Abstract
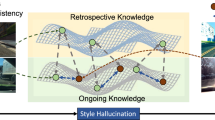
In this paper, we study the task of synthetic-to-real domain generalized semantic segmentation, which aims to learn a model that is robust to unseen real-world scenes using only synthetic data. The large domain shift between synthetic and real-world data, including the limited source environmental variations and the large distribution gap between synthetic and real-world data, significantly hinders the model performance on unseen real-world scenes. In this work, we propose the Style-HAllucinated Dual consistEncy learning (SHADE) framework to handle such domain shift. Specifically, SHADE is constructed based on two consistency constraints, Style Consistency (SC) and Retrospection Consistency (RC). SC enriches the source situations and encourages the model to learn consistent representation across style-diversified samples. RC leverages real-world knowledge to prevent the model from overfitting to synthetic data and thus largely keeps the representation consistent between the synthetic and real-world models. Furthermore, we present a novel style hallucination module (SHM) to generate style-diversified samples that are essential to consistency learning. SHM selects basis styles from the source distribution, enabling the model to dynamically generate diverse and realistic samples during training. Experiments show that our SHADE yields significant improvement and outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 5.05% and 8.35% on the average mIoU of three real-world datasets on single- and multi-source settings, respectively.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, H., et al.: Diverse image style transfer via invertible cross-space mapping. In: ICCV (2021)
Chen, L.-C., Zhu, Y., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11211, pp. 833–851. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_49
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., Hinton, G.: A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: ICML (2020)
Choi, S., Jung, S., Yun, H., Kim, J.T., Kim, S., Choo, J.: Robustnet: Improving domain generalization in urban-scene segmentation via instance selective whitening. In: CVPR (2021)
Cordts, M., et al.: The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In: CVPR (2016)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: CVPR (2009)
Dumoulin, V., Shlens, J., Kudlur, M.: A learned representation for artistic style. In: ICLR (2017)
French, G., Laine, S., Aila, T., Mackiewicz, M., Finlayson, G.: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation needs strong, varied perturbations. In: BMVC (2020)
Halmos, P.R.: Finite-Dimensional Vector Spaces. Springer, New York (1987)
He, K., Fan, H., Wu, Y., Xie, S., Girshick, R.: Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In: CVPR (2020)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR (2016)
Hendrycks, D., Mu, N., Cubuk, E.D., Zoph, B., Gilmer, J., Lakshminarayanan, B.: AugMix: a simple data processing method to improve robustness and uncertainty. In: ICLR (2020)
Hoyer, L., Dai, D., Van Gool, L.: Daformer: improving network architectures and training strategies for domain-adaptive semantic segmentation. In: CVPR (2022)
Huang, J., Guan, D., Xiao, A., Lu, S.: FSDR: frequency space domain randomization for domain generalization. In: CVPR (2021)
Huang, L., Zhou, Y., Zhu, F., Liu, L., Shao, L.: Iterative normalization: Beyond standardization towards efficient whitening. In: CVPR (2019)
Huang, X., Belongie, S.: Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization. In: ICCV (2017)
Kannan, H., Kurakin, A., Goodfellow, I.: Adversarial logit pairing. In: ICML (2018)
Liu, W., Rabinovich, A., Berg, A.C.: Parsenet: Looking wider to see better. In: CoRR (2015)
Liu, Z., et al.. Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: ICCV (2021)
Liu, Z., Mao, H., Wu, C.Y., Feichtenhofer, C., Darrell, T., Xie, S.: A convnet for the 2020s. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.03545 (2022)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: CVPR (2015)
MacQueen, J.: Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In: Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability (1967)
Meng, R., et al.: Attention diversification for domain generalization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.04206 (2022)
Neuhold, G., Ollmann, T., Rota Bulo, S., Kontschieder, P.: The mapillary vistas dataset for semantic understanding of street scenes. In: ICCV (2017)
Pan, F., Shin, I., Rameau, F., Lee, S., Kweon, I.S.: Unsupervised intra-domain adaptation for semantic segmentation through self-supervision. In: CVPR (2020)
