Abstract
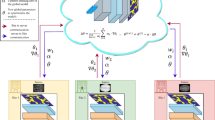
Federated learning aims at improving data privacy by training local models on distributed nodes and at integrating information on a central node, without data sharing. However, this calls for effective integration methods that are currently missing as existing strategies, e.g., averaging model gradients, are unable to deal with data multimodality due to different distributions at multiple nodes. In this work, we tackle this problem by having multiple nodes that share a synthetic version of their own data, built in a way to hide patient-specific visual cues, with a central node that is responsible for training a deep model for medical image classification. Synthetic data are generated through an aggregation strategy consisting in: 1) learning the distribution of original data via a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN); 2) projecting private data samples in the GAN latent space; 3) clustering the projected samples and generating synthetic images by interpolating the cluster centroids, thus reducing the possibility of collision with latent vectors corresponding to real samples and a consequent leak of sensitive information. The proposed approach is tested over two X-ray datasets for Tuberculosis classification to simulate a realistic scenario with two different nodes and non-i.i.d. data. Experimental results show that our approach yields performance comparable to, or even outperforming, training on the full joint dataset. We also show quantitatively and qualitatively that images synthesized with our approach are significantly different from original images, thus limiting the possibility to recover original data through attacks.
M. Pennisi and F. Proietto Salanitri—These authors contributed equally to this work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
This dataset was released by National Library of Medicine, National Institute Of health, Bethesda, USA.
References
Abadi, M., et al.: Deep learning with differential privacy. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, pp. 308–318 (2016)
Candemir, S., et al.: Lung segmentation in chest radiographs using anatomical atlases with nonrigid registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33(2), 577–590 (2013)
Chen, D., Orekondy, T., Fritz, M.: GS-WGAN: a gradient-sanitized approach for learning differentially private generators. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 12673–12684 (2020)
Dayan, I., et al.: Federated learning for predicting clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 27(10), 1735–1743 (2021)
Feki, I., Ammar, S., Kessentini, Y., Muhammad, K.: Federated learning for COVID-19 screening from chest x-ray images. Appl. Soft Comput. 106, 107330 (2021)
Geiping, J., Bauermeister, H., Dröge, H., Moeller, M.: Inverting gradients-how easy is it to break privacy in federated learning? Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 16937–16947 (2020)
Goodfellow, I., et al.: Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 27 (2014)
Guo, S., Zhang, T., Xu, G., Yu, H., Xiang, T., Liu, Y.: Topology-aware differential privacy for decentralized image classification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. (2021)
Jaeger, S., Candemir, S., Antani, S., Wáng, Y.X.J., Lu, P.X., Thoma, G.: Two public chest x-ray datasets for computer-aided screening of pulmonary diseases. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 4(6), 475 (2014)
Jaeger, S., et al.: Automatic tuberculosis screening using chest radiographs. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33(2), 233–245 (2013)
Karras, T., Aittala, M., Hellsten, J., Laine, S., Lehtinen, J., Aila, T.: Training generative adversarial networks with limited data. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 12104–12114 (2020)
Karras, T., Laine, S., Aittala, M., Hellsten, J., Lehtinen, J., Aila, T.: Analyzing and improving the image quality of StyleGAN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8110–8119 (2020)
Lecuyer, M., Atlidakis, V., Geambasu, R., Hsu, D., Jana, S.: Certified robustness to adversarial examples with differential privacy. In: 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), pp. 656–672. IEEE (2019)
Li, T., Sahu, A.K., Zaheer, M., Sanjabi, M., Talwalkar, A., Smith, V.: Federated optimization in heterogeneous networks. Proc. Mach. Learn. Syst. 2, 429–450 (2020)
