Abstract
Attention modules for Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are an effective method to enhance performance on multiple computer-vision tasks. While existing methods appropriately model channel-, spatial- and self-attention, they primarily operate in a feedforward bottom-up manner. Consequently, the attention mechanism strongly depends on the local information of a single input feature map and does not incorporate relatively semantically-richer contextual information available at higher layers that can specify “what and where to look” in lower-level feature maps through top-down information flow.
Accordingly, in this work, we propose a lightweight top-down attention module (TDAM) that iteratively generates a “visual searchlight” to perform channel and spatial modulation of its inputs and outputs more contextually-relevant feature maps at each computation step. Our experiments indicate that TDAM enhances the performance of CNNs across multiple object-recognition benchmarks and outperforms prominent attention modules while being more parameter and memory efficient. Further, TDAM-based models learn to “shift attention” by localizing individual objects or features at each computation step without any explicit supervision resulting in a 5% improvement for ResNet50 on weakly-supervised object localization. Source code and models are publicly available at: https://github.com/shantanuj/TDAM_Top_down_attention_module.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, P., et al.: Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6077–6086 (2018)
Ba, J., Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K.: Multiple object recognition with visual attention. In: ICLR (Poster) (2015). http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.7755
Bello, I., Zoph, B., Vaswani, A., Shlens, J., Le, Q.V.: Attention augmented convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), October 2019
Byeon, W., Breuel, T.M., Raue, F., Liwicki, M.: Scene labeling with lstm recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3547–3555 (2015)
Cao, C., et al.: Look and think twice: capturing top-down visual attention with feedback convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2956–2964 (2015)
Cao, Y., Xu, J., Lin, S., Wei, F., Hu, H.: Gcnet: non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (2019)
Chen, L., et al.: Sca-cnn: spatial and channel-wise attention in convolutional networks for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5659–5667 (2017)
Chen, Y., Kalantidis, Y., Li, J., Yan, S., Feng, J.: A\(\hat{\,}\)2-nets: double attention networks. In: Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Grauman, K., Cesa-Bianchi, N., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 31. Curran Associates, Inc. (2018). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2018/file/e165421110ba03099a1c0393373c5b43-Paper.pdf
Crick, F.: Function of the thalamic reticular complex: the searchlight hypothesis. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 81(14), 4586–4590 (1984)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 248–255. IEEE (2009)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020)
Fu, J., Zheng, H., Mei, T.: Look closer to see better: recurrent attention convolutional neural network for fine-grained image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4438–4446 (2017)
Gao, Z., Xie, J., Wang, Q., Li, P.: Global second-order pooling convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3024–3033 (2019)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hochstein, S., Ahissar, M.: View from the top: hierarchies and reverse hierarchies in the visual system. Neuron 36(5), 791–804 (2002)
Howard, A., et al.: Searching for mobilenetv3. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1314–1324 (2019)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Albanie, S., Sun, G., Vedaldi, A.: Gather-excite: exploiting feature context in convolutional neural networks. In: Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Grauman, K., Cesa-Bianchi, N., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 31. Curran Associates, Inc. (2018). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2018/file/dc363817786ff182b7bc59565d864523-Paper.pdf
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Hu, P., Ramanan, D.: Bottom-up and top-down reasoning with hierarchical rectified gaussians. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5600–5609 (2016)
Hu, T., Qi, H., Huang, Q., Lu, Y.: See better before looking closer: weakly supervised data augmentation network for fine-grained visual classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.09891 (2019)
Huang, Z., Liang, S., Liang, M., Yang, H.: Dianet: dense-and-implicit attention network. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 4206–4214 (2020)
Khosla, A., Jayadevaprakash, N., Yao, B., Fei-Fei, L.: Novel dataset for fine-grained image categorization. In: First Workshop on Fine-Grained Visual Categorization, IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, June 2011
Kok, P., Bains, L.J., van Mourik, T., Norris, D.G., de Lange, F.P.: Selective activation of the deep layers of the human primary visual cortex by top-down feedback. Curr. Biol. 26(3), 371–376 (2016)
Kreiman, G., Serre, T.: Beyond the feedforward sweep: feedback computations in the visual cortex. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1464(1), 222–241 (2020)
Liao, Q., Poggio, T.: Bridging the gaps between residual learning, recurrent neural networks and visual cortex. arXiv preprint arXiv:1604.03640 (2016)
Lin, T.-Y., et al.: Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8693, pp. 740–755. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
