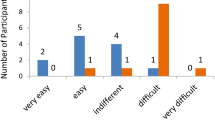
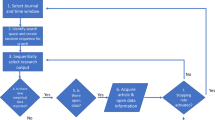
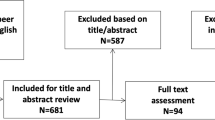
Abstract
Existing approaches for evaluating data quality were established for settings where user requirements regarding data use could be explicitly gathered. Currently, however, users are often faced with new, unfamiliar, and repurposed datasets where they have not been involved in the data collection and creation processes. Furthermore, there is evidence that despite various standardisation initiatives, supporting information or metadata for such datasets is provided in a variety of ways or even lacking altogether. Yet, users need to evaluate the quality of such data to determine if it is suitable for their intended purposes. In this regard, there is limited understanding of the role of metadata in evaluating the quality of repurposed datasets. Thus, in this paper, we aim to investigate how users engage with metadata during data repurposing tasks. In particular, we gather multi-modal user behaviour data through a lab experiment, using eye-tracking techniques and cued-retrospective think-aloud analysis to explore when, how and why users use metadata in such tasks. The results of our study shed light on the critical role metadata plays in evaluating repurposed data, highlight the existence of relationships between data quality error type and metadata, and identify a number of metadata usage patterns relative to the task. This bears implications for the design of systems or tools related to data quality discovery and evaluation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
For more specifications of the eye tracker, please visit: https://www.tobiipro.com/product-listing/tobii-pro-tx300/, last accessed 2022/04/19.
- 2.
A fixation is the time span when the eye remains still at a specific position of the stimulus.
- 3.
https://www.ataccama.com/platform/data-quality, last accessed 2022/04/19.
- 4.
https://data.gov/, last accessed 2022/04/19.
- 5.
https://rapidminer.com, last accessed 2022/04/19.
- 6.
- 7.
We extracted the subjective insights from the transcripts using Nvivo 12, following a methodology to develop recurring aspects and group them into categories [32].
- 8.
1). How do you define missing data in the data quality context? 2). Can you please give one example of missing data? 3). Can you please mention some data quality dimensions/attributes? 4). Can you please explain what is meant by data quality dimensions/attributes?
References
Fisher, T.: The Data Asset: How Smart Companies Govern their Data for Business Success. John Wiley & Sons (2009)
Redman, T.C.: If your data is bad, your machine learning tools are useless. Harvard Business Review 2, (2018)
Jaya, I., Sidi, F., Affendey, L., Jabar, M., Ishak, I.: Systematic review of data quality research. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 97, 3043 (2019)
Krishnan, S., Haas, D., Franklin, M.J., Wu, E.: Towards reliable interactive data cleaning: A user survey and recommendations. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Human-In-the-Loop Data Analytics, pp. 1–5 (2016)
Borek, A., Woodall, P., Oberhofer, M., Parlikad, A.K.: A classification of data quality assessment methods. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Information Quality Presented at the ICIQ 2011, January 1 (2011)
Belkin, R., Patil, D.: Everything we wish we’d known about building data products (2018)
Zhang, R., Indulska, M., Sadiq, S.: Discovering data quality problems. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 61(5), 575–593 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12599-019-00608-0
Stonebraker, M., et al.: Data curation at scale: the data tamer system. In: CIDR. Citeseer (2013)
Cichy, C., Rass, S.: An overview of data quality frameworks. IEEE Access 7, 24634–24648 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2899751
Lee, Y.W., Pipino, L., Funk, J.D., Wang, R.Y.: Journey to Data Quality. MIT Press, Cambridge (2006)
Fisher, C.W., Chengalur-Smith, I., Ballou, D.P.: The impact of experience and time on the use of data quality information in decision making. Inf. Syst. Res. 14, 170–188 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.14.2.170.16017
Shankaranarayanan, G., Even, A., Watts, S.: The role of process metadata and data quality perceptions in decision making: an empirical framework and investigation. J. Inf. Technol. Manage. 17, 50–67 (2006)
Van Gog, T., Paas, F., Van Merriënboer, J.J., Witte, P.: Uncovering the problem-solving process: cued retrospective reporting versus concurrent and retrospective reporting. J. Exp. Psychol. Appl. 11, 237 (2005)
Sadiq, S., Indulska, M.: Open data: quality over quantity. Int. J. Inf. Manage. 37, 150–154 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2017.01.003
Jayawardene, V., Sadiq, S., Indulska, M.: An analysis of data quality dimensions (2015)