Li, W., et al.: Privacy-preserving federated brain tumour segmentation. In: Suk, H.-I., Liu, M., Yan, P., Lian, C. (eds.) MLMI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11861, pp. 133–141. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32692-0_16
McMahan, B., Moore, E., Ramage, D., Hampson, S., Arcas, B.A.: Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data. In: Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pp. 1273–1282. PMLR (2017)
Ng, A., Jordan, M., Weiss, Y.: On spectral clustering: analysis and an algorithm. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 14 (2001)
Pang, J., Huang, Y., Xie, Z., Li, J., Cai, Z.: Collaborative city digital twin for the COVID-19 pandemic: a federated learning solution. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 26(5), 759–771 (2021)
Rajotte, J.F., et al.: Reducing bias and increasing utility by federated generative modeling of medical images using a centralized adversary. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Information Technology for Social Good, pp. 79–84 (2021)
Roy, A.G., Siddiqui, S., Pölsterl, S., Navab, N., Wachinger, C.: Braintorrent: a peer-to-peer environment for decentralized federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.06731 (2019)
Sheller, M.J., Reina, G.A., Edwards, B., Martin, J., Bakas, S.: Multi-institutional deep learning modeling without sharing patient data: a feasibility study on brain tumor segmentation. In: Crimi, A., Bakas, S., Kuijf, H., Keyvan, F., Reyes, M., van Walsum, T. (eds.) BrainLes 2018. LNCS, vol. 11383, pp. 92–104. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11723-8_9
Song, J., Ye, J.C.: Federated CycleGAN for privacy-preserving image-to-image translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.09246 (2021)
Wang, H., Yurochkin, M., Sun, Y., Papailiopoulos, D., Khazaeni, Y.: Federated learning with matched averaging. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.06440 (2020)
Wang, Z., Song, M., Zhang, Z., Song, Y., Wang, Q., Qi, H.: Beyond inferring class representatives: user-level privacy leakage from federated learning. In: IEEE INFOCOM 2019-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, pp. 2512–2520. IEEE (2019)
Xie, L., Lin, K., Wang, S., Wang, F., Zhou, J.: Differentially private generative adversarial network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.06739 (2018)
Yang, Q., Liu, Y., Chen, T., Tong, Y.: Federated machine learning: concept and applications. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 10(2), 1–19 (2019)
Zech, J.R., Badgeley, M.A., Liu, M., Costa, A.B., Titano, J.J., Oermann, E.K.: Variable generalization performance of a deep learning model to detect pneumonia in chest radiographs: a cross-sectional study. PLoS Med. 15(11), e1002683 (2018)
Zhang, L., Shen, B., Barnawi, A., Xi, S., Kumar, N., Wu, Y.: FedDPGAN: federated differentially private generative adversarial networks framework for the detection of COVID-19 pneumonia. Inf. Syst. Front. 23(6), 1403–1415 (2021)
Zhang, R., Isola, P., Efros, A.A., Shechtman, E., Wang, O.: The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 586–595 (2018)
Zhao, B., Mopuri, K.R., Bilen, H.: iDLG: improved deep leakage from gradients. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.02610 (2020)
Zhu, L., Liu, Z., Han, S.: Deep leakage from gradients. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the following grants: 1) Rehastart funded by PO FESR 2014-2020 Sicilia, Azione 1.1.5; project number 08ME6201000222, CUP: G79J18000610007); 2) the “Adaptive Brain-Derived Artificial Intelligence Methods for Event Detection” - BrAIn funded by the “Programma per la ricerca di ateneo UNICT 2020-22 linea 3”.
Matteo Pennisi is a PhD student enrolled in the National PhD in Artificial Intelligence, XXXVII cycle, course on Health and life sciences, organized by Universitá Campus Bio-Medico di Roma.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pennisi, M. et al. (2022). GAN Latent Space Manipulation and Aggregation for Federated Learning in Medical Imaging. In: Albarqouni, S., et al. Distributed, Collaborative, and Federated Learning, and Affordable AI and Healthcare for Resource Diverse Global Health. DeCaF FAIR 2022 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13573. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18523-6_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18523-6_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-18522-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-18523-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)