Abstract
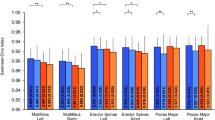
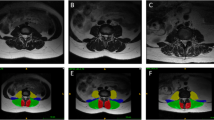
Recent studies have associated morphological and composition changes in paraspinal muscles with low back pain (LBP), which is the most common, but poorly understood musculoskeletal disorder in adults. Accurate paraspinal muscle segmentation from MRI is crucial to enable new image-based biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of LBP. Manual segmentation is laborious and time-consuming. In addition, high individual anatomical variations also pose challenges, resulting in inconsistent segmentation across different raters. While automatic segmentation algorithms can help mitigate the issues, techniques that predict and visualize inter-rater segmentation variability will be highly instrumental to help interpret reliability of automatic segmentation, but they are rarely attempted. In this paper, we propose a novel multi-task TransUNet model to accurately segment paraspinal muscles while predicting inter-rater labeling variability visualized using a variance map of three raters’ annotations. Our technique is validated on MRIs of paraspinal muscles at four different disc levels from 118 LBP patients. Benefiting from the transformer mechanism and convolution neural networks, our algorithm is shown to perform better or similar to the state-of-the-art methods and a newly proposed multi-task U-Net model while predicting and visualizing multi-rater annotation variance per muscle group in an intuitive manner.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, J., et al.: Transunet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.04306 (2021)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020)
Durasov, N., Bagautdinov, T., Baque, P., Fua, P.: Masksembles for uncertainty estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13539–13548 (2021)
Fortin, M., Lazáry, A., Varga, P.P., Battié, M.C.: Association between paraspinal muscle morphology clinical symptoms and functional status in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur. Spine J. 26, 2543–2551 (2017)
Huang, J., Shen, H., Chen, B., Wang, Y., Li, S.: Segmentation of paraspinal muscles at varied lumbar spinal levels by explicit saliency-aware learning. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12266, pp. 652–661. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_63
Kokkinos, I.: Ubernet: training a universal convolutional neural network for low-, mid-, and high-level vision using diverse datasets and limited memory. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.02132 (2016)
Ji, W., et al.: Learning calibrated medical image segmentation via multi-rater agreement modeling. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 12336–12346 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01216
Lemay, A., Gros, C., Cohen-Adad, J.: Label fusion and training methods for reliable representation of inter-rater uncertainty. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.07550 (2022)
Li, H., Luo, H., Liu, Y.: Paraspinal muscle segmentation based on deep neural network. Sensors 19, 2650 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122650
Mirikharaji, Z., Abhishek, K., Izadi, S., Hamarneh, G.: D-LEMA: deep learning ensembles from multiple annotations-application to skin lesion segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1837–1846 (2021)
Mukhoti, J., van Amersfoort, J., Torr, P.H., Gal, Y.: Deep deterministic uncertainty for semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.00079 (2021)
Oktay, O., et al.: Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999 (2018)
Pohl, K.M., et al.: Using the logarithm of odds to define a vector space on probabilistic atlases. Med. Image Anal. 11(5), 465–77 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2007.06.003
Schlemper, J., et al.: Attention gated networks: learning to leverage salient regions in medical images. Med. Image Anal. 53, 197–207 (2019)
Tustison, N.J., Avants, B.B., Cook, P.A., et al.: N4ITK: improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 29(6), 1310 (2010)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 5998–6008 (2017)
Ward, S.R., Kim, C.W., Eng, C.M., Gottschalk, L.J., Tomiya, A., Garfin, S.R.: Architectural analysis and intraoperative measurements demonstrate the unique design of the multifidus muscle for lumbar spine stability. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 91, 176–185 (2009)
Xia, W., et al.: Automatic paraspinal muscle segmentation in patients with lumbar pathology using deep convolutional neural network. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11765, pp. 318–325. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32245-8_36
Xiao, Y., Fortin, M., Ahn, J., et al.: Statistical morphological analysis reveals characteristic paraspinal muscle asymmetry in unilateral lumbar disc herniation. Sci. Rep. 11, 15576 (2021)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and NVIDIA for donation of the GPU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Roshanzamir, P. et al. (2022). Joint Paraspinal Muscle Segmentation and Inter-rater Labeling Variability Prediction with Multi-task TransUNet. In: Sudre, C.H., et al. Uncertainty for Safe Utilization of Machine Learning in Medical Imaging. UNSURE 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13563. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16749-2_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16749-2_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16748-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16749-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)