Abstract
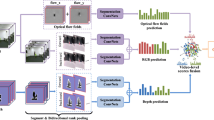
There is the problem of strong spatio-temporal complexity of actions and low differentiation of similar action features in Action Recognition. Unimodal input, such as RGB image, can provide rich appearance and context information, but background motion and object occlusion make it difficult to extract human motion information. Multimodal-based human action recognition methods can solve these problems. However, the problems of inadequate fusion of multimodal features lead to poor algorithm robustness and insufficient consideration of modal differences in existing multimodal-based human action recognition methods. We proposed a two-stream adaptive weight convolutional neural network based on spatial attention for human action recognition, SA-AWCNN, to achieve cross-modality feature complementarity. This method constructs a local feature interaction module from depth to RGB to effectively improve the network modal information interaction ability by using the complementarity between modes. At the same time, the spatial attention module is introduced to strengthen the spatial dimension feature information, and the effectiveness of network feature extraction is improved without increasing network parameters. Experiments show that the proposed method is effective in completing human action recognition tasks. The accuracy of our method on NTU RGB+ D dataset and SBU Kinect interaction dataset reaches 91.85% and 94.30%.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duan, J., Wan, J., Zhou, S., et al.: A unified framework for multi-modal isolated gesture recognition. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 14(1s), 1–16 (2018)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., et al.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Ren, Z., Zhang, Q., Gao, X., et al.: Multi-modality learning for human action recognition. Multimedia Tools Appl. 80(11), 16185–16203 (2021)
Qin, X., Ge, Y., Feng, J., et al.: DTMMN: deep transfer multi-metric network for RGB-D action recognition. Neurocomputing 406, 127–134 (2020)
Lu, Y., Wu, Y., Liu, B., et al.: Cross-modality person re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13379–13389 (2020)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Wang, Q., Wu, B., Zhu, P., et al.: ECA-Net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11531–11539 (2020)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: CBAM: convolutional block attention module. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11211, pp. 3–19. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., et al.: Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4489–4497 (2015)
Wang, L., et al.: Temporal segment networks: towards good practices for deep action recognition. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9912, pp. 20–36. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_2
Xiao, Y., Chen, J., Wang, Y., et al.: Action recognition for depth video using multi-view dynamic images. Inf. Sci. 480, 287–304 (2019)
Wang, P., Li, W., Gao, Z., et al.: Depth pooling based large-scale 3D action recognition with convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 20(5), 1051–1061 (2018)
Carreira, J., Zisserman, A.: Quo vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6299–6308 (2017)
Shi, L., Zhang, Y., Cheng, J., et al.: Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12026–12035 (2019)
Cheng, K., Zhang, Y., He, X., et al.: Skeleton-based action recognition with shift graph convolutional network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 183–192 (2020)
Baradel, F., Wolf, C., Mille, J.: Human activity recognition with pose-driven attention to RGB. In: 29th British Machine Vision Conference, pp. 1–14 (2018)
Moon, G., Kwon, H., Lee, K.M., et al.: IntegralAction: pose-driven feature integration for robust human action recognition in videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3339–3348 (2021)
Ijjina, E.P., Chalavadi, K.M.: Human action recognition in RGB-D videos using motion sequence information and deep learning. Pattern Recogn. 72, 504–516 (2017)
Lin, L., Wang, K., Zuo, W., et al.: A deep structured model with radius–margin bound for 3D human activity recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vision 118(2), 256–273 (2016)
Berlin, S.J., John, M.: Particle swarm optimization with deep learning for human action recognition. Multimedia Tools Appl. 79(25), 17349–17371 (2020)
Peng, C., Huang, H., Tsoi, A.C., et al.: Motion boundary emphasized optical flow method for human action recognition. IET Comput. Vision 14(6), 378–390 (2020)
Liu, B., Yu, H., Zhou, X., et al.: Combining 3D joints moving trend and geometry property for human action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, pp. 000332–000337 (2016)
Baradel, F., Wolf, C., Mille, J.: Pose-conditioned spatio-temporal attention for human action recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.10106 (2017)
Song, S., Lan, C., Xing, J., et al.: An end-to-end spatio-temporal attention model for human action recognition from skeleton data. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 4263–4270 (2017)
Li, Y., Guo, T., Liu, X., et al.: Action status based novel relative feature representations for interaction recognition. Chin. J. Electron. 31(1), 168–180 (2022)
Lin, J., Gan, C., Han, S.: TSM: temporal shift module for efficient video understanding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 7083–7093 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, G., Yao, L., Xu, J., Liu, Q., Chen, S. (2022). Two-Stream Adaptive Weight Convolutional Neural Network Based on Spatial Attention for Human Action Recognition. In: Liu, H., et al. Intelligent Robotics and Applications. ICIRA 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13458. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13841-6_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13841-6_30
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-13840-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-13841-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)