Pan, X., Luo, P., Shi, J., Tang, X.: Two at once: enhancing learning and generalization capacities via IBN-net. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11208, pp. 484–500. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01225-0_29
Pan, X., Zhan, X., Shi, J., Tang, X., Luo, P.: Switchable whitening for deep representation learning. In: ICCV (2019)
Qi, C.R., Yi, L., Su, H., Guibas, L.J.: Pointnet++: deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. In: NeurIPS (2017)
Richter, S.R., Vineet, V., Roth, S., Koltun, V.: Playing for data: ground truth from computer games. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9906, pp. 102–118. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_7
Ros, G., Sellart, L., Materzynska, J., Vazquez, D., Lopez, A.M.: The synthia dataset: a large collection of synthetic images for semantic segmentation of urban scenes. In: CVPR (2016)
Sakaridis, C., Dai, D., Gool, L.V.: Guided curriculum model adaptation and uncertainty-aware evaluation for semantic nighttime image segmentation. In: ICCV (2019)
Sakaridis, C., Dai, D., Van Gool, L.: ACDC: the adverse conditions dataset with correspondences for semantic driving scene understanding. In: ICCV (2021)
Tang, Z., Gao, Y., Zhu, Y., Zhang, Z., Li, M., Metaxas, D.: Selfnorm and crossnorm for out-of-distribution robustness. In: ICCV (2021)
Tarvainen, A., Valpola, H.: Mean teachers are better role models: weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results. In: NeurIPS (2017)
Tsai, Y.H., Hung, W.C., Schulter, S., Sohn, K., Yang, M.H., Chandraker, M.: Learning to adapt structured output space for semantic segmentation. In: CVPR (2018)
Wang, H., Xiao, C., Kossaifi, J., Yu, Z., Anandkumar, A., Wang, Z.: Augmax: adversarial composition of random augmentations for robust training. In: NeurIPS (2021)
Wang, P., Li, Y., Vasconcelos, N.: Rethinking and improving the robustness of image style transfer. In: CVPR (2021)
Wang, Z., Luo, Y., Qiu, R., Huang, Z., Baktashmotlagh, M.: Learning to diversify for single domain generalization. In: ICCV (2021)
Xie, E., Wang, W., Yu, Z., Anandkumar, A., Alvarez, J.M., Luo, P.: Segformer: simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. In: NeurIPS (2021)
Yu, F., et al.: Bdd100k: a diverse driving dataset for heterogeneous multitask learning. In: CVPR (2020)
Yue, X., Zhang, Y., Zhao, S., Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, A., Keutzer, K., Gong, B.: Domain randomization and pyramid consistency: simulation-to-real generalization without accessing target domain data. In: ICCV (2019)
Zhao, Y., Zhong, Z., Luo, Z., Lee, G.H., Sebe, N.: Source-free open compound domain adaptation in semantic segmentation. In: IEEE TCSVT (2022)
Zhong, Z., Zhao, Y., Lee, G.H., Sebe, N.: Adversarial style augmentation for domain generalized urban-scene segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2207.04892 (2022)
Zhou, K., Yang, Y., Qiao, Y., Xiang, T.: Domain generalization with mixstyle. In: ICLR (2021)
Zhou, Q., et al.: Uncertainty-aware consistency regularization for cross-domain semantic segmentation. In: Computer Vision and Image Understanding (2022)
Zhou, Q., et al.: Context-aware mixup for domain adaptive semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.03557 (2021)
Zhou, Q., Zhuang, C., Yi, R., Lu, X., Ma, L.: Domain adaptive semantic segmentation with regional contrastive consistency regularization. In: ICME (2022)
Zhu, J.Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: ICCV (2017)
Zou, Y., Yu, Z., Vijaya Kumar, B.V.K., Wang, J.: Unsupervised domain adaptation for semantic segmentation via class-balanced self-training. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11207, pp. 297–313. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01219-9_18
Acknowledgment
This research/project is supported by the National Research Foundation Singapore and DSO National Laboratories under the AI Singapore Programme (AISG Award No: AISG2-RP-2020-016), the Tier 2 grant MOE-T2EP20120-0011 from the Singapore Ministry of Education, and the EU H2020 project AI4Media (No. 951911).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhao, Y., Zhong, Z., Zhao, N., Sebe, N., Lee, G.H. (2022). Style-Hallucinated Dual Consistency Learning for Domain Generalized Semantic Segmentation. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13688. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19815-1_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19815-1_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-19814-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-19815-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)