Abstract
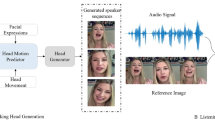
We present a new listening head generation benchmark, for synthesizing responsive feedbacks of a listener (e.g., nod, smile) during a face-to-face conversation. As the indispensable complement to talking heads generation, listening head generation has seldomly been studied in literature. Automatically synthesizing listening behavior that actively responds to a talking head, is critical to applications such as digital human, virtual agents and social robots. In this work, we propose a novel dataset “ViCo”, highlighting the listening head generation during a face-to-face conversation. A total number of 92 identities (67 speakers and 76 listeners) are involved in ViCo, featuring 483 clips in a paired “speaking-listening" pattern, where listeners show three listening styles based on their attitudes: positive, neutral, negative. Different from traditional speech-to-gesture or talking-head generation, listening head generation takes as input both the audio and visual signals from the speaker, and gives non-verbal feedbacks (e.g., head motions, facial expressions) in a real-time manner. Our dataset supports a wide range of applications such as human-to-human interaction, video-to-video translation, cross-modal understanding and generation. To encourage further research, we also release a listening head generation baseline, conditioning on different listening attitudes. Code & ViCo dataset: https://project.mhzhou.com/vico.
M. Zhou—This work was done at JD Explore Academy.
M. Zhou and Y. Bai—Equal contribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afouras, T., Chung, J.S., Zisserman, A.: Lrs3-ted: a large-scale dataset for visual speech recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.00496 (2018)
Bansal, A., Ma, S., Ramanan, D., Sheikh, Y.: Recycle-gan: unsupervised video retargeting. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 119–135 (2018)
Barker, L.L.: Listening behavior (1971)
Beltagy, I., Peters, M.E., Cohan, A.: Longformer: the long-document transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.05150 (2020)
Berger, C.R.: Interpersonal communication: theoretical perspectives, future prospects. J. Commun. 55, 415–477 (2005)
Blanz, V., Vetter, T.: A morphable model for the synthesis of 3d faces. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, pp. 187–194 (1999)
Bohr, P., Gargote, R., Vhorkate, R., Yawle, R., Bairagi, V.: A no reference image blur detection using cumulative probability blur detection (cpbd) metric. Int. J. Sci. Modern Eng. 1(5) (2013)
Buschmeier, H., et al.: Alico: a multimodal corpus for the study of active listening. In: LREC 2014, Ninth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Reykjavik, Iceland,, 26–31 May 2014, pp. 3638–3643 (2014)
Cao, C., Weng, Y., Zhou, S., Tong, Y., Zhou, K.: Facewarehouse: a 3d facial expression database for visual computing. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 20(3), 413–425 (2013)
Cassel, N.N.W.W.: Elements of face-to-face conversation for embodied conversational agents, embodied conversational agents (2000)
Chung, J.S., Jamaludin, A., Zisserman, A.: You said that? arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.02966 (2017)
Chung, J.S., Nagrani, A., Zisserman, A.: Voxceleb2: deep speaker recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.05622 (2018)
Chung, J., Gulcehre, C., Cho, K., Bengio, Y.: Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.3555 (2014)
Deng, Y., Yang, J., Xu, S., Chen, D., Jia, Y., Tong, X.: Accurate 3D face reconstruction with weakly-supervised learning: from single image to image set. In: IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (2019)
Fassaert, T., van Dulmen, S., Schellevis, F., Bensing, J.: Active listening in medical consultations: development of the active listening observation scale (alos-global). Patient Educ. Counsel. 68(3), 258–264 (2007)
Gillies, M., Pan, X., Slater, M., Shawe-Taylor, J.: Responsive listening behavior. Comput. Anim. Virt. Worlds 19(5), 579–589 (2008)
Ginosar, S., Bar, A., Kohavi, G., Chan, C., Owens, A., Malik, J.: Learning individual styles of conversational gesture. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3497–3506 (2019)
Hadar, U., Steiner, T.J., Rose, F.C.: Head movement during listening turns in conversation. J. Nonverbal Behav. 9(4), 214–228 (1985)
Heusel, M., Ramsauer, H., Unterthiner, T., Nessler, B., Hochreiter, S.: Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. Adv. Neural Inf. Processi. Syst. 30 (2017)
Heylen, D., Bevacqua, E., Pelachaud, C., Poggi, I., Gratch, J., Schröder, M.: Generating listening behaviour. In: Emotion-Oriented Systems, pp. 321–347. Springer, Heidleberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15184-2_17
Heylen, D., Bevacqua, E., Tellier, M., Pelachaud, C.: Searching for prototypical facial feedback signals. In: Pelachaud, C., Martin, J.-C., André, E., Chollet, G., Karpouzis, K., Pelé, D. (eds.) IVA 2007. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 4722, pp. 147–153. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74997-4_14
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Hömke, P., Holler, J., Levinson, S.C.: Eye blinks are perceived as communicative signals in human face-to-face interaction. PloS One 13(12), e0208030 (2018)
Honeycutt, J.M., Ford, S.G.: Mental imagery and intrapersonal communication: a review of research on imagined interactions (iis) and current developments. Ann. Int. Commun. Assoc. 25(1), 315–345 (2001)
Huang, Z., Zhang, T., Heng, W., Shi, B., Zhou, S.: Real-time intermediate flow estimation for video frame interpolation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (2022)
Jalongo, M.R.: Promoting active listening in the classroom. Childhood Educ. 72(1), 13–18 (1995)
Joo, H., Simon, T., Cikara, M., Sheikh, Y.: Towards social artificial intelligence: nonverbal social signal prediction in a triadic interaction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10873–10883 (2019)
