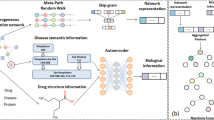
Abstract
Predicting the relationships between drugs and targets is a crucial step in the course of drug discovery and development. Computational prediction of associations between drugs and targets greatly enhances the probability of finding new interactions by reducing the cost of in vitro experiments. In this paper, a Meta-path-based Representation Learning model, namely MRLDTI, is proposed to predict unknown DTIs. Specifically, we first design a random walk strategy with a meta-path to collect the biological relations of drugs and targets. Then, the representations of drugs and targets are captured by a heterogeneous skip-gram algorithm. Finally, a machine learning classifier is employed by MRLDTI to discover novel DTIs. Experimental results indicate that MRLDTI performs better than several state-of-the-art models under ten-fold cross-validation on the gold standard dataset.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Su, X., Hu, L., You, Z., Hu, P., Wang, L., Zhao, B.: A deep learning method for repurposing antiviral drugs against new viruses via multi-view nonnegative matrix factorization and its application to SARS-CoV-2. Brief. Bioinform. 23, bbab526 (2022)
Zhao, B.-W., Hu, L., You, Z.-H., Wang, L., Su, X.-R.: HINGRL: predicting drug–disease associations with graph representation learning on heterogeneous information networks. Brief. Bioinform. 23, bbab515 (2022)
Hu, L., Chan, K.C.: A density-based clustering approach for identifying overlapping protein complexes with functional preferences. BMC Bioinform. 16, 1–16 (2015)
Hu, L., Chan, K.C.: Extracting coevolutionary features from protein sequences for predicting protein-protein interactions. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 14, 155–166 (2016)
You, Z.-H., Li, X., Chan, K.C.: An improved sequence-based prediction protocol for protein-protein interactions using amino acids substitution matrix and rotation forest ensemble classifiers. Neurocomputing 228, 277–282 (2017)
Ezzat, A., Wu, M., Li, X.-L., Kwoh, C.-K.J.B.i.b.: Computational prediction of drug–target interactions using chemogenomic approaches: an empirical survey, 20, 1337–1357 (2019)
Hu, L., Yuan, X., Liu, X., Xiong, S., Luo, X.: Efficiently detecting protein complexes from protein interaction networks via alternating direction method of multipliers. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 16, 1922–1935 (2018)
Guo, Z.-H., Yi, H.-C., You, Z.-H.: Construction and comprehensive analysis of a molecular association network via lncRNA–miRNA–disease–drug–protein graph. Cells 8, 866 (2019)
Hu, L., Chan, K.C., Yuan, X., Xiong, S.: A variational Bayesian framework for cluster analysis in a complex network. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 32, 2115–2128 (2019)
Wang, L., You, Z.-H., Li, Y.-M., Zheng, K., Huang, Y.-A.: GCNCDA: a new method for predicting circRNA-disease associations based on graph convolutional network algorithm. PLoS Comput. Biol. 16, e1007568 (2020)
Yi, H.-C., You, Z.-H., Wang, M.-N., Guo, Z.-H., Wang, Y.-B., Zhou, J.-R.: RPI-SE: a stacking ensemble learning framework for ncRNA-protein interactions prediction using sequence information. BMC Bioinform. 21, 1–10 (2020)
Wang, L., You, Z.-H., Huang, D.-S., Zhou, F.: Combining high speed ELM learning with a deep convolutional neural network feature encoding for predicting protein-RNA interactions. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 17, 972–980 (2018)
Hu, L., Wang, X., Huang, Y., Hu, P., You, Z.-H.: A novel network-based algorithm for predicting protein-protein interactions using gene ontology. Front. Microbiol. 2441 (2021)
Pan, X., Hu, L., Hu, P., You, Z.-H.: Identifying protein complexes from protein-protein interaction networks based on fuzzy clustering and GO semantic information. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. (2021)
Hu, L., Zhang, J., Pan, X., Yan, H., You, Z.-H.: HiSCF: leveraging higher-order structures for clustering analysis in biological networks. Bioinformatics 37, 542–550 (2021)
Li, Z., Hu, L., Tang, Z., Zhao, C.: Predicting HIV-1 protease cleavage sites with positive-unlabeled learning. Front. Genet. 12, 658078 (2021)
