Abstract
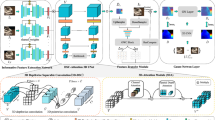
The self-attention mechanism, successfully employed with the transformer structure is shown promise in many computer vision tasks including image recognition, and object detection. Despite the surge, the use of the transformer for the problem of stereo matching remains relatively unexplored. In this paper, we comprehensively investigate the use of the transformer for the problem of stereo matching, especially for laparoscopic videos, and propose a new hybrid deep stereo matching framework (HybridStereoNet) that combines the best of the CNN and the transformer in a unified design. To be specific, we investigate several ways to introduce transformers to volumetric stereo matching pipelines by analyzing the loss landscape of the designs and in-domain/cross-domain accuracy. Our analysis suggests that employing transformers for feature representation learning, while using CNNs for cost aggregation will lead to faster convergence, higher accuracy and better generalization than other options. Our extensive experiments on Sceneflow, SCARED2019 and dVPN datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our HybridStereoNet.
X. Cheng and Y. Zhong—Equal contribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan, M., et al.: Stereo correspondence and reconstruction of endoscopic data challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.01133 (2021)
Cartucho, J., Tukra, S., Li, Y., S. Elson, D., Giannarou, S.: Visionblender: a tool to efficiently generate computer vision datasets for robotic surgery. CMBBE Imaging Vis. 9(4), 331–338 (2021)
Chaudhari, P., et al.: Entropy-SGD: biasing gradient descent into wide valleys. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2019(12), 124018 (2019)
Cheng, X., Zhong, Y., Dai, Y., Ji, P., Li, H.: Noise-aware unsupervised deep lidar-stereo fusion. In: CVPR (2019)
Cheng, X., et al.: Hierarchical neural architecture search for deep stereo matching. In: NeurIPS, vol. 33 (2020)
Chong, N., et al.: Virtual reality application for laparoscope in clinical surgery based on siamese network and census transformation. In: Su, R., Zhang, Y.-D., Liu, H. (eds.) MICAD 2021. LNEE, vol. 784, pp. 59–70. Springer, Singapore (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-3880-0_7
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020)
Geiger, A., Roser, M., Urtasun, R.: Efficient large-scale stereo matching. In: Kimmel, R., Klette, R., Sugimoto, A. (eds.) ACCV 2010. LNCS, vol. 6492, pp. 25–38. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-19315-6_3
Hore, A., Ziou, D.: Image quality metrics: Psnr vs. ssim. In: 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 2366–2369. IEEE (2010)
Huang, B., et al.: Self-supervised generative adversarial network for depth estimation in laparoscopic images. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12904, pp. 227–237. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87202-1_22
Keskar, N.S., Mudigere, D., Nocedal, J., Smelyanskiy, M., Tang, P.T.P.: On large-batch training for deep learning: Generalization gap and sharp minima. ICLR (2017)
Li, H., Xu, Z., Taylor, G., Studer, C., Goldstein, T.: Visualizing the loss landscape of neural nets. NeurIPS 31 (2018)
Li, Z., et al.: Revisiting stereo depth estimation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. In: ICCV, pp. 6197–6206, October 2021
Lipson, L., Teed, Z., Deng, J.: RAFT-Stereo: Multilevel Recurrent Field Transforms for Stereo Matching. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.07547 (2021)
Liu, Z., et al.: Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: ICCV, pp. 10012–10022 (2021)
Liu, Z., et al.: Video swin transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.13230 (2021)
Long, Y., et al.: E-DSSR: efficient dynamic surgical scene reconstruction with transformer-based stereoscopic depth perception. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12904, pp. 415–425. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87202-1_40
Mayer, N., et al.: A large dataset to train convolutional networks for disparity, optical flow, and scene flow estimation. In: CVPR, pp. 4040–4048 (2016)
Menze, M., Geiger, A.: Object scene flow for autonomous vehicles. In: CVPR (2015)
Nicolau, S., Soler, L., Mutter, D., Marescaux, J.: Augmented reality in laparoscopic surgical oncology. Surg. Oncol. 20(3), 189–201 (2011)
Overley, S.C., Cho, S.K., Mehta, A.I., Arnold, P.M.: Navigation and robotics in spinal surgery: where are we now? Neurosurgery 80(3S), S86–S99 (2017)
Qin, Z., et al.: Cosformer: Rethinking softmax in attention. In: ICLR (2022)
Scharstein, D., et al.: High-resolution stereo datasets with subpixel-accurate ground truth. In: Jiang, X., Hornegger, J., Koch, R. (eds.) GCPR 2014. LNCS, vol. 8753, pp. 31–42. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11752-2_3
Schölkopf, B., Smola, A., Müller, K.R.: Nonlinear component analysis as a kernel eigenvalue problem. Neural Comput. 10(5), 1299–1319 (1998)
Sun, W., Qin, Z., Deng, H., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, K., Barnes, N., Birchfield, S., Kong, L., Zhong, Y.: Vicinity vision transformer. In: arxiv. p. 2206.10552 (2022)
Wang, J., et al.: Deep two-view structure-from-motion revisited. In: CVPR, pp. 8953–8962, June 2021
Wang, J., Zhong, Y., Dai, Y., Zhang, K., Ji, P., Li, H.: Displacement-invariant matching cost learning for accurate optical flow estimation. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Wang, W., et al.: Pyramid vision transformer: a versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In: ICCV, pp. 568–578 (2021)
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. TIP 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Yamaguchi, K., McAllester, D., Urtasun, R.: Efficient joint segmentation, occlusion labeling, stereo and flow estimation. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8693, pp. 756–771. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_49
Ye, M., Johns, E., Handa, A., Zhang, L., Pratt, P., Yang, G.Z.: Self-supervised siamese learning on stereo image pairs for depth estimation in robotic surgery. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.08260 (2017)
Zhong, Y., Dai, Y., Li, H.: Self-supervised learning for stereo matching with self-improving ability (2017)
Zhong, Y., Dai, Y., Li, H.: 3d geometry-aware semantic labeling of outdoor street scenes. In: ICPR (2018)
Zhong, Y., Dai, Y., Li, H.: Stereo computation for a single mixture image. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11213, pp. 441–456. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01240-3_27
Zhong, Y., Ji, P., Wang, J., Dai, Y., Li, H.: Unsupervised deep epipolar flow for stationary or dynamic scenes. In: CVPR (2019)
Zhong, Y., Li, H., Dai, Y.: Open-world stereo video matching with deep RNN. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11206, pp. 104–119. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01216-8_7
Zhong, Y., et al.: Displacement-invariant cost computation for stereo matching. In: IJCV, March 2022
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cheng, X., Zhong, Y., Harandi, M., Drummond, T., Wang, Z., Ge, Z. (2022). Deep Laparoscopic Stereo Matching with Transformers. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2022. MICCAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13437. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16449-1_44
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16449-1_44
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16448-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16449-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)