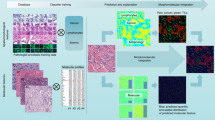
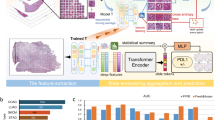
Abstract
Previous efforts to learn histology features that correlate with specific genetic/molecular traits resort to tile-level multi-instance learning (MIL) which relies on a fixed pretrained model for feature extraction and an instance-bag classifier. We argue that such a two-step approach is not optimal at capturing both fine-grained features at tile level and global features at slide level optimal to the task. We propose a self-interactive MIL that iteratively feedbacks training information between the fine-grained and global context features. We validate the proposed approach on 4 subtyping tasks: EMT status (ovarian), KRAS mutation (colon and lung), EGFR mutation (colon), and HER2 status (breast). Our approach yields an average improvement of \(7.05\%-8.34\%\) (in terms of AUC) over the baseline.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campanella, G., et al.: Clinical-grade computational pathology using weakly supervised deep learning on whole slide images. Nat. Med. 25(8), 1301–1309 (2019)
Ciga, O., Xu, T., Martel, A.L.: Self supervised contrastive learning for digital histopathology. Mach. Learn. Appl. 7, 100198 (2022)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 248–255 (2009)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2020)
Ganin, Y., et al.: Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 17(1), 2096–2300 (2016)
Hashimoto, N., et al.: Multi-scale domain-adversarial multiple-instance CNN for cancer subtype classification with unannotated histopathological images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3852–3861 (2020)
Hu, Z., et al.: The repertoire of serous ovarian cancer non-genetic heterogeneity revealed by single-cell sequencing of normal fallopian tube epithelial cells. Cancer Cell 37(2), 226–242 (2020)
Hu, Z., et al.: The oxford classic links epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition to immunosuppression in poor prognosis ovarian cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 27(5), 1570–1579 (2021)
Ilse, M., Tomczak, J., Welling, M.: Attention-based deep multiple instance learning. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 2127–2136. PMLR (2018)
Kalra, S., et al.: Pay attention with focus: a novel learning scheme for classification of whole slide images. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12908, pp. 350–359. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87237-3_34
Li, B., Li, Y., Eliceiri, K.W.: Dual-stream multiple instance learning network for whole slide image classification with self-supervised contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 14318–14328 (2021)
Li, H., et al.: DT-MIL: deformable transformer for multi-instance learning on histopathological image. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12908, pp. 206–216. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87237-3_20
Li, J., et al.: A multi-resolution model for histopathology image classification and localization with multiple instance learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 131, 104253 (2021)
Lu, M.Y., et al.: Ai-based pathology predicts origins for cancers of unknown primary. Nature 594(7861), 106–110 (2021)
Lu, M.Y., Williamson, D.F., Chen, T.Y., Chen, R.J., Barbieri, M., Mahmood, F.: Data-efficient and weakly supervised computational pathology on whole-slide images. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 5(6), 555–570 (2021)
Van der Maaten, L., Hinton, G.: Visualizing data using t-sne. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9(11) (2008)
Selvaraju, R.R., Cogswell, M., Das, A., Vedantam, R., Parikh, D., Batra, D.: Grad-cam: visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 618–626 (2017)
Shao, Z., et al.: Transmil: transformer based correlated multiple instance learning for whole slide image classification. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34 (2021)
Sirinukunwattana, K., et al.: Image-based consensus molecular subtype (imCMS) classification of colorectal cancer using deep learning. Gut 70(3), 544–554 (2021)
Tomczak, K., Czerwińska, P., Wiznerowicz, M.: The cancer genome atlas (TCGA): an immeasurable source of knowledge. Contemp. Oncol. 19(1A), A68 (2015)
Acknowledgements
We thank Stefano Malacrino and Nasullah Khalid Alham for providing technical support. Financial support: YU, CV and JR - National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Oxford Biomedical Research Centre; KS, CV, and JR - Innovate UK funded PathLAKE consortium; KG - Clinical Lectureship from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR, grant no. CL-2017-13-001); RW - EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Health Data Science (EP/S02428X/1) and Oxford CRUK Centre for Cancer Research. Computation used the Oxford Biomedical Research Computing (BMRC) facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hu, Y., Sirinukunwattana, K., Gaitskell, K., Wood, R., Verrill, C., Rittscher, J. (2022). Predicting Molecular Traits from Tissue Morphology Through Self-interactive Multi-instance Learning. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2022. MICCAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13432. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16434-7_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16434-7_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16433-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16434-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)