Liu, J.J., Hou, Q., Cheng, M.M., Wang, C., Feng, J.: Improving convolutional networks with self-calibrated convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10096–10105 (2020)
Liu, Z., et al.: Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 10012–10022 (2021)
Liu, Z., Mao, H., Wu, C.Y., Feichtenhofer, C., Darrell, T., Xie, S.: A convnet for the 2020s. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.03545 (2022)
Mnih, V., Heess, N., Graves, A., kavukcuoglu, K.: Recurrent models of visual attention. In: Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N., Weinberger, K.Q. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 27. Curran Associates, Inc. (2014). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2014/file/09c6c3783b4a70054da74f2538ed47c6-Paper.pdf
Park, J., Woo, S., Lee, J., Kweon, I.S.: BAM: bottleneck attention module. In: British Machine Vision Conference 2018, BMVC 2018, Newcastle, UK, 3–6 September 2018, p. 147. BMVA Press (2018). http://bmvc2018.org/contents/papers/0092.pdf
Paszke, A., et al.: Pytorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In: Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Beygelzimer, A., d’Alché-Buc, F., Fox, E., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32. Curran Associates, Inc. (2019). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2019/file/bdbca288fee7f92f2bfa9f7012727740-Paper.pdf
Pinheiro, P., Collobert, R.: Recurrent convolutional neural networks for scene labeling. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 82–90. PMLR (2014)
Qin, Z., Zhang, P., Wu, F., Li, X.: Fcanet: frequency channel attention networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 783–792 (2021)
Recht, B., Roelofs, R., Schmidt, L., Shankar, V.: Do imagenet classifiers generalize to imagenet? In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 5389–5400. PMLR (2019)
Ridnik, T., et al.: Asymmetric loss for multi-label classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 82–91 (2021)
Roy, A.G., Navab, N., Wachinger, C.: Recalibrating fully convolutional networks with spatial and channel “squeeze and excitation’’ blocks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(2), 540–549 (2018)
Selvaraju, R.R., Cogswell, M., Das, A., Vedantam, R., Parikh, D., Batra, D.: Grad-cam: visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 618–626 (2017)
Touvron, H., Cord, M., Douze, M., Massa, F., Sablayrolles, A., Jégou, H.: Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 10347–10357. PMLR (2021)
Touvron, H., Vedaldi, A., Douze, M., Jegou, H.: Fixing the train-test resolution discrepancy. In: Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Beygelzimer, A., d’Alché-Buc, F., Fox, E., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32. Curran Associates, Inc. (2019). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2019/file/d03a857a23b5285736c4d55e0bb067c8-Paper.pdf
Treisman, A.M., Gelade, G.: A feature-integration theory of attention. Cogn. Psychol. 12(1), 97–136 (1980)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30 (2017)
Wang, F., et al.: Residual attention network for image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3156–3164 (2017)
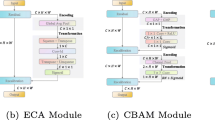
Wang, Q., Wu, B., Zhu, P., Li, P., Zuo, W., Hu, Q.: Eca-net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks, 2020 IEEE. In: CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE (2020)
Wang, Y., Huang, R., Song, S., Huang, Z., Huang, G.: Not all images are worth 16 x 16 words: dynamic transformers for efficient image recognition. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34 (2021)
Welinder, P., et al.: Caltech-UCSD Birds 200. Technical Report, CNS-TR-2010-001, California Institute of Technology (2010)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.Y., Kweon, I.S.: Cbam: convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19 (2018)
Xu, K., et al.: Show, attend and tell: neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 2048–2057. PMLR (2015)
Yang, J., Ren, Z., Gan, C., Zhu, H., Lin, J., Parikh, D.: Cross-channel communication networks (2019)
Yang, Z., He, X., Gao, J., Deng, L., Smola, A.: Stacked attention networks for image question answering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 21–29 (2016)
Zamir, A.R., et al.: Feedback networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1308–1317 (2017)
Zeiler, M.D., Fergus, R.: Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8689, pp. 818–833. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10590-1_53
Zhang, M., Tseng, C., Kreiman, G.: Putting visual object recognition in context. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12985–12994 (2020)
Zhao, J., Fang, Y., Li, G.: Recurrence along depth: deep convolutional neural networks with recurrent layer aggregation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 10627–10640 (2021)
Acknowledgment
This research/project is supported in part by the National Research Foundation, Singapore under its AI Singapore Program (Award Number: AISG-RP-2019-010). This research is also supported by funding allocation to C.T. and B.F. by the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) under its SERC Central Research Fund (CRF), as well as its Centre for Frontier AI Research (CFAR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jaiswal, S., Fernando, B., Tan, C. (2022). TDAM: Top-Down Attention Module for Contextually Guided Feature Selection in CNNs. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13685. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19806-9_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19806-9_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-19805-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-19806-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)