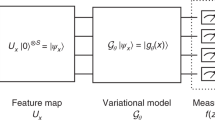
Abstract
As restricted quantum computers are slowly becoming a reality, the search for meaningful first applications intensifies. In this domain, one of the more investigated approaches is the use of a special type of quantum circuit – a so-called quantum neural network – to serve as a basis for a machine learning model. Roughly speaking, as the name suggests, a quantum neural network can play a similar role to a neural network. However, specifically for applications in machine learning contexts, very little is known about suitable circuit architectures, or model hyperparameters one should use to achieve good learning performance. In this work, we apply the functional ANOVA framework to quantum neural networks to analyze which of the hyperparameters were most influential for their predictive performance. We analyze one of the most typically used quantum neural network architectures. We then apply this to 7 open-source datasets from the OpenML-CC18 classification benchmark whose number of features is small enough to fit on quantum hardware with less than 20 qubits. Three main levels of importance were detected from the ranking of hyperparameters obtained with functional ANOVA. Our experiment both confirmed expected patterns and revealed new insights. For instance, setting well the learning rate is deemed the most critical hyperparameter in terms of marginal contribution on all datasets, whereas the particular choice of entangling gates used is considered the least important except on one dataset. This work introduces new methodologies to study quantum machine learning models and provides new insights toward quantum model selection.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
A 10-fold cross-validation run in our experiment takes on average 262 minutes for 100 epochs with Tensorflow Quantum [7].
References
ANIS, M.S., et al.: Qiskit: an open-source framework for quantum computing (2021). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2573505
Benedetti, M., Lloyd, E., Sack, S., Fiorentini, M.: Parameterized quantum circuits as machine learning models. Quantum Sci. Technol. 4(4), 043001 (2019)
Bergholm, V., Izaac, J.A., Schuld, M., Gogolin, C., Killoran, N.: Pennylane: Automatic differentiation of hybrid quantum-classical computations. CoRR abs/1811.04968 (2018)
Bischl, B., et al.: OpenML benchmarking suites. In: Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Track on Datasets and Benchmarks (2021)
Brazdil, P., van Rijn, J.N., Soares, C., Vanschoren, J.: Metalearning: Applications to Automated Machine Learning and Data Mining. Springer, 2nd edn. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67024-5
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45(1), 5–32 (2001)
Broughton, M., et al.: TensorFlow quantum: a software framework for quantum machine learning. arXiv:2003.02989 (2020)
Caro, M.C., Gil-Fuster, E., Meyer, J.J., Eisert, J., Sweke, R.: Encoding-dependent generalization bounds for parametrized quantum circuits. Quantum 5, 582 (2021)
Eggensperger, K., Hutter, F., Hoos, H.H., Leyton-Brown, K.: Efficient benchmarking of hyperparameter optimizers via surrogates. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 1114–1120. AAAI Press (2015)
Farhi, E., Goldstone, J., Gutmann, S.: A quantum approximate optimization algorithm. arXiv:1411.4028 (2014)
Feurer, M., Eggensperger, K., Falkner, S., Lindauer, M., Hutter, F.: Auto-Sklearn 2.0: hands-free automl via meta-learning. arXiv:2007.04074v2 [cs.LG] (2021)
Georgescu, I.M., Ashhab, S., Nori, F.: Quantum simulation. Review of modern. Physics 86, 153–185 (2014)
Haug, T., Self, C.N., Kim, M.S.: Large-scale quantum machine learning. CoRR abs/2108.01039 (2021)
Havlíček, V., et al.: Supervised learning with quantum-enhanced feature spaces. Nature 567(7747), 209–212 (2019)
Heimann, D., Hohenfeld, H., Wiebe, F., Kirchner, F.: Quantum deep reinforcement learning for robot navigation tasks. CoRR abs/2202.12180 (2022)
Hutter, F., Hoos, H., Leyton-Brown, K.: An efficient approach for assessing hyperparameter importance. In: Proceedings of the 31th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2014. JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, vol. 32, pp. 1130–1144 (2014)
Jerbi, S., Fiderer, L.J., Nautrup, H.P., Kübler, J.M., Briegel, H.J., Dunjko, V.: Quantum machine learning beyond kernel methods. CoRR abs/2110.13162 (2021)
Jerbi, S., Gyurik, C., Marshall, S., Briegel, H.J., Dunjko, V.: Parametrized quantum policies for reinforcement learning. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34, pp. 28362–28375 (2021)
Kandala, A., et al.: Hardware-efficient variational quantum eigensolver for small molecules and quantum magnets. Nature 549(7671), 242–246 (2017)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization (2015)
Liu, J.G., Wang, L.: Differentiable learning of quantum circuit born machines. Phys. Rev. A 98, 062324 (2018)
Liu, Y., Arunachalam, S., Temme, K.: A rigorous and robust quantum speed-up in supervised machine learning. Nat. Phys. 17(9), 1013–1017 (2021)
Marshall, S.C., Gyurik, C., Dunjko, V.: High dimensional quantum machine learning with small quantum computers. CoRR abs/2203.13739 (2022)
