Abstract
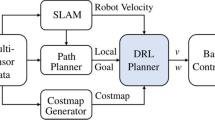
This paper proposed an improved reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm to develop a strategy for a mobile robot to avoid obstacles with deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) in order to solve the problem that the robot spends invalid time exploring obstacles in the initial exploration and speed up the stability and speed of the robot learning. An environment map is used to generate range sensor readings, detect obstacles, and check collisions that the robot may make. The range sensor readings are the observations for the DDPG agent, and the linear and angular velocity controls are the action. The experiment scenario trains a mobile robot to avoid obstacles given range sensor readings that detect obstacles in the map. The objective of the reinforcement learning algorithm is to learn what controls including linear and angular velocity, the robot should use to avoid colliding into obstacles. Simulations results show that the feasibility and certain application value of the method and the algorithm can effectively solve the rewards problem in the process of robot moving, and the execution efficiency of the algorithm is significantly improved. Therefore there are some value of reference and application for development of mobile robot obstacle avoidance system owing to the work of this paper.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levine, S., Pastor, P., Krizhevsky, A., et al.: Learning hand-eye coordination for robotic grasping with deep learning and large-scale data collection. Int. J. Robot. Res. 37, 421–436 (2017)
Tang, L., Liu, Y.-J., Tong, S.: Adaptive neural control using reinforcement learning for a class of robot manipulator. Neural Comput. Appl. 25(1), 135–141 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1455-2
Yu, H., Gao, H., Deng, Z.: Toward a unified approximate analytical representation for spatially running spring-loaded inverted pendulum model. IEEE Trans. Rob. 99, 1–8 (2020)
Xu, Y., Ding, S.X., Luo, H., et al.: A real-time performance recovery framework for vision-based control systems. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 99, 1 (2020)
Riedmiller, M., Gabel, T., Hafner, R., et al.: Reinforcement learning for robot soccer. Auton. Robot. 27(1), 55–73 (2009)
Lillicrap, T.P., Hunt, J.J., Pritzel, A ., et al.: Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. In: Computer Science (2015)
Zhang, B.W., Jinlong, Z., et al.: Reinforcement Learning Energy Management for Hybrid Electric Tracked Vehicle with Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient, 2020 China Society of Automotive Engineering Annual Conference and Exhibition (2020)
Cai, K., et al.: mobile robot path planningin dynamic environments: a survey. Instrumentation 6(02), 92–102(2019)
Chen, CT., Quinn, R.D., Ritzmann, R.E.: A crash avoidance system based upon the cockroach escape response circuit. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation, Pp. 2007–2012. IEEE (2002)
Fan, J., Wu, G., Ma, F., Liu, J.: Reinforcement learning and ART2 neural network based collision avoidance system of mobile robot. In: Yin, F.-L., Wang, J., Guo, C. (eds.) ISNN 2004. LNCS, vol. 3174, pp. 35–41. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-28648-6_6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, M., Li, W., Fei, S., Wei, Y., Tu, M., Li, J. (2022). Reinforcement Learning for Mobile Robot Obstacle Avoidance with Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient. In: Liu, H., et al. Intelligent Robotics and Applications. ICIRA 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13457. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13835-5_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13835-5_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-13834-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-13835-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)