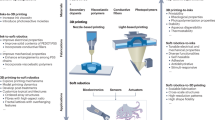
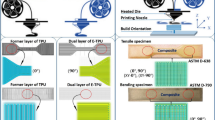
Abstract
The use of Electro-Active Polymers (EAPs) for the fabrication of evermore sophisticated miniaturised soft robotic actuators has seen an impressive development in recent years. This paper unveils the latest computational developments of the group related to three significant challenges presented in the in-silico modelling of EAPs, that are being explored with our in-house computational platform. These challenges, unique to the simulation of EAPs, include (i) robustly resolving the onset of potentially massive strains as a result of the significant flexibility of EAP components for soft robotics; (ii) accurately capturing the properties of multi-phased composites at a micro-scale within the macroscopic fields used in well-established computational modelling approaches (i.e. Finite Element Method); and (iii) optimising the electrode meso-architecture to enable device customisation for specific application required deformations. This paper also aims to demonstrate the in-silico design tools capability, robustness and flexibility, provided through a comprehensive set of numerical examples, including some novel results in electrode and EAP multi-material optimisation. With the upcoming addition of a 3D Direct-Ink-Writer (DIW) printer, the authors aim to close the loop allowing for in-house device design and optimisation, simulation and analysis as well as fabrication and testing.
The first and fourth authors acknowledge the financial support received from the UK Defence Science and Technology Laboratory.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aage, N., Andreassen, E., Lazarov, B., Sigmund, O.: Giga-voxel computational morphogenesis for structural design. Nature 550, 84–86 (2017)
Duduta, M., Hajiesmaili, E., Zhao, H., Wood, R., Clarke, D.: Realizing the potential of dielectric elastomer artificial muscles. PNAS 116, 2476–2481 (2019)
Gil, A.J., Ortigosa, R.: A new framework for large strain electromechanics based on convex multi-variable strain energies: variational formulation and material characterisation. CMAME 302, 293–328 (2016)
Guo, Y., Liu, L., Liu, Y., Leng, J.: Review of dielectric elastomer actuators and their applications in soft robots. Adv. Intell. Syst. 3, 2000282 (2021)
Hajiesmaili, E., Clarke, D.: Reconfigurable shape-morphing dielectric elastomers using spatially varying electric fields. Nature Communicationes 10(183), 1–7 (2019)
Horák, M., Gil, A., Ortigosa, R., Kruzik, M.: A polyconvex transversely-isotropic invariant-based formulation for electro-mechanics: stability, minimisers and computational implementation. Under review (2022)
Hossain, M., Navaratne, R., Peric, D.: 3D printed elastomeric polyurethane: viscoelastic experimental characterizations and constitutive modelling with nonlinear viscosity functions. IJNLM 126, 293–328 (2020)
Li, T., Keplinger, C., Baumgartner, R., Bauer, S., Yang, W., Suo, Z.: Giant voltage-induced deformation in dielectric elastomers near the verge of snap-through instability. JMPS 61(2), 611–628 (2013)
Marín, F., Martínez-Frutos, J., Ortigosa, R., Gil, A.: A convex multi-variable based computational framework for multilayered electro-active polymers. CMAME 374, 113567 (2021)
Martínez-Frutos, J., Ortigosa, R., Gil, A.J.: In-silico design of electrode meso-architecture for shape morphing dielectric elastomers. JMPS 157 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2021.104594
Munk, D.J., Vio, G.A., Steven, G.P.: Topology and shape optimization methods using evolutionary algorithms: a review. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 52(3), 613–631 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1261-9
Ortigosa, R., Gil, A.J.: A new framework for large strain electromechanics based on convex multi-variable strain energies: conservation laws, hyperbolicity and extension to electro-magneto-mechanics. CMAME 309, 202–242 (2016)
Ortigosa, R., Gil, A.J.: A new framework for large strain electromechanics based on convex multi-variable strain energies: finite element discretisation and computational implementation. CMAME 302, 329–360 (2016)
Ortigosa, R., Gil, A.J., Martínez-Frutos, J., Franke, M., Bonet, J.: A new energy-momentum time integration scheme for non-linear thermo-mechanics. CMAME 372, 113395 (2020)
Siboni, M.H., Castañeda, P.P.: Fiber-constrained, dielectric-elastomer composites: finite-strain response and stability analysis. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 68, 211–238 (2014)
Takezawa, A., Nishiwaki, S., Kitamura, M.: Shape and topology optimization based on the phase field method and sensitivity analysis. J. Comput. Phys. 229(7), 2697–2718 (2010)
Wang, M., Wang, X., Guo, D.: A level-set method for structural topology optimization. CMAME 192, 227–246 (2003)
Zhao, Y., Yin, L.J., Zhong, S.L., Zha, J.W., Dang, Z.M.: Review of dielectric elastomers for actuators, generators and sensors. IET Nanodielectr. 3, 99–106 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gil, A.J., Ortigosa, R., Martínez-Frutos, J., Ellmer, N. (2022). In-silico Design and Computational Modelling of Electroactive Polymer Based Soft Robotics. In: Pacheco-Gutierrez, S., Cryer, A., Caliskanelli, I., Tugal, H., Skilton, R. (eds) Towards Autonomous Robotic Systems. TAROS 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13546. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15908-4_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15908-4_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-15907-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-15908-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)