Mensa, S., Sahin, E., Tacchino, F., Barkoutsos, P.K., Tavernelli, I.: Quantum machine learning framework for virtual screening in drug discovery: a prospective quantum advantage. CoRR abs/2204.04017 (2022)
Mitarai, K., Negoro, M., Kitagawa, M., Fujii, K.: Quantum circuit learning. Phys. Rev. A 98, 032309 (2018)
Mohr, F., van Rijn, J.N.: Learning curves for decision making in supervised machine learning - a survey. CoRR abs/2201.12150 (2022)
Moll, N., et al.: Quantum optimization using variational algorithms on near-term quantum devices. Quantum Sci. Technol. 3(3), 030503 (2018)
Moussa, C., Calandra, H., Dunjko, V.: To quantum or not to quantum: towards algorithm selection in near-term quantum optimization. Quantum Sci. Technol. 5(4), 044009 (2020)
Moussa, C., Wang, H., Bäck, T., Dunjko, V.: Unsupervised strategies for identifying optimal parameters in quantum approximate optimization algorithm. EPJ Quantum Technol. 9(1) (2022)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information: 10th Anniversary. Cambridge University Press, New York (2011)
Pérez-Salinas, A., Cervera-Lierta, A., Gil-Fuster, E., Latorre, J.I.: Data re-uploading for a universal quantum classifier. Quantum 4, 226 (2020)
Peters, E., et al.: Machine learning of high dimensional data on a noisy quantum processor. NPJ Quantum Inf. 7(1), 161 (2021)
Preskill, J.: Quantum Computing in the NISQ era and beyond. Quantum 2, 79 (2018)
van Rijn, J.N., Hutter, F.: Hyperparameter importance across datasets. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, KDD 2018, pp. 2367–2376. ACM (2018)
Sajjan, M., et al.: Quantum computing enhanced machine learning for physico-chemical applications. CoRR arXiv:2111.00851 (2021)
Saltelli, A., Sobol, I.: Sensitivity analysis for nonlinear mathematical models: numerical experience. Matematicheskoe Modelirovanie 7 (1995)
Sauvage, F., Sim, S., Kunitsa, A.A., Simon, W.A., Mauri, M., Perdomo-Ortiz, A.: Flip: a flexible initializer for arbitrarily-sized parametrized quantum circuits. CoRR abs/2103.08572 (2021)
Schetakis, N., Aghamalyan, D., Boguslavsky, M., Griffin, P.: Binary classifiers for noisy datasets: a comparative study of existing quantum machine learning frameworks and some new approaches. CoRR abs/2111.03372 (2021)
Schuld, M., Killoran, N.: Is quantum advantage the right goal for quantum machine learning? Corr abs/2203.01340 (2022)
Schuld, M., Sweke, R., Meyer, J.J.: Effect of data encoding on the expressive power of variational quantum-machine-learning models. Phys. Rev. A 103, 032430 (2021)
Sharma, A., van Rijn, J.N., Hutter, F., Müller, A.: Hyperparameter importance for image classification by residual neural networks. In: Kralj Novak, P., Šmuc, T., Džeroski, S. (eds.) DS 2019. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 11828, pp. 112–126. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33778-0_10
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM Rev. 41, 303–332 (1999)
Sim, S., Johnson, P.D., Aspuru-Guzik, A.: Expressibility and entangling capability of parameterized quantum circuits for hybrid quantum-classical algorithms. Advanced Quantum Technologies 2(12), 1900070 (2019)
Skolik, A., Jerbi, S., Dunjko, V.: Quantum agents in the gym: a variational quantum algorithm for deep q-learning. CoRR abs/2103.15084 (2021)
Sobol, I.M.: Sensitivity estimates for nonlinear mathematical models. Math. Model. Comput. Exp. 1(4), 407–414 (1993)
Sweke, R., Seifert, J., Hangleiter, D., Eisert, J.: On the quantum versus classical learnability of discrete distributions. Quantum 5, 417 (2021)
Wang, H., Gu, J., Ding, Y., Li, Z., Chong, F.T., Pan, D.Z., Han, S.: QuantumNAT: quantum noise-aware training with noise injection, quantization and normalization. CoRR abs/2110.11331 (2021)
Wang, H., Li, Z., Gu, J., Ding, Y., Pan, D.Z., Han, S.: QOC: quantum on-chip training with parameter shift and gradient pruning. CoRR abs/2202.13239 (2022)
Wossnig, L.: Quantum machine learning for classical data. CoRR abs/2105.03684 (2021)
Zoufal, C., Lucchi, A., Woerner, S.: Quantum generative adversarial networks for learning and loading random distributions. NPJ Quantum Inf. 5(1), 103 (2019)
Acknowledgements
CM and VD acknowledge support from TotalEnergies. This work was supported by the Dutch Research Council (NWO/OCW), as part of the Quantum Software Consortium programme (project number 024.003.037). This research is also supported by the project NEASQC funded from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement No. 951821).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Moussa, C., van Rijn, J.N., Bäck, T., Dunjko, V. (2022). Hyperparameter Importance of Quantum Neural Networks Across Small Datasets. In: Pascal, P., Ienco, D. (eds) Discovery Science. DS 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13601. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18840-4_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18840-4_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-18839-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-18840-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)