Kendon, A.: Movement coordination in social interaction: some examples described. Acta Psychologica 32, 101–125 (1970)
Kendon, A., Harris, R.M., Key, M.R.: Organization of behavior in face-to-face interaction. Walter de Gruyter (2011)
Kim, H.: Deep video portraits. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 37(4), 1–14 (2018)
Kong, L., et al.: Ifrnet: Intermediate feature refine network for efficient frame interpolation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1969–1978 (2022)
Li, L., et al.: Write-a-speaker: text-based emotional and rhythmic talking-head generation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 1911–1920 (2021)
Loshchilov, I., Hutter, F.: Decoupled weight decay regularization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.05101 (2017)
Luhmann, N.: What is communication? Commun. Theory 2(3), 251–259 (1992)
Maatman, R.M., Gratch, J., Marsella, S.: Natural behavior of a listening agent. In: Panayiotopoulos, T., Gratch, J., Aylett, R., Ballin, D., Olivier, P., Rist, T. (eds.) IVA 2005. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 3661, pp. 25–36. Springer, Heidelberg (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/11550617_3
McKeown, G., Valstar, M., Cowie, R., Pantic, M., Schroder, M.: The semaine database: annotated multimodal records of emotionally colored conversations between a person and a limited agent. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 3(1), 5–17 (2011)
McNaughton, D., Hamlin, D., McCarthy, J., Head-Reeves, D., Schreiner, M.: Learning to listen: teaching an active listening strategy to preservice education professionals. Topics Early Childhood Spec. Educ. 27(4), 223–231 (2008)
Melis, G., Kočiskỳ, T., Blunsom, P.: Mogrifier lstm. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.01792 (2019)
Mineyama, S., Tsutsumi, A., Takao, S., Nishiuchi, K., Kawakami, N.: Supervisors’ attitudes and skills for active listening with regard to working conditions and psychological stress reactions among subordinate workers. J. Occup. Health 49(2), 81–87 (2007)
Oertel, C., Jonell, P., Kontogiorgos, D., Mora, K.F., Odobez, J.M., Gustafson, J.: Towards an engagement-aware attentive artificial listener for multi-party interactions. Front. Rob. AI 189 (2021)
Park, J., Lee, C., Kim, C.S.: Asymmetric bilateral motion estimation for video frame interpolation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 14539–14548 (2021)
Parker, J., Coiera, E.: Improving clinical communication: a view from psychology. J. Am. Med. Inf. Assoc. 7(5), 453–461 (2000)
Paysan, P., Knothe, R., Amberg, B., Romdhani, S., Vetter, T.: A 3D face model for pose and illumination invariant face recognition. In: 2009 Sixth IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance, pp. 296–301. IEEE (2009)
Petridis, S., Martinez, B., Pantic, M.: The mahnob laughter database. Image Vision Comput. 31(2), 186–202 (2013)
Prajwal, K., Mukhopadhyay, R., Namboodiri, V.P., Jawahar, C.: A lip sync expert is all you need for speech to lip generation in the wild. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 484–492 (2020)
Ramamoorthi, R., Hanrahan, P.: An efficient representation for irradiance environment maps. In: Proceedings of the 28th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, pp. 497–500 (2001)
Ren, Y., Li, G., Chen, Y., Li, T.H., Liu, S.: Pirenderer: controllable portrait image generation via semantic neural rendering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 13759–13768 (2021)
Richard, A., Zollhöfer, M., Wen, Y., De la Torre, F., Sheikh, Y.: Meshtalk: 3D face animation from speech using cross-modality disentanglement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1173–1182 (2021)
Robertson, K.: Active listening: more than just paying attention. Aust. Family Phys. 34(12) (2005)
Rogers, C.R., Farson, R.E.: Active listening (1957)
Rost, M., Wilson, J.: Active Listening. Routledge, Abingdon (2013)
Stacks, D.W., Salwen, M.B.: An Integrated Approach to Communication Theory and Research. Routledge, Abingdon (2014)
Sutskever, I., Vinyals, O., Le, Q.V.: Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 27, 3104–3112 (2014)
Tomasello, M.: Origins of Human Communication. MIT press, London (2010)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30 (2017)
Wang, K., et al.: MEAD: a large-scale audio-visual dataset for emotional talking-face generation. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12366, pp. 700–717. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58589-1_42
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Wu, W., Zhang, Y., Li, C., Qian, C., Loy, C.C.: Reenactgan: learning to reenact faces via boundary transfer. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 603–619 (2018)
Zhang, C., Ni, S., Fan, Z., Li, H., Zeng, M., Budagavi, M., Guo, X.: 3d talking face with personalized pose dynamics. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. (2021)
Zhang, C., et al.: Facial: synthesizing dynamic talking face with implicit attribute learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3867–3876 (2021)
Zhang, K., Zhang, Z., Li, Z., Qiao, Y.: Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(10), 1499–1503 (2016)
Zhu, H., Luo, M.D., Wang, R., Zheng, A.H., He, R.: Deep audio-visual learning: a survey. Int. J. Autom. Comput., 1–26 (2021)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Key R &D Program of China under Grant No. 2020AAA0108600.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhou, M., Bai, Y., Zhang, W., Yao, T., Zhao, T., Mei, T. (2022). Responsive Listening Head Generation: A Benchmark Dataset and Baseline. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13698. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19839-7_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19839-7_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-19838-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-19839-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)