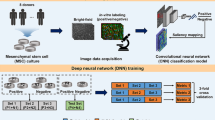
Abstract
iPSC-derived mesenchymal stem cells (iMSCs) can differentiate into a wide range of mesodermal cell types for tissue repair, and play an important role in cell therapy in regenerative medicine. The therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) is largely affected by their differentiation ability and cell activity, and the therapeutic effect of senescent cells is often worse than that of young cells. Biologically senescent detection of iMSCs can only be performed by vital staining, which is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and financial-intensive. To solve this problem, we apply a deep learning method to the senescence identification research of iMSCs to achieve the purpose of rapid and accurate detection without vital staining. We propose a Swin Transformer-based Faster R-CNN network for senescence identification of MSCs in bright-field images. In particular, we exploit the self-attention mechanism of the Swin Transformer to extract features of dense cell regions in the picture, enabling the network to learn the strong discriminative properties of different classes of cells. In addition, we perform multi-scale fusion on the features extracted by the backbone network to address the problem of inconsistent cell sizes in the data. Experiments on self-collected datasets show that our method achieves good performance on each generation of datasets and achieves the highest detection precision (mAP) of 0.816 on our collected mixed datasets.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horwitz, E., et al.: Clarification of the nomenclature for MSC: the international society for cellular therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 7(5), 393–395 (2005)
Piñeiro-Ramil, M., et al.: Usefulness of mesenchymal cell lines for bone and cartilage regeneration research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20(24), 6286 (2019)
Jiang, Y., et al.: Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature 418(6893), 41–49 (2002)
Zhao, C., Ikeya, M.: Generation and applications of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 9601623 (2018)
Wagner, W., et al.: Replicative senescence of mesenchymal stem cells: a continuous and organized process. PLoS ONE 3(5), e2213 (2008)
Ho, A.D., Wagner, W., Mahlknecht, U.: Stem cells and ageing: the potential of stem cells to overcome age-related deteriorations of the body in regenerative medicine. EMBO Rep. 6(S1), S35–S38 (2005)
Evangelou, K., et al.: Robust, universal biomarker assay to detect senescent cells in biological specimens. Aging Cell 16(1), 192–197 (2017)
Lin, M., et al.: Label-free light-sheet microfluidic cytometry for the automatic identification of senescent cells. Biomed. Opt. Express 9(4), 1692–1703 (2018)
Zhang, J., Hu, H., Chen, S., Huang, Y., Guan, Q.: Cancer cells detection in phase-contrast microscopy images based on faster R-CNN. In: 2016 9th international symposium on computational intelligence and design (ISCID), vol. 1, pp. 363–367. IEEE, Hangzhou, China (2016)
Yi, J., Wu, P., Hoeppner, D.J., Metaxas, D.: Fast neural cell detection using light-weight SSD neural network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 108–112. Hawaii, USA (2017)
Liu, W., et al.: SSD: single shot multiBox detector. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNIP, vol. 9905, pp. 21–37. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2
Kusumoto, D., et al.: Anti-senescent drug screening by deep learning-based morphology senescence scoring. Circulation 142(Suppl_3), A13576–A13576 (2020)
Kusumoto, D., et al.: Anti-senescent drug screening by deep learning-based morphology senescence scoring. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 257 (2021)
Sun, Y., Huang, X., Zhou, H., Zhang, Q.: SRPN: similarity-based region proposal networks for nuclei and cells detection in histology images. Med. Image Anal. 72, 102142 (2021)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 28 (2015)
Liu, Z., et al.: Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 10012–10022. Montreal, Canada (2021)
Lin, T.-Y., et al.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2117–2125. Hawaii, USA (2017)
Cai, Z., Vasconcelos, N.: Cascade R-CNN: delving into high quality object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6154–6162. Salt Lake City, USA (2018)
Feng, C., Zhong, Y., Gao, Y., Scott, M.R., Huang, W.: Tood: task-aligned one-stage object detection. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE Computer Society, pp. 3490–3499. Montreal, Canada (2021)
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: Yolov3: An incremental improvement, arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.02767 (2018)
Long, X., et al.: PP-YOLO: An effective and efficient implementation of object detector, arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.12099 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xiao, C., Li, M., He, L., Song, X., Wang, T., Lei, B. (2022). Swin Faster R-CNN for Senescence Detection of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Bright-Field Images. In: Huo, Y., Millis, B.A., Zhou, Y., Wang, X., Harrison, A.P., Xu, Z. (eds) Medical Optical Imaging and Virtual Microscopy Image Analysis. MOVI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13578. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16961-8_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16961-8_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16960-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16961-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)