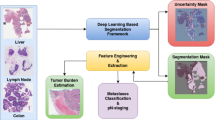
Abstract
Semantic segmentation of whole slide images (WSIs) helps pathologists identify lesions and cancerous nests. However, training fully supervised segmentation networks usually requires plenty of pixel-level annotations, which consume lots of time and human efforts. Coming from tissues of different patients with large amounts of pixels, WSIs exhibit various patterns, resulting in intra-class heterogeneity and inter-class homogeneity. Meanwhile, most existing methods for WSIs focus on extracting a certain type of features, neglecting the relations between different features and their joint effect on segmentation. Therefore, we propose a novel weakly supervised network based on tensor graphs (WSNTG) for WSI segmentation. Using only sparse point annotations, it efficiently segments WSIs by superpixel-wise classification and credible node reweighting. To deal with the variability of WSIs, the proposed network represents multiple hand-crafted features and hierarchical features yielded by a pretrained Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). Particularly, it learns over the semi-labeled tensor graphs constructed on the hierarchical features to exploit nonlinear data structures and associations. It gains robustness via the tensor-graph Laplacian of the hand-crafted features superimposed on the segmentation loss. We evaluated WSNTG on two WSI datasets, DigestPath2019 and SICAPV2. Results show that it outperforms many fully supervised and weakly supervised methods with minimal point annotations in WSI segmentation. The codes are published at https://github.com/zqh369/WSNTG.
This work was funded by the “Chenguang Program” supported by Shanghai Education Development Foundation and Shanghai Municipal Education Commission under Grant 18CG38.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng, R., Liu, X., Chen, J., Chen, D.Z., Gao, H., Wu, J.: A deep learning approach for colonoscopy pathology WSI analysis: accurate segmentation and classification. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 25(10), 3700–3708 (2020)
Feng, Y., Hafiane, A., Laurent, H.: A deep learning based multiscale approach to segment the areas of interest in whole slide images. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 90, 101923 (2021)
Ni, H., Liu, H., Wang, K., Wang, X., Zhou, X., Qian, Y.: WSI-Net: branch-based and hierarchy-aware network for segmentation and classification of breast histopathological whole-slide images. In: Suk, H.-I., Liu, M., Yan, P., Lian, C. (eds.) MLMI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11861, pp. 36–44. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32692-0_5
Wang, X., et al.: A hybrid network for automatic hepatocellular carcinoma segmentation in H&E-stained whole slide images. Med. Image Anal. 68, 101914 (2021)
Xu, G., et al.: CAMEL: a weakly supervised learning framework for histopathology image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 10682–10691 (2019)
Xu, Y., Zhu, J.-Y., Eric, I., Chang, C., Lai, M., Tu, Z.: Weakly supervised histopathology cancer image segmentation and classification. Med. Image Anal. 18, 591–604 (2014)
Lu, M.Y., Williamson, D.F., Chen, T.Y., Chen, R.J., Barbieri, M., Mahmood, F.: Data-efficient and weakly supervised computational pathology on whole-slide images. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 5(6), 555–570 (2021)
Zhang, J., et al.: Joint fully convolutional and graph convolutional networks for weakly-supervised segmentation of pathology images. Med. Image Anal. 73, 102183 (2021)
Qu, H., et al.: Weakly supervised deep nuclei segmentation using partial points annotation in histopathology images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(11), 3655–3666 (2020)
Tian, K., et al.: Weakly-supervised nucleus segmentation based on point annotations: a coarse-to-fine self-stimulated learning strategy. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12265, pp. 299–308. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59722-1_29
Chen, Z., et al.: Weakly supervised histopathology image segmentation with sparse point annotations. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 25(5), 1673–1685 (2021)
Li, S., Gao, Z., He, X.: Superpixel-guided iterative learning from noisy labels for medical image segmentation. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12901, pp. 525–535. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_50
Meng, Y., et al.: CNN-GCN aggregation enabled boundary regression for biomedical image segmentation. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12264, pp. 352–362. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59719-1_35
Wolterink, J.M., Leiner, T., Išgum, I.: Graph convolutional networks for coronary artery segmentation in cardiac CT angiography. In: Zhang, D., Zhou, L., Jie, B., Liu, M. (eds.) GLMI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11849, pp. 62–69. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-35817-4_8
Anklin, V., et al.: Learning whole-slide segmentation from inexact and incomplete labels using tissue graphs. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12902, pp. 636–646. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87196-3_59
Liu, X., You, X., Zhang, X., Wu, J., Lv, P.: Tensor graph convolutional networks for text classification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, no. 05, pp. 8409–8416 (2020)
Ioannidis, V.N., Marques, A.G., Giannakis, G.B.: Tensor graph convolutional networks for multi-relational and robust learning. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 68, 6535–6546 (2020)
Achanta, R., Shaji, A., Smith, K., Lucchi, A., Fua, P., Süsstrunk, S.: SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(11), 2274–2282 (2012)
Dong, N., Zhao, L., Wu, C.H., Chang, J.F.: Inception v3 based cervical cell classification combined with artificially extracted features. Appl. Soft Comput. 93, 106311 (2020)
Cheng, L., Su, Y., Ye, L., Yuan, P., Han, S.: Learning from large-scale noisy web data with ubiquitous reweighting for image classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(5), 1808–1814 (2021)
Jia, Z., Huang, X., Chang, E.I.C., Xu, Y.: Constrained deep weak supervision for histopathology image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 36(11), 2376–2388 (2017)
Kervadec, H., Dolz, J., Tang, M., Granger, E., Boykov, Y., Ben Ayed, I.: Constrained-CNN losses for weakly supervised segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 54, 88–99 (2019)
Shelhamer, E., Long, J., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39, 640–651 (2017)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Valanarasu, J.M.J., Oza, P., Hacihaliloglu, I., Patel, V.M.: Medical transformer: gated axial-attention for medical image segmentation. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12901, pp. 36–46. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_4
Samanta, P., Singhal, N.: YAMU: yet another modified U-Net architecture for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 5th Conference on Medical Imaging with Deep Learning (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, Q., Chen, Z. (2022). Weakly Supervised Segmentation by Tensor Graph Learning for Whole Slide Images. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2022. MICCAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13432. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16434-7_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16434-7_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16433-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16434-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)