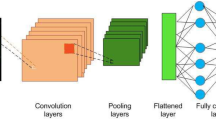
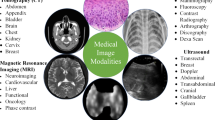
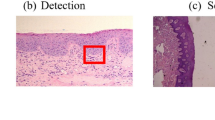
Abstract
Two paradigms have historically formed in artificial intelligence: neurocybernetics and black box cybernetics. The cybernetics of the “black box” is based on a logical approach. The rapid development of modern medicine is due to the use of technical diagnostic tools, and the use of new information technologies. Technical means of diagnosing allow you to visualize the processes of diagnosing. Intelligent information technologies use the methods and tools of artificial intelligence and can speed up the diagnosis and improve its accuracy. The authors of the work have been working on biomedical images for many years, building CAD systems with elements of artificial intelligence. Biomedical (cytological, histological, and immunohistochemical) images are used for diagnosis in oncology. The problems of classification, generation, segmentation, and clustering of biomedical images are solved in the work. For these purposes, the following means of computational intelligence were used: CNN, GAN, and U-net. CNN is used in the paper to classify images. Several models for the classification of biomedical images are proposed and a comparative analysis with existing analogs is given. The accuracy of classification for cytological images was 86%, for histological was 84%. The authors analyzed the architectures of convolutional neural networks of the U-net type for automatic segmentation of immunohistochemical images. A modified neural network architecture for the segmentation of immunohistochemical images has been developed. Computer experiments were performed on different numbers of stages and iterations. ROC curves are built to assess the quality of segmentation of known and modified network architectures such as U-net.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, R., Durkee, M.: Application and generalizability of U-Net segmentation of immune cells in inflamed tissue. In: Tomaszewski, J.E., Ward, A.D. (eds.) Medical Imaging 2021: Digital Pathology. SPIE, Online Only, United Stat, p. 40 (2021)
Al-Tam, R., Narangale, S.: Breast cancer detection and diagnosis using machine learning: a survey. J. Sci. Res. 65(5), 265–285 (2021)
de Almeida Thomaz, V., Sierra-Franco, C., Raposo, A.: Training data enhancements for improving colonic polyp detection using deep convolutional neural networks. Artif. Intell. Med. 111, 101988 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101988
Alom, M., Yakopcic, C., Taha, T.: Nuclei segmentation with recurrent residual convolutional neural networks based U-Net (R2U-Net), pp. 228–233 (2018)
Arjovsky, M., Chintala, S., Bottou, L.: Wasserstein GAN (2017)
Bai, J., Posner, R., Wang, T.: Applying deep learning in digital breast tomosynthesis for automatic breast cancer detection: a review. Med. Image Anal. 71, 102049 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2021.102049
Benny, S., Varma, S.: Semantic segmentation in immunohistochemistry breast cancer image using deep learning. In: 2021 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication, and Control (ICAC3), pp. 1–2. IEEE, Mumbai, India (2021)
Berezsky, O., Batko, Y., Berezka, K., Verbovyi, S.: Methods, algorithms and software for processing biomedical images. Ekonomichna dumka, p. 330 (2017)
Berezsky, O., Liashchynskyi, P.: Comparison of generative adversarial networks architectures for biomedical images synthesis. AAIT 4, 250–260 (2021). https://doi.org/10.15276/aait.03.2021.4
Berezsky, O., Pitsun, O. Derish, B.: Adaptive immunohistochemical image pre-processing method. In: International Conference on Advanced Computer Information Technologies (ACIT), pp. 820–823. IEEE, Deggendorf, Germany (2020)
Berezsky, O., Pitsun, O., Batryn, N.: Modern automated microscopy systems in oncology. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Informatics and Data-Driven Medicine, Lviv, Ukraine, pp. 311–325 (2018)
Berezsky, O., Pitsun, O., Datsko, T.: Specified diagnosis of breast cancer on the basis of immunogistochemical images analysis. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Informatics and Data-Driven Medicine, CEUR, Växjö, Sweden, pp. 129–135 (2020)
Berezsky, O., Pitsun, O., Derysh, B.: Automatic segmentation of immunohistochemical images based on U-Net architectures. In: CEUR, pp. 22–33 (2021). http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3038
Berezsky, O., Pitsun, O., Dolynyuk, T.: Cytological image classification using data reduction. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Informatics and Data-Driven Medicine (IDDM 2019), CEUR, Lviv, Ukraine, pp. 16–29 (2019)
Berezsky, O., Pitsun, O., Dolynyuk, T.: Cytological images clustering of breast pathologies. In: PIEEE 15th International Conference on Computer Sciences and Information Technologies (CSIT), pp. 62–65. IEEE, Zbarazh, Ukraine (2020)
IARC, I.: Marks Breast Cancer Awareness Month 2021. http://www.iarc.who.int/news-events/iarc-marks-breast-cancer-awareness-month-2021 (2022)
Brock, A., Donahue, J., Simonyan, K.: Large scale GAN training for high fidelity natural image synthesis (2019)
Das, A., Nair, M.: Batch mode active learning on the Riemannian manifold for automated scoring of nuclear pleomorphism in breast cancer. Artif. Intell. Med. 103, 101805 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101805
Filipczuk, P., Kowal, M., Obuchowicz, A.: Breast fibroadenoma automatic detection using k-means based hybrid segmentation method. In: 9th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp. 1623–1626. IEEE, Barcelona, Spain (2012)
Gandomkar, Z., Brennan, P., Mello-Thoms, C.: MuDeRN: multi-category classification of breast histopathological image using deep residual networks. Artif. Intell. Med. 88, 14–24 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2018.04.005
