Abstract
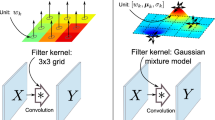
Most image denoising networks apply a single set of static convolutional kernels across the entire input image. This is sub-optimal for natural images, as they often consist of heterogeneous visual patterns. Dynamic convolution tries to address this issue by using per-pixel convolution kernels, but this greatly increases computational cost. In this work, we present Malleable Convolution (MalleConv), which performs spatial-varying processing with minimal computational overhead. MalleConv uses a smaller set of spatially-varying convolution kernels, a compromise between static and per-pixel convolution kernels. These spatially-varying kernels are produced by an efficient predictor network running on a downsampled input, making them much more efficient to compute than per-pixel kernels produced by a full-resolution image, and also enlarging the network’s receptive field compared with static kernels. These kernels are then jointly upsampled and applied to a full-resolution feature map through an efficient on-the-fly slicing operator with minimum memory overhead. To demonstrate the effectiveness of MalleConv, we use it to build an efficient denoising network we call MalleNet. MalleNet achieves high-quality results without very deep architectures, making it 8.9\(\times \) faster than the best performing denoising algorithms while achieving similar visual quality. We also show that a single MalleConv layer added to a standard convolution-based backbone can significantly reduce the computational cost or boost image quality at a similar cost. More information are on our project page: https://yifanjiang.net/MalleConv.html.
Y. Jiang—This work was performed while Yifan Jiang worked at Google.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhamed, A., Lin, S., Brown, M.S.: A high-quality denoising dataset for smartphone cameras. In: CVPR (2018)
Agustsson, E., Timofte, R.: Ntire 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: dataset and study. In: CVPR Workshops (2017)
Aharon, M., Elad, M., Bruckstein, A.: K-SVD: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54, 4311–22 (2006)
Anwar, S., Barnes, N.: Real image denoising with feature attention. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3155–3164 (2019)
Bako, S., et al.: Kernel-predicting convolutional networks for denoising monte carlo renderings. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 1–14 (2017)
Buades, A., Coll, B., Morel, J.-M.: A non-local algorithm for image denoising. In: CVPR (2005)
Burger, H.C., Schuler, C.J., Harmeling, S.: Image denoising: can plain neural networks compete with bm3d? In: CVPR (2012)
Chen, H., et al.: Pre-trained image processing transformer. In: CVPR (2021)
Chen, L., Xin, L., Zhang, J., Chu, X., Chen, C.: Half instance normalization network for image restoration. In: CVPR (2021)
Chen, Y., Pock, T.: Trainable nonlinear reaction diffusion: a flexible framework for fast and effective image restoration. In: TPAMI (2016)
Chen, Z., Jiang, Y., Liu, D., Wang, Z.: CERL: a unified optimization framework for light enhancement with realistic noise. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 4162–4172 (2022)
Cheng, S., Wang, Y., Huang, H., Liu, D., Fan, H., Liu, S.: NBNet: noise basis learning for image denoising with subspace projection. In: CVPR (2021)
Dabov, K., Foi, A., Katkovnik, V., Egiazarian, K.: Image denoising by sparse 3-d transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16, 2080–2095 (2007)
Dai, J., et al.: Deformable convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 764–773 (2017)
Dong, C., Loy, C.C., He, K., Tang, X.: Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. In: TPAMI (2015)
Elad, M., Aharon, M.: Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15, 3736–3745 (2006)
Franzen, R.: Kodak lossless true color image suite (1999). source: http://r0k.us/graphics/kodak
Getreuer, P., et al.: Blade: filter learning for general purpose computational photography. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), pp. 1–11. IEEE (2018)
Gharbi, M., Chen, J., Barron, J.T., Hasinoff, S.W., Durand, F.: Deep bilateral learning for real-time image enhancement. In: SIGGRAPH (2017)
Glasner, D., Bagon, S., Irani, M.: Super-resolution from a single image. In: ICCV (2009)
Gu, S., Li, W., Van Gool, L., Timofte, R.: Fast image restoration with multi-bin trainable linear units. In: ICCV (2019)
Gu, S., Li, Y., Van Gool, L., Timofte, R.: Self-guided network for fast image denoising. In: ICCV (2019)
Gu, S., Zhang, L., Zuo, W., Feng, X.: Weighted nuclear norm minimization with application to image denoising. In: CVPR (2014)
Guo, S., Yan, Z., Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Zhang, L.: Toward convolutional blind denoising of real photographs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1712–1722 (2019)
Ha, D., Dai, A., Le, Q.V.: Hypernetworks. arXiv:1609.09106 (2016)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In: ICCV (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR (2016)
Howard, A.G.: Mobilenets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv:1704.04861 (2017)
Jia, X., Brabandere, B.D., Tuytelaars, T., Gool, L.V.: Dynamic filter networks. In: NeurIPS (2016)
Jiang, Y., et al.: Enlightengan: deep light enhancement without paired supervision. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 2340–2349 (2021)
Jiang, Y., et al.: SSH: a self-supervised framework for image harmonization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4832–4841 (2021)
Kataoka, H., et al.: Pre-training without natural images. In: ACCV (2020)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: ICLR (2015)
Kupyn, O., Budzan, V., Mykhailych, M., Mishkin, D., Matas, J.: Deblurgan: blind motion deblurring using conditional adversarial networks. In: CVPR (2018)
Kupyn, O., Martyniuk, T., Wu, J., Wang, Z.: Deblurgan-v2: deblurring (orders-of-magnitude) faster and better. In: ICCV (2019)
Li, D., et al.: Involution: inverting the inherence of convolution for visual recognition. In: CVPR (2021)
