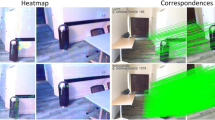
Abstract
We tackle the essential task of finding dense visual correspondences between a pair of images. This is a challenging problem due to various factors such as poor texture, repetitive patterns, illumination variation, and motion blur in practical scenarios. In contrast to methods that use dense correspondence ground-truths as direct supervision for local feature matching training, we train 3DG-STFM: a multi-modal matching model (Teacher) to enforce the depth consistency under 3D dense correspondence supervision and transfer the knowledge to 2D unimodal matching model (Student). Both teacher and student models consist of two transformer-based matching modules that obtain dense correspondences in a coarse-to-fine manner. The teacher model guides the student model to learn RGB-induced depth information for the matching purpose on both coarse and fine branches. We also evaluate 3DG-STFM on a model compression task. To the best of our knowledge, 3DG-STFM is the first student-teacher learning method for the local feature matching task. The experiments show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods on indoor and outdoor camera pose estimations, and homography estimation problems. Code is available at: https://github.com/Ryan-prime/3DG-STFM.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ba, L.J., Caruana, R.: Do deep nets really need to be deep? arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6184 (2013)
Balntas, V., Lenc, K., Vedaldi, A., Mikolajczyk, K.: HPatches: a benchmark and evaluation of handcrafted and learned local descriptors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5173–5182 (2017)
Bay, H., Tuytelaars, T., Van Gool, L.: SURF: speeded up robust features. In: Leonardis, A., Bischof, H., Pinz, A. (eds.) ECCV 2006. LNCS, vol. 3951, pp. 404–417. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/11744023_32
Bian, J., Lin, W.Y., Matsushita, Y., Yeung, S.K., Nguyen, T.D., Cheng, M.M.: GMS: grid-based motion statistics for fast, ultra-robust feature correspondence. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4181–4190 (2017)
Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., Usunier, N., Kirillov, A., Zagoruyko, S.: End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12346, pp. 213–229. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58452-8_13
Chen, H., et al.: Data-free learning of student networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3514–3522 (2019)
Chen, H., et al.: Learning to match features with seeded graph matching network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6301–6310 (2021)
Chen, T., Goodfellow, I., Shlens, J.: Net2Net: accelerating learning via knowledge transfer. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.05641 (2015)
Choy, C.B., Gwak, J., Savarese, S., Chandraker, M.: Universal correspondence network. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2016)
Dai, A., Chang, A.X., Savva, M., Halber, M., Funkhouser, T., Nießner, M.: ScanNet: richly-annotated 3D reconstructions of indoor scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5828–5839 (2017)
DeTone, D., Malisiewicz, T., Rabinovich, A.: Toward geometric deep SLAM. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.07410 (2017)
DeTone, D., Malisiewicz, T., Rabinovich, A.: SuperPoint: self-supervised interest point detection and description. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 224–236 (2018)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth \(16\times 16\) words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020)
Dusmanu, M., et al.: D2-Net: a trainable CNN for joint description and detection of local features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8092–8101 (2019)
Garcia, N.C., Morerio, P., Murino, V.: Modality distillation with multiple stream networks for action recognition. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11212, pp. 106–121. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01237-3_7
Graham, B., Engelcke, M., Van Der Maaten, L.: 3D semantic segmentation with submanifold sparse convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9224–9232 (2018)
Gupta, S., Hoffman, J., Malik, J.: Cross modal distillation for supervision transfer, pp. 2827–2836 (2016)
Hinton, G., Vinyals, O., Dean, J.: Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1503.02531 (2015)
Huang, Z., Wang, N.: Like what you like: knowledge distill via neuron selectivity transfer. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.01219 (2017)
Yu, J.J., Harley, A.W., Derpanis, K.G.: Back to basics: unsupervised learning of optical flow via brightness constancy and motion smoothness. In: Hua, G., Jégou, H. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9915, pp. 3–10. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49409-8_1
Jiang, W., Trulls, E., Hosang, J., Tagliasacchi, A., Yi, K.M.: COTR: correspondence transformer for matching across images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 6207–6217, October 2021
Leutenegger, S., Chli, M., Siegwart, R.Y.: BRISK: binary robust invariant scalable keypoints. In: 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2548–2555 (2011)
Li, X., Han, K., Li, S., Prisacariu, V.: Dual-resolution correspondence networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33 (2020)
Li, Z., Snavely, N.: MegaDepth: learning single-view depth prediction from internet photos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2041–2050 (2018)
Lin, T.Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2117–2125 (2017)