Wang, R.Y.: A product perspective on total data quality management. Commun. ACM 41, 58–65 (1998)
Sebastian-Coleman, L.: Measuring data quality for ongoing improvement: a data quality assessment framework. Newnes (2012)
Batini, C., Cappiello, C., Francalanci, C., Maurino, A.: Methodologies for data quality assessment and improvement. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR). 41, 1–52 (2009)
Abedjan, Z., Golab, L., Naumann, F.: Profiling relational data: a survey. VLDB J. 24(4), 557–581 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00778-015-0389-y
Aljumaili, M., Karim, R., Tretten, P.: Metadata-based data quality assessment. VINE J. Inf. Knowl. Manage. Syst. 46, 232–250 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1108/VJIKMS-11-2015-0059
Méndez, E., van Hooland, S.: Metadata typology and metadata uses. In: Handbook of Metadata, Semantics and Ontologies, pp. 9–39. World Scientific (2014)
Clarke, R.: Big data, big risks. Inf. Syst. J. 26, 77–90 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/isj.12088
Zhou, H., Demartini, G., Indulska, M., Sadiq, S.: Evaluating the Quality of Repurposed Data–The Role of Metadata. (2021)
Bera, P., Soffer, P., Parsons, J.: Using eye tracking to expose cognitive processes in understanding conceptual models. MIS Q. 43, 1105–1126 (2019)
Chen, F., Zhou, J., Wang, Y., Yu, K., Arshad, S.Z., Khawaji, A., Conway, D.: Robust Multimodal Cognitive Load Measurement. Springer (2016) https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31700-7
Abbad Andaloussi, A., Zerbato, F., Burattin, A., Slaats, T., Hildebrandt, T.T., Weber, B.: Exploring how users engage with hybrid process artifacts based on declarative process models: a behavioral analysis based on eye-tracking and think-aloud. Softw. Syst. Model. 20(5), 1437–1464 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10270-020-00811-8
Hart, S.G., Staveland, L.E.: Development of NASA-TLX (task load index): results of empirical and theoretical research. Adv. Psychol. 52, 139–183 (1988)
Han, L., Chen, T., Demartini, G., Indulska, M., Sadiq, S.: On understanding data worker interaction behaviors. In: Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 269–278. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA (2020)
Visengeriyeva, L., Abedjan, Z.: Anatomy of metadata for data curation. J. Data Inf. Qual. (JDIQ). 12, 1–30 (2020)
Black, J.L., Macinko, J., Dixon, L.B., Fryer, G.E., Jr.: Neighborhoods and obesity in New York City. Health Place 16, 489–499 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthplace.2009.12.007
Scannapieco, M., Catarci, T.: Data quality under a computer science perspective. J. ACM 2 (2002)
Charmaz, K.: Constructing Grounded Theory. Sage (2014)
Kendall, M.G.: A new measure of rank correlation. Biometrika 30, 81–93 (1938)
Ray, S., Turi, R.H.: Determination of number of clusters in k-means clustering and application in colour image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Advances in Pattern Recognition and Digital Techniques, pp. 137–143. Citeseer (1999)
Syakur, M.A., Khotimah, B.K., Rochman, E.M.S., Satoto, B.D.: Integration k-means clustering method and elbow method for identification of the best customer profile cluster. In: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, p. 012017. IOP Publishing (2018)
Moges, H.-T., Vlasselaer, V.V., Lemahieu, W., Baesens, B.: Determining the use of data quality metadata (DQM) for decision making purposes and its impact on decision outcomes — An exploratory study. Decis. Support Syst. 83, 32–46 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2015.12.006
Guo, A., Liu, X., Sun, T.: Research on key problems of data quality in large industrial data environment. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Robotics, Control and Automation - ICRCA 2018, pp. 245–248. ACM Press, Chengdu, China (2018)
Miles, M.B., Huberman, A.M.: Qualitative Data Analysis: An Expanded Sourcebook. Sage (1994)
Gartner, R.: What metadata is and why it matters. In: Metadata, pp. 1–13. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40893-4_1
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Australian Research Council through ARC Discovery Grant DP190102141.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhou, H., Han, L., Dermatini, G., Indulska, M., Sadiq, S. (2022). A Behavioural Analysis of Metadata Use in Evaluating the Quality of Repurposed Data. In: Ralyté, J., Chakravarthy, S., Mohania, M., Jeusfeld, M.A., Karlapalem, K. (eds) Conceptual Modeling. ER 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13607. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17995-2_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17995-2_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-17994-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-17995-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)