Hu, L., Yang, S., Luo, X., Yuan, H., Sedraoui, K., Zhou, M.: A distributed framework for large-scale protein-protein interaction data analysis and prediction using mapreduce. IEEE/CAA J. Automatica Sinica 9, 160–172 (2021)
Luo, Y., et al.: A network integration approach for drug-target interaction prediction and computational drug repositioning from heterogeneous information. Nat. Commun. 8, 1–13 (2017)
Hu, P., Huang, Y., You, Z., Li, S., Chan, K.C.C., Leung, H., Hu, L.: Learning from deep representations of multiple networks for predicting drug–target interactions. In: Huang, D.-S., Jo, K.-H., Huang, Z.-K. (eds.) ICIC 2019. LNCS, vol. 11644, pp. 151–161. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26969-2_14
Wan, F., Hong, L., Xiao, A., Jiang, T., Zeng, J.: NeoDTI: neural integration of neighbor information from a heterogeneous network for discovering new drug–target interactions. Bioinformatics 35, 104–111 (2019)
Hu, A.L., Chan, K.C.: Utilizing both topological and attribute information for protein complex identification in ppi networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 10, 780–792 (2013)
Hu, L., Chan, K.C.: Fuzzy clustering in a complex network based on content relevance and link structures. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 24, 456–470 (2015)
Xing, W., et al.: A gene–phenotype relationship extraction pipeline from the biomedical literature using a representation learning approach. Bioinformatics 34, i386–i394 (2018)
Hu, P., Huang, Y.-A., Chan, K.C., You, Z.-H.: Learning multimodal networks from heterogeneous data for prediction of lncRNA-miRNA interactions. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. (2019)
Jiang, H.-J., You, Z.-H., Hu, L., Guo, Z.-H., Ji, B.-Y., Wong, L.: A highly efficient biomolecular network representation model for predicting drug-disease associations. In: Huang, D.-S., Premaratne, P. (eds.) ICIC 2020. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 12465, pp. 271–279. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60796-8_23
Hu, L., Yang, S., Luo, X., Zhou, M.: An algorithm of inductively identifying clusters from attributed graphs. IEEE Trans. Big Data (2020)
Wang, L., You, Z.-H., Li, J.-Q., Huang, Y.-A.: IMS-CDA: prediction of CircRNA-disease associations from the integration of multisource similarity information with deep stacked autoencoder model. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 51, 5522–5531 (2020)
Guo, Z.-H., et al.: MeSHHeading2vec: a new method for representing MeSH headings as vectors based on graph embedding algorithm. Brief. Bioinform. 22, 2085–2095 (2021)
Wang, L., You, Z.-H., Huang, Y.-A., Huang, D.-S., Chan, K.C.: An efficient approach based on multi-sources information to predict circRNA–disease associations using deep convolutional neural network. Bioinformatics 36, 4038–4046 (2020)
Hu, L., Zhang, J., Pan, X., Luo, X., Yuan, H.: An effective link-based clustering algorithm for detecting overlapping protein complexes in protein-protein interaction networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 8, 3275–3289 (2021)
Wang, L., You, Z.-H., Zhou, X., Yan, X., Li, H.-Y., Huang, Y.-A.: NMFCDA: combining randomization-based neural network with non-negative matrix factorization for predicting CircRNA-disease association. Appl. Soft Comput. 110, 107629 (2021)
Hu, L., Zhao, B.-W., Yang, S., Luo, X., Zhou, M.: Predicting large-scale protein-protein interactions by extracting coevolutionary patterns with MapReduce paradigm. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), pp. 939–944. IEEE (2021)
Zhao, B.-W., You, Z.-H., Hu, L., Wong, L., Ji, B.-Y., Zhang, P.: A multi-graph deep learning model for predicting drug-disease associations. In: Huang, D.-S., Jo, K.-H., Li, J., Gribova, V., Premaratne, P. (eds.) ICIC 2021. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 12838, pp. 580–590. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84532-2_52
Hu, L., Wang, X., Huang, Y.-A., Hu, P., You, Z.-H.: A survey on computational models for predicting protein–protein interactions. Brief. Bioinform. 22, bbab036 (2021)
Su, X.-R., You, Z.-H., Yi, H.-C., Zhao, B.-W.: Detection of drug-drug interactions through knowledge graph integrating multi-attention with capsule network. In: Huang, D.-S., Jo, K.-H., Li, J., Gribova, V., Premaratne, P. (eds.) ICIC 2021. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 12838, pp. 423–432. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84532-2_38
