetic interaction mapping in mammalian cells using CRISPR interference. Nat. Methods 14(6), 577–580 (2017)
Luo, J., Emanuele, M.J., Li, D., et al.: A genome-wide RNAi screen identifies multiple synthetic lethal interactions with the Ras oncogene. Cell 137(5), 835–848 (2009)
Zhong, W., Sternberg, P.W.: Genome-wide prediction of C. elegans genetic interactions. Science 311(5766), 1481–1484 (2006)
Long, Y., Wu, M., Liu, Y., et al.: Graph contextualized attention network for predicting synthetic lethality in human cancers. Bioinformatics 37(16), 2432–2440 (2021)
Huang, J., Wu, M., Lu, F., et al.: Predicting synthetic lethal interactions in human cancers using graph regularized self-representative matrix factorization. BMC Bioinformatics 20(19), 1–8 (2019)
Cai, R., Chen, X., Fang, Y., et al.: Dual-dropout graph convolutional network for predicting synthetic lethality in human cancers. Bioinformatics 36(16), 4458–4465 (2020)
Clark, W.T., Radivojac, P.: Analysis of protein function and its prediction from amino acid sequence. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 79(7), 2086–2096 (2011)
Ashburner, M., Ball, C.A., Blake, J.A., et al.: Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 25(1), 25–29 (2000)
Keshava Prasad, T.S., Goel, R., Kandasamy, K., et al.: Human protein reference database—2009 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(suppl_1), D767–D772 (2009)
Liu, Y., Wu, M., Liu, C., et al.: SL2MF: Predicting synthetic lethality in human cancers via logistic matrix factorization. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 17(3), 748–757 (2019)
Kipf, T.N., Welling, M.: Variational graph auto-encoders (2016)
Vizeacoumar, F.J., Arnold, R., Vizeacoumar, F.S., et al.: A negative genetic interaction map in isogenic cancer cell lines reveals cancer cell vulnerabilities. Mol. Syst. Biol. 9(1), 696 (2013)
Martin, T.D., Cook, D.R., Choi, M.Y., et al.: A role for mitochondrial translation in promotion of viability in K-Ras mutant cells. Cell Rep. 20(2), 427–438 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61972141) and Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (Grant No. 2021JJ30144).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sun, F., Lu, X., Chen, G., Zhang, X., Jiang, K., Li, J. (2022). A Novel Synthetic Lethality Prediction Method Based on Bidirectional Attention Learning. In: Huang, DS., Jo, KH., Jing, J., Premaratne, P., Bevilacqua, V., Hussain, A. (eds) Intelligent Computing Theories and Application. ICIC 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13394. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13829-4_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13829-4_30
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-13828-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-13829-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)