Li, S., et al.: Single image deraining: a comprehensive benchmark analysis. In: CVPR (2019)
Liang, J., Cao, J., Sun, G., Zhang, K., Van Gool, L., Timofte, R.: Swinir: image restoration using Swin transformer. In: ICCV (2021)
Liang, J., Zeng, H., Zhang, L.: High-resolution photorealistic image translation in real-time: a laplacian pyramid translation network. In: CVPR (2021)
Lim, B., Son, S., Kim, H., Nah, S., Lee, K.M.: Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In: CVPR Workshops (2017)
Lin, X., Ma, L., Liu, W., Chang, S.-F.: Context-Gated Convolution. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12363, pp. 701–718. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58523-5_41
Ma, K., et al.: Waterloo exploration database: new challenges for image quality assessment models. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26, 1004–1016 (2016)
Mairal, J., Bach, F., Ponce, J., Sapiro, G., Zisserman, A.: Non-local sparse models for image restoration. In: ICCV (2009)
Martin, D., Fowlkes, C., Tal, D., Malik, J.: A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Computer Vision, vol. 2, pp. 416–423, July 2001
Mildenhall, B., Barron, J.T., Chen, J., Sharlet, D., Ng, R., Carroll, R.: Burst denoising with kernel prediction networks. In: CVPR (2018)
Peng, Y., Zhang, L., Liu, S., Wu, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, X.: Dilated residual networks with symmetric skip connection for image denoising. Neurocomputing 345, 67–76 (2019)
Perona, P., Malik, J.: Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. In: TPAMI (1990)
Peyré, G., Bougleux, S., Cohen, L.: Non-local regularization of inverse problems. In: Forsyth, D., Torr, P., Zisserman, A. (eds.) ECCV 2008. LNCS, vol. 5304, pp. 57–68. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88690-7_5
Plotz, T., Roth, S.: Benchmarking denoising algorithms with real photographs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1586–1595 (2017)
Ren, D., Zuo, W., Qinghua, Hu., Zhu, P., Meng, D.: Progressive image deraining networks: a better and simpler baseline. In: CVPR (2019)
Rudin, L.I., Osher, S., Fatemi, E.: Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D 60, 259–268 (1992)
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.-C.: Mobilenetv 2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: CVPR (2018)
Shi, W., et al.: Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1874–1883 (2016)
Tao, X., Gao, H., Shen, X., Wang, J., Jia, J.: Scale-recurrent network for deep image deblurring. In: CVPR (2018)
Tian, C., Xu, Y., Zuo, W.: Image denoising using deep CNN with batch renormalization. Neural Networks (2020)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: NeurIPS (2017)
Wang, J., Chen, K., Rui, X., Liu, Z., Loy, C.C., Lin, D.: Carafe: content-aware reassembly of features. In: ICCV (2019)
Wang, Z., Miao, Z., Hu, J., Qiu, Q.: Adaptive convolutions with per-pixel dynamic filter atom. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 12302–12311 (2021)
Wei, C., Wang, W., Yang, W., Liu, J.: Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. arXiv:1808.04560 (2018)
Xia, Z., Chakrabarti, A.: Identifying recurring patterns with deep neural networks for natural image denoising. In: WACV (2020)
Xu, Y.-S., Tseng, S.-Y.R., Tseng, Y., Kuo, H.-K., Tsai, Y.-M.: Unified dynamic convolutional network for super-resolution with variational degradations. In: CVPR (2020)
Yang, W., Tan, R.T., Wang, S., Fang, Y., Liu, J.: Single image deraining: from model-based to data-driven and beyond. In: TPAMI (2020)
Yue, Z., Yong, H., Zhao, Q., Zhang, L., Meng, D.: Variational denoising network: toward blind noise modeling and removal. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.11314 (2019)
Zamir, S.W., et al.: Learning enriched features for real image restoration and enhancement. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12370, pp. 492–511. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58595-2_30
Zamir, S.W., et al.: Multi-stage progressive image restoration. In: CVPR (2021)
Zhang, K., Li, Y., Zuo, W., Zhang, L., Van Gool, L., Timofte, R.: Plug-and-play image restoration with deep denoiser prior. In: TPAMI (2021)
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Chen, Y., Meng, D., Zhang, L.: Beyond a gaussian denoiser: residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26, 3142–3155 (2017)
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Gu, S., Zhang, L.: Learning deep CNN denoiser prior for image restoration. In: CVPR (2017)
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Zhang, L.: FFDNet: toward a fast and flexible solution for CNN-based image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27, 4608–4622 (2018)
Zhang, L., Wu, X., Buades, A., Li, X.: Color demosaicking by local directional interpolation and nonlocal adaptive thresholding. J. Electron. imaging 20, 023016 (2011)
Zhang, Y., Li, K., Li, K., Zhong, B., Fu, Y.: Residual non-local attention networks for image restoration. arXiv:1903.10082 (2019)
Zhang, Y., Tian, Y., Kong, Y., Zhong, B., Fu, Y.: Residual dense network for image super-resolution. In: CVPR (2018)
Zhang, Y., Wei, D., Qin, C., Wang, H., Pfister, H., Fu, Y.: Context reasoning attention network for image super-resolution. In: ICCV (2021)
Acknowledgement
We would like to express our gratitude to the Google Research Luma team, in particular Zhengzhong Tu for generously providing us with the concrete training recipes on real-world denoising benchmarks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jiang, Y., Wronski, B., Mildenhall, B., Barron, J.T., Wang, Z., Xue, T. (2022). Fast and High Quality Image Denoising via Malleable Convolution. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13678. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19797-0_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19797-0_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-19796-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-19797-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)