Zhao, B.-W., You, Z.-H., Wong, L., Zhang, P., Li, H.-Y., Wang, L.J.F.i.G.: MGRL: predicting drug-disease associations based on multi-graph representation learning. Front. Genet. 12, 491 (2021)
Su, X., et al.: SANE: a sequence combined attentive network embedding model for COVID-19 drug repositioning. Appl. Soft Comput. 111, 107831 (2021)
Zhang, H.-Y., Wang, L., You, Z.-H., Hu, L., Zhao, B.-W., Li, Z.-W., Li, Y.-M.: iGRLCDA: identifying circRNA–disease association based on graph representation learning. Brief. Bioinform. 23, bbac083 (2022)
Su, X.-R., Huang, D.-S., Wang, L., Wong, L., Ji, B.-Y., Zhao, B.-W.: Biomedical knowledge graph embedding with capsule network for multi-label drug-drug interaction prediction. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. (2022)
Chen, Z.-H., You, Z.-H., Guo, Z.-H., Yi, H.-C., Luo, G.-X., Wang, Y.-B.: Prediction of drug-target interactions from multi-molecular network based on deep walk embedding model. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8, 338 (2020)
Zhao, B.-W., et al.: A novel method to predict drug-target interactions based on large-scale graph representation learning. Cancers 13, 2111 (2021)
Dong, Y., Chawla, N.V., Swami, A.: metapath2vec: Scalable representation learning for heterogeneous networks. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 135–144 (2017)
Wang, L., You, Z.-H., Huang, D.-S., Li, J.-Q.: MGRCDA: metagraph recommendation method for predicting CircRNA-disease association. IEEE Trans. Cybern. (2021)
Li, J., Wang, J., Lv, H., Zhang, Z., Wang, Z.: IMCHGAN: inductive matrix completion with heterogeneous graph attention networks for drug-target interactions prediction. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 19, 655–665 (2021)
Friedman, J.H.: Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 1189–1232 (2001)
Wang, W., Yang, S., Zhang, X., Li, J.: Drug repositioning by integrating target information through a heterogeneous network model. Bioinformatics 30, 2923–2930 (2014)
Zheng, X., Ding, H., Mamitsuka, H., Zhu, S.: Collaborative matrix factorization with multiple similarities for predicting drug-target interactions. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 1025–1033. 2013)
Yan, X.-Y., Zhang, S.-W., Zhang, S.-Y.: Prediction of drug–target interaction by label propagation with mutual interaction information derived from heterogeneous network. Mol. BioSyst. 12, 520–531 (2016)
Guo, Z.-H., You, Z.-H., Yi, H.-C.: Integrative construction and analysis of molecular association network in human cells by fusing node attribute and behavior information. Mol. Therapy-Nucl. Acids 19, 498–506 (2020)
Yi, H.-C., You, Z.-H., Guo, Z.-H., Huang, D.-S., Chan, K.C.: Learning representation of molecules in association network for predicting intermolecular associations. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. (2020)
Guo, Z.-H., You, Z.-H., Wang, Y.-B., Huang, D.-S., Yi, H.-C., Chen, Z.-H.: Bioentity2vec: attribute-and behavior-driven representation for predicting multi-type relationships between bioentities. GigaScience9, giaa032 (2020)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region under grant 2021D01D05, in part by the Pioneer Hundred Talents Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, under Grants 61702444, 62002297, 61902342, in part by Awardee of the NSFC Excellent Young Scholars Program, under Grant 61722212, and in part by the Tianshan youth - Excellent Youth, under Grant 2019Q029.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhao, BW. et al. (2022). MRLDTI: A Meta-path-Based Representation Learning Model for Drug-Target Interaction Prediction. In: Huang, DS., Jo, KH., Jing, J., Premaratne, P., Bevilacqua, V., Hussain, A. (eds) Intelligent Computing Theories and Application. ICIC 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13394. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13829-4_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13829-4_39
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-13828-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-13829-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)