Ghasemi, M., Kelarestaghi, M., Eshghi, F.: FDSR: a new fuzzy discriminative sparse representation method for medical image classification. Artif. Intell. Med. 106, 101876 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101876
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M.: Generative adversarial networks (2014)
Heusel, M.: GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule. http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.08500 (2017)
Hlavcheva, D., Yaloveha, V., Podorozhniak, A.: A comparison of classifiers applied to the problem of biopsy images analysis. AIS 4, 12–16 (2022). https://doi.org/10.20998/2522-9052.2020.2.03
Jain, P., Kulsum, S.: Analysis of deep learning algorithms for breast cancer diagnosis on WBC. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 8(15) (2020)
Jin, D., Vasilakos, A.: Neural networks for computer-aided diagnosis in medicine: a review. Neurocomputing 216, 700–708 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.08.039
Kang, M., Park, J.: ContraGAN: Contrastive learning for conditional image generation (2021)
Kazeminia, S., Baur, C., Kuijper, A.: GANs for medical image analysis. Artif. Intell. Med. 109, 101938 (2020)
Kumar, Y., Gupta, S., Singla, R., Hu, Y.-C.: A systematic review of artificial intelligence techniques in cancer prediction and diagnosis. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 29(4), 2043–2070 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-021-09648-w
Latif, M., Faye, I.: Automated tibiofemoral joint segmentation based on deeply supervised 2D-3D ensemble U-Net: Data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Artif. Intell. Med. 122, 102213 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2021.102213
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. arXiv:1411.4038 (2015)
de Matos, J., Ataky, S., de Souza Britto, A.: Machine learning methods for histopathological image analysis: a review. Electronics 562(10), 700–708 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10050562
Menze, B., Jakab, A., Bauer, S.: The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 34, 1993–2024 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2014.2377694
Mitra, S., Das, N., Dey, S.: Cytology image analysis techniques towards automation: systematically revisited. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.07529 (2020)
Nassif, A., Talib, M.: Breast cancer detection using artificial intelligence techniques: a systematic literature review. Artif. Intell. Med. 127, 102276 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2022.102276
Nitefor, L.: Clinical features of immunogistochemical diagnosis of sarcoma and philoid tumors of the breast. APP (2017). https://doi.org/10.11603/24116-4944.2017.2.8036
Olatunji, S., Alotaibi, S., Almutairi, E.: Early diagnosis of thyroid cancer diseases using computational intelligence techniques: a case study of a Saudi Arabian dataset. Comput. Biol. Med. 131, 104267 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104267
de Oliveira Silva, L., Barros, A., Lopes, M.: Detecting masses in dense breast using independent component analysis. Artif. Intell. Med. 80, 29–38 (2017)
Peng, Y., Yao, B., Jiang, J.: Knowledge-discovery incorporated evolutionary search for microcalcification detection in breast cancer diagnosis. Artif. Intell. Med. 37(1), 43–53 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2005.09.001
Pham, B., Gaonkar, B., Whitehead, W.: Cell counting and segmentation of immunohistochemical images in the spinal cord: comparing deep learning and traditional approaches. In: 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 842–845. IEEE, Honolulu, HI (2018)
Pouliakis, A., Karakitsou, E., Margari, N.: Artificial neural networks as decision support tools in cytopathology: past, present, and future. Biomed. Eng. Comput. Biol. (2016). https://doi.org/10.4137/BECB.S31601
Prasad, R., Udupa, K.: BCHisto-Net: breast histopathological image classification by global and local feature aggregation. Artif. Intell. Med. 121, 102191 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2021.102191
Ramos-Vara, J.: Technical aspects of immunohistochemistry. Vet. Pathol. 42, 405–426 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1354/vp.42-4-405
Salimans, T.: Improved techniques for training GAN. Improved techniques for training GAN. http://arxiv.org/abs/1606.03498 (2021)
Xiong, H., Sharan, R.: Weak label based Bayesian U-Net for optic disc segmentation in fundus images. Artif. Intell. Med. 126, 102261 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2022.102261
Yager, J., Davidson, N.: Estrogen carcinogenesis in breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 354, 270–282 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra050776
Zhang, C., Gu, J.: AI in spotting high-risk characteristics of medical imaging and molecular pathology. Precis. Clin. Med. 4, 271–286 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1093/pcmedi/pbab026
Zhang, H., Goodfellow, I., Metaxas, D.: Self-attention generative adversarial networks (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Berezsky, O., Pitsun, O., Liashchynskyi, P., Derysh, B., Batryn, N. (2023). Computational Intelligence in Medicine. In: Babichev, S., Lytvynenko, V. (eds) Lecture Notes in Data Engineering, Computational Intelligence, and Decision Making. ISDMCI 2022. Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies, vol 149. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16203-9_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16203-9_28
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16202-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16203-9
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)