Liu, Y., et al.: Knowledge distillation via instance relationship graph. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7096–7104 (2019)
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60(2), 91–110 (2004)
Luo, Z., et al.: ContextDesc: local descriptor augmentation with cross-modality context. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2527–2536 (2019)
Mahmud, J., Singh, R.V., Akiva, P., Kundu, S., Peng, K., Frahm, J.: ViewSynth: learning local features from depth using view synthesis. In: 31st British Machine Vision Conference (2020)
Meister, S., Hur, J., Roth, S.: Unflow: unsupervised learning of optical flow with a bidirectional census loss. In: Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2018)
Ren, Z., Yan, J., Ni, B., Liu, B., Yang, X., Zha, H.: Unsupervised deep learning for optical flow estimation. In: Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2017)
Revaud, J., De Souza, C., Humenberger, M., Weinzaepfel, P.: R2D2: reliable and repeatable detector and descriptor. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32, pp. 12405–12415 (2019)
Rocco, I., Cimpoi, M., Arandjelović, R., Torii, A., Pajdla, T., Sivic, J.: Neighbourhood consensus networks. In: Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (2018)
Rocco, I., Arandjelović, R., Sivic, J.: Efficient neighbourhood consensus networks via submanifold sparse convolutions. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12354, pp. 605–621. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58545-7_35
Romero, A., Ballas, N., Kahou, S.E., Chassang, A., Gatta, C., Bengio, Y.: FitNets: hints for thin deep nets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6550 (2014)
Rosten, E., Drummond, T.: Machine learning for high-speed corner detection. In: Leonardis, A., Bischof, H., Pinz, A. (eds.) ECCV 2006. LNCS, vol. 3951, pp. 430–443. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/11744023_34
Rublee, E., Rabaud, V., Konolige, K., Bradski, G.: ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In: 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2564–2571 (2011)
Sarlin, P.E., Cadena, C., Siegwart, R., Dymczyk, M.: From coarse to fine: robust hierarchical localization at large scale. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12716–12725 (2019)
Sarlin, P.E., DeTone, D., Malisiewicz, T., Rabinovich, A.: SuperGlue: learning feature matching with graph neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4938–4947 (2020)
Schmidt, T., Newcombe, R., Fox, D.: Self-supervised visual descriptor learning for dense correspondence. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2(2), 420–427 (2016)
Schönberger, J.L., Frahm, J.M.: Structure-from-motion revisited. In: Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2016)
Sun, J., Shen, Z., Wang, Y., Bao, H., Zhou, X.: LoFTR: detector-free local feature matching with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8922–8931 (2021)
Tarvainen, A., Valpola, H.: Weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results. CORR abs/1703.01780. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.01780 (2017)
Tyszkiewicz, M.J., Fua, P., Trulls, E.: DISK: learning local features with policy gradient. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.13566 (2020)
Wang, H., Lian, D., Ge, Y.: Binarized collaborative filtering with distilling graph convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.01829 (2019)
Wang, H., Zhu, Y., Green, B., Adam, H., Yuille, A., Chen, L.-C.: Axial-DeepLab: stand-alone axial-attention for panoptic segmentation. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12349, pp. 108–126. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58548-8_7
Wang, Z., Deng, Z., Wang, S.: Accelerating convolutional neural networks with dominant convolutional kernel and knowledge pre-regression. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9912, pp. 533–548. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_32
Yang, T.Y., Hsu, J.H., Lin, Y.Y., Chuang, Y.Y.: DeepCD: learning deep complementary descriptors for patch representations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3314–3322 (2017)
Yang, Y., Qiu, J., Song, M., Tao, D., Wang, X.: Distilling knowledge from graph convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7074–7083 (2020)
Yi, K.M., Trulls, E., Ono, Y., Lepetit, V., Salzmann, M., Fua, P.: Learning to find good correspondences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2666–2674 (2018)
Yim, J., Joo, D., Bae, J., Kim, J.: A gift from knowledge distillation: fast optimization, network minimization and transfer learning, pp. 4133–4141 (2017)
Zagoruyko, S., Komodakis, N.: Paying more attention to attention: improving the performance of convolutional neural networks via attention transfer. arXiv preprint arXiv:1612.03928 (2016)
Zhang, J., et al.: Learning two-view correspondences and geometry using order-aware network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5845–5854 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 2 (mp4 2657 KB)
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mao, R., Bai, C., An, Y., Zhu, F., Lu, C. (2022). 3DG-STFM: 3D Geometric Guided Student-Teacher Feature Matching. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13688. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19815-1_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19815-1_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-19814-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-19815-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)