Abstract
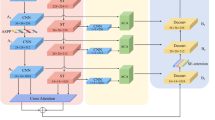
Over the past few years, convolution neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs) have been two dominant architectures in medical image segmentation. Although CNNs can efficiently capture local representations, they experience difficulty establishing long-distance dependencies. Comparably, ViTs achieve impressive success owing to their powerful global contexts modeling capabilities, but they may not generalize well on insufficient datasets due to the lack of inductive biases inherent to CNNs. To inherit the merits of these two different design paradigms while avoiding their respective limitations, we propose a concurrent structure termed ConTrans, which can couple detailed localization information with global contexts to the maximum extent. ConTrans consists of two parallel encoders, i.e., a Swin Transformer encoder and a CNN encoder. Specifically, the CNN encoder is progressively stacked by the novel Depthwise Attention Block (DAB), with the aim to provide the precise local features we need. Furthermore, a well-designed Spatial-Reduction-Cross-Attention (SRCA) module is embedded in the decoder to form a comprehensive fusion of these two distinct feature representations and eliminate the semantic divergence between them. This allows to obtain accurate semantic information and ensure the up-sampling features with semantic consistency in a hierarchical manner. Extensive experiments across four typical tasks show that ConTrans significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on ten famous benchmarks.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
COVID-19 CT segmentation dataset. https://medicalsegmentation.com/covid19/. Accessed 11 Apr 2014
Bernal, J., Sánchez, F.J., Fernández-Esparrach, G., Gil, D., Rodríguez, C., Vilariño, F.: WM-DOVA maps for accurate polyp highlighting in colonoscopy: Validation vs. saliency maps from physicians. Comput. Medi. Imaging Graph. 43, 99–111 (2015)
Caicedo, J.C., et al.: Nucleus segmentation across imaging experiments: the 2018 data science bowl. Nat. MethodsD 16(12), 1247–1253 (2019)
Cao, H., et al.: Swin-UNet: UNet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.05537 (2021)
Chen, J., et al.: Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.04306 (2021)
Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.05587 (2017)
Codella, N., et al.: Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection 2018: a challenge hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (ISIC). arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.03368 (2019)
Codella, N.C., et al.: Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: a challenge at the 2017 international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI), hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (ISIC). In: 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), pp. 168–172. IEEE (2018)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020)
Fan, D.P., et al.: PraNet: parallel reverse attention network for polyp segmentation. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12266, pp. 263–273. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_26
Fan, D.P., Zhou, T., Ji, G.P., Zhou, Y., Chen, G., Fu, H., Shen, J., Shao, L.: Inf-Net: automatic covid-19 lung infection segmentation from CT images. IEEE Trans. Med, Imaging 39(8), 2626–2637 (2020)
Gamper, J., Alemi Koohbanani, N., Benet, K., Khuram, A., Rajpoot, N.: PanNuke: an open pan-cancer histology dataset for nuclei instance segmentation and classification. In: Reyes-Aldasoro, C.C., Janowczyk, A., Veta, M., Bankhead, P., Sirinukunwattana, K. (eds.) ECDP 2019. LNCS, vol. 11435, pp. 11–19. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23937-4_2
Gu, Z., et al.: Ce-Net: context encoder network for 2D medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(10), 2281–2292 (2019)
Jha, D., et al.: Kvasir-SEG: a segmented polyp dataset. In: Ro, Y.M., et al. (eds.) MMM 2020. LNCS, vol. 11962, pp. 451–462. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-37734-2_37
Ji, Y., et al.: Multi-compound transformer for accurate biomedical image segmentation. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12901, pp. 326–336. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_31
Liu, Z., et al.: Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.14030 (2021)
Oktay, O., et al.: Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999 (2018)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Silva, J., Histace, A., Romain, O., Dray, X., Granado, B.: Toward embedded detection of polyps in WCE images for early diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 9(2), 283–293 (2014)
Sirinukunwattana, K., et al.: Gland segmentation in colon histology images: the glas challenge contest. Med. Image Anal. 35, 489–502 (2017)
Tschandl, P., Rosendahl, C., Kittler, H.: The ham10000 dataset, a large collection of multi-source dermatoscopic images of common pigmented skin lesions. Sci. Data 5(1), 1–9 (2018)
Valanarasu, J.M.J., Oza, P., Hacihaliloglu, I., Patel, V.M.: Medical transformer: gated axial-attention for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.10662 (2021)
Valanarasu, J.M.J., Sindagi, V.A., Hacihaliloglu, I., Patel, V.M.: KiU-Net: towards accurate segmentation of biomedical images using over-complete representations. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12264, pp. 363–373. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59719-1_36
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.03762 (2017)
Vázquez, D.: A benchmark for endoluminal scene segmentation of colonoscopy imageA benchmark for endoluminal scene segmentation of colonoscopy images. J. Healthc Eng. 2017 (2017)
Wang, W., et al.: Pyramid vision transformer: a versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 568–578 (2021)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: CBAM: convolutional block attention module. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11211, pp. 3–19. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1
Xie, E., Wang, W., Yu, Z., Anandkumar, A., Alvarez, J.M., Luo, P.: SegFormer: simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Liu, H., Hu, Q.: TransFuse: fusing transformers and cnns for medical image segmentation. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12901, pp. 14–24. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_2
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2881–2890 (2017)
Zheng, S., et al.: Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.15840 (2020)
Zhou, Z., Rahman Siddiquee, M.M., Tajbakhsh, N., Liang, J.: UNet++: a nested U-Net architecture for medical image segmentation. In: Stoyanov, D., et al. (eds.) DLMIA/ML-CDS -2018. LNCS, vol. 11045, pp. 3–11. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00889-5_1
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the NSFC fund (62176077, 61906162), in part by the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation under Grant 2019Bl515120055, in part by the Shenzhen Key Technical Project under Grant 2020N046, in part by the Shenzhen Fundamental Research Fund under Grant JCYJ20210324132210025, in part by the Medical Biometrics Perception and Analysis Engineering Laboratory, Shenzhen, China, in part by Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (RCBS20200714114910193), and in part by Education Center of Experiments and Innovations at Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lin, A., Xu, J., Li, J., Lu, G. (2022). ConTrans: Improving Transformer with Convolutional Attention for Medical Image Segmentation. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2022. MICCAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13435. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16443-9_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16443-9_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16442-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16443-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)