Abstract
The massive usage of social networks has recently opened up new research avenues in the fields of data mining and decision-making. One of the most relevant forms of data generated by users in social media is an unstructured text that identifies their emotions on a given topic. Analyzing this new form of writing to extract valuable information is a challenging task, and could be of great interest in several fields such as healthcare, business intelligence, marketing strategies,\(\ldots \) to name but a few. This article considers topic and polarity extraction in application to Online Social Media (OSM) analysis, in the benefit of numerous domain applications. Implementing sentiment analysis and topic extraction algorithms for the purpose of detecting the polarity of a given comment towards a certain topic requires a sophisticated machine and deep learning supervised models and, at the same time, collecting, preparing and annotating a huge amount of data to train those models.
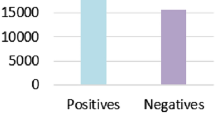
In this paper, we propose a special dataset that can be used to extract both topic and polarity features from dialectical messages used in Tunisian daily electronic writing across the most popular OSM networks. We collected our data by crawling posts and comments’ text from Facebook, Twitter and YouTube using related network graph API. In this work, we describe the whole pipeline used to prepare our corpus as well as the several extensive experiments setup and results conducted to evaluate the generated dataset. Up to our knowledge, the proposed multivariate Arabic dataset (Topic and Polarity) of Tunisian dialect is a first-time introduced in the NLP community up to now, and we made it publicly available on GitHub (https://github.com/DescoveryAmine/TunTap).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu Kwaik, K., Chatzikyriakidis, S., Dobnik, S., Saad, M., Johansson, R.: An arabic tweets sentiment analysis dataset (ATSAD) using distant supervision and self training. In: Proceedings of the 4th Workshop on Open-Source Arabic Corpora and Processing Tools, with a Shared Task on Offensive Language Detection, pp. 1–8. European Language Resource Association (05 2020)
Al-khurayji, R., Sameh, A.: An effective Arabic text classification approach based on kernel Naive Bayes classifier (2017). https://doi.org/10.5121/IJAIA.2017.8601
Alayba, A.M., Palade, V., England, M., Iqbal, R.: A combined CNN and LSTM model for Arabic sentiment analysis. arXiv:1807.02911 [cs] 11015, 179–191 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99740-7_12
Baly, R., et al.: Comparative evaluation of sentiment analysis methods across arabic dialects. Procedia Comput. Sci. 117, 266–273 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.10.118
Baly, R., Khaddaj, A., Hajj, H., El-Hajj, W., Shaban, K.B.: ArSentD-LEV: a multi-topic corpus for target-based sentiment analysis in Arabic levantine tweets. arXiv:1906.01830 [cs, stat], 25 May 2019
Cotterell, R., Callison-Burch, C.: A multi-dialect, multi-genre corpus of informal written Arabic. In: Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2014), pp. 241–245. European Language Resources Association (ELRA), May 2014
Fairon, C., Klein, J., Sébastien, P.: Le langage SMS : révélateur d’1compétence, 01 January 2006
Fourati, C., Messaoudi, A., Haddad, H.: TUNIZI: a tunisian arabizi sentiment analysis dataset. arXiv:2004.14303 [cs] (2020–04-29)
Meftouh, K., Bouchemal, N., Smaïli, K.: A study of a non-resourced language: an Algerian dialect. In: SLTU (2012)
Mohammed, A., Kora, R.: Deep learning approaches for Arabic sentiment analysis. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 9(1), 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-019-0596-4
Moudjari, L., Aklii Astouati, K.: An experimental study on sentiment classification of Algerian dialect texts. Procedia Comput. Sci. 176, 1151–1159 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.09.111
Nabil, M., Aly, M., Atiya, A.: ASTD: Arabic sentiment tweets dataset. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 2515–2519. Association for Computational Linguistics, September 2015. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D15-1299
Taoufiq, Z., Chiheb, R., Moumen, R., Faizi, R., El Afia, A.: Topic and sentiment model applied to the colloquial Arabic: a case study of Maghrebi Arabic, 21 June 2017. https://doi.org/10.1145/3128128.3128155
Wahdan, A., Hantoobi, S., Salloum, S., Shaalan, K.: A systematic review of text classification research based on deep learning models in Arabic language, pp. 6629–6643, 12 January 2020. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijece.v10i6.pp6629-6643
Younes, J., Hadhémi, A., Souissi, E.: Constructing linguistic resources for the Tunisian dialect using textual user-generated contents on the social web. vol. 9396, pp. 3–14, 23 June 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24800-4_1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Djebbi, M.A., Ouersighni, R. (2022). TunTap: A Tunisian Dataset for Topic and Polarity Extraction in Social Media. In: Nguyen, N.T., Manolopoulos, Y., Chbeir, R., Kozierkiewicz, A., Trawiński, B. (eds) Computational Collective Intelligence. ICCCI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13501. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16014-1_40
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16014-1_40
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